A Quick Snapshot of Concepts of AS/IND-AS/IFRS
Accounting standards deal with recognition of events and transactions, measurement of transactions and events, presentation of transactions and events and disclosure requirements. In India ICAI issues accounting standards on the relevant subject for non-corporate bodies and The Central Government of India issues the accounting standards for the corporate bodies.
Indian Accounting Standards converged with IFRS (IND-AS) are the new set of Accounting Standards which India has started to adopt in phased Manner from year 2016 onwards.
Earlier we were following 27 Accounting standards (AS) issued by Institute of Chartered Accountants of India in the year 2000.IND-AS has 41 new standards which replaces our 27 standards.
The International Financial Reporting Standards, also known by its acronym IFRS, issued by International Accounting Standard Board(IASB) are a set of global accounting standards which are already adopted by more than 150 countries across the globe. IND-AS is 98 percent inspired from IFRS. If you are adopting IND-AS, you are almost at par with IFRS.
The IFRS include
- International Financial Reporting standards (IFRSs)—developed by the IASB;
- International Accounting Standards (IASs)—adopted by the IASB;
- Interpretations originated from the International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (IFRICs); and
- Standing Interpretations Committee (SICs).
Idea of migrating to IND-AS is to facilitate:
- the capital inflows in India.
- global recognition for our balance sheet.
- movement of learned accounting professionals across the world inside and outside of India.
- international acquisitions and consolidation of financial statements of multinational enterprises operating in India and Indian enterprises operating abroad.
Concept of Carve-Out/Carve-In
- IND-AS are converged standards of IFRS.
- IFRS are not adopted as it is.
- Certain changes have been made in IFRS considering the economic environment of the country.
- Carve-Out: IND-As deviations form IFRS.
- Carve-In: Additional note in IND-AS which is not present in IFRS.
Components of Financial Statements (IND-AS Vs IFRS)
| IND-AS | IFRS |
| Balance Sheet | Statement of Financial Position |
| Profit and Loss account/Statement of Profit and Loss | Statement of Profit and Loss and other comprehensive Income |
| Cash Flow Statement | Statement of cash flows for the period |
| Statement of changes in Equity | Statement of Changes in Equity for the period |
| Notes to Accounts/Financial Statements and Disclosure of significant accounting policies |
Applicability of IND-AS
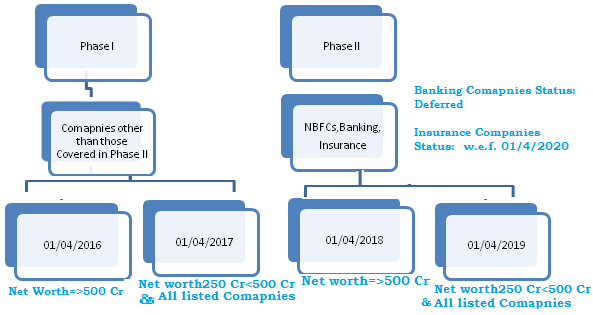
Once Applicable on a company, its holding, subsidiary, joint venture or associate companies shall also be required to apply the IND-As from the same period
Consequences of non compliance
In pursuance of Section 134 (5) of the companies Act, 2013 the directors have to be confirmed and ensure that the compliance of all applicable laws have been fulfilled. In pursuance of section 134 (8) if a company contravenes the provisions of this section,
- the company shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than fifty thousand rupees but which may extend to twenty-five lakh rupees
- and every officer of the company who is in default shall be punishable with imprisonment for a term which may extend to three years or with fine which shall not be less than fifty thousand rupees but which may extend to five lakh rupees, or with both.
Impact of implementation of IND-As on Indian companies:
- Implementation of IND-AS has changed the base and face of Financial Statements and Reports of Indian Corporate.
- It has changed not only the manner of presentation of Financials statements but also the principle of recognition and measurement of financial transactions and records.
- Therefore, we can say the conversion or transition to IND- AS is going to impact in both way qualitatively as well as quantitatively.





