Most Important Points While Credit Selling
(Receivables Management Policy)
Receivables Form One of the major part and backbone of the Business be it any time whether Trader , Manufacturer & Service Provider, This is about how to place an effective credit management policy and will give the readers an inner dive into the why Credit Management Policy is important , what it has impact on profits.
At the end of the financial year the foremost indicator of the business is profits & hence any item which may increase profit by significant amount is of utmost importance.
This Article Is Very Basic And Laymen Specifically For
- Businesses Which are Small To Medium Scale
- However material and basic concepts inside are useful for Every Business
- Students
Page Contents
1. Introduction To Receivables Management
Ques : What are Account Receivables Or Sundry Debtors?
Ans : Accounts receivable represent the amount due form customers (book debts) or debtors as a result of selling goods on credit. “The term debtors is defined as ‘debt’ owed to the firm by customers arising from sale of goods or services in the ordinary course of business.”
Ques : Why this article is written?
Ans : Cash sales , are riskless in terms of realization , but however credit sales possesses an inherent risk of realization , therefore Credit Management policy becomes the heart beat of the business involved in credit sales.
Ques : What is the Relevance of Credit Management Policy?
Ans : Credit Management Policy forms backbone of the business , its goals is neither to maximize sales ( if it was the business would do all credit sales on longer credit period ) , nor minimize bad debts ( if it was the business would not do a single penny credit sales) but the aim is to maximize sales in such a way that factor risk and profitability are not compromised.
Ques : What is the Financial Impact of Credit Management Policy?
Ans : Granting of credit and its management involve costs. To maximize the value of the firm, these costs must be controlled. These thus include the credit administration expenses, Interest Costs , and opportunity costs of the funds tied up in receivable.
Hence here’s the deal , while Quoting the prices of product the above shall be considered that the price is designed in such a way that above costs are not neglected , and the firm earns profits after considering these costs .
Let us understand by way of an example
Under this example we have only consider the Finance Cost in case of trading Concer
| S.No | Particulars | Amount | |||||||||||||||
| 1 | Finance Availed @ 12% From “x” to Purchase Goods “A” | Rs 1,00,000.00 | |||||||||||||||
| 2 | Sold Goods “A” on Credit of Three Months to Z Pvt Ltd | Rs. 1,15,000.00 | |||||||||||||||
| 3 | Sale Price if Same is Sold On Cash | Rs. 1,15,000.00 | |||||||||||||||
| 4 | Actual Profit Earned Net of Finance Cost in Case of Credit Sale
|
Rs. 12,000.00 | |||||||||||||||
| 5 | Actual Profit If Sold on Cash | Rs. 15,000.00 | |||||||||||||||
| Ø So , the major Difference Lies here , Keeping the Rate unchanged for Cash and Credit sales , Slashes the profit by Direct 3% , if proper credit policy is not maintained and implemented.
Ø Granting of credit and its management involve costs. To maximize the value of the firm, these costs must be controlled . Ø The granting of Credit period to Debtors is like investments and hence shall be focused that there is no opportunity loss of investing the amount somewhere else than that in debtors. Ø No doubt the level of debtors are forced by external factors , like market competitions, Type of industries etc but internal factors do matters for the optimization of debtors & Receivables. |
|||||||||||||||||
2. Credit Policy
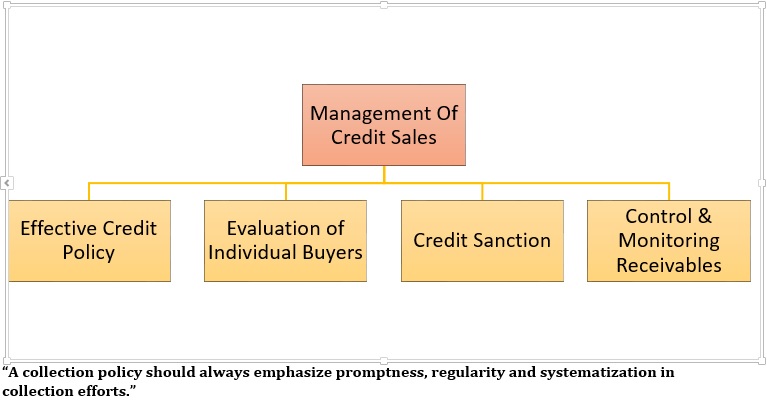
A) Effective Credit Policy
Aspects of Effective Credit Policy Includes
- Credit terms
(a) Credit Period : Means For How many days Credit is Given.
(b) Cash Discounts : What are Cash Discounts offered if pre-payment from Due date.
- Credit Standard of The Firm : it depends upon the 3 C of Customer
- Character: The willingness of Customer to pay.
- Capacity: The Ability of Customer to pay
- Condition: The prevailing economy Condition
- Collection policy or collection efforts.
B) Evaluation of Buyers
Each of Buyer prior to giving credit must be evaluation , that whether then Buyer has 3c for Repayment of The same.
The Risk Classification of Each Buyer to be done based on Risk Matrix , and based on that matrix credit granting decision is to be made.
| S. No | Risk Classification WRT Defaults | Percentage |
| 1 | Customers with Nil risk of default | X% |
| 2 | Customer with negligible risk of default | X% |
| 3 | Customer with less risk of default | X% |
| 4 | Customer with some risk of default | X% |
| 5 | Customer with significant risk of default | X% |
Credit granting Decision can be based on past experience of the Business, based on statistical analysis such as
- Standard Deviation Deadlines Number of Payment Missed, or
- If the customer is new the investigation with respect to various sources ,
- such as Buyer’s bank ,
- Its Audited Financial Statement ,
- Its Average Payment Period ,
- Suits filed against the buyer for non-Payment , etc.
are various sources on which a person can make a judgment on whether to grant or not.
3. Control & Monitoring Receivables
- Traditional Approach
- (a) Average collection period
- (b) Aging Schedule
- Collection Margin approach or Payment Pattern Approach
Traditional Approach
(A) Average Collection Period :
The average collection period is calculated by dividing the average balance of accounts receivable by total net credit sales for the period and multiplying the quotient by the number of days in the period.
In simple terms , in Laymen Terms , it defines in how many average days the credit sale is realized.
(B) Agining Schedule :
It is a report Generated by the ERP / Accounting Software which depicts about the Receivables Outstanding For 0-30 . 30-60 , 60-90 , 90-120 , 120-180 & 180 Above. It is a customizable report which can be customized WRT Number of days.
Collection Margin approach or Payment Pattern Approach
It is defined in terms of proportion or percentage.
- For analyzing the payment pattern of several months, it is necessary to prepare a conversion matrix which shows the credit sales in each month and the pattern of collection associated with it. The payment pattern approach is not dependent on sales level.
- It focuses on the key issue, the payment behavior. It enables one to analyze month by month pattern as against the combined sales and payment patterns. From the collection pattern, one can judge whether the collection is improving, stable, or deteriorating.
- A secondary analysis is that it provides a historical record of collection percentage that can be useful in projecting monthly receipts for each budgeting period.
- The Primary Requirement of this is that Bill-To-Bill Income Recognition is Mandatory to access the payment of Buyer and convert it into matrix
Thank-You For Reading
The credit Management policy forms the backbone of all Businesses , hence it shall be managed properly and according .We are very well verse with Taxation , Whether it be Income Tax , GST and other Various laws, the main essence of business lies in profits that are realized in cash.
I would like to thank the readers who have taken out time and read the above article Hope you’ve found it useful.
In case of any query kindly let us know.
Article Authored By CA Sushant Basra, B.Com , ACA
The Author Can Be Reached At:-cabasrasushant@gmail.com





