The Reserve Bank of India’s (RBI) Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) on Wednesday announced a reduction in the policy repo rate by 25 basis points, bringing it down to 6.00 percent with immediate effect. This decision, made during the MPC’s first meeting for the financial year 2025-26, comes against a backdrop of increasing anxieties in the global economy, particularly concerning escalating trade frictions that are unsettling the international community. The MPC, acknowledging these global headwinds, also revised its monetary policy stance from neutral to accommodative, signaling a potential for further rate cuts if economic conditions warrant. This move aims to support domestic growth, which is showing signs of recovery after a subdued performance in the first half of the previous fiscal year, while also keeping a close watch on inflation.
The RBI highlighted the rapidly evolving global economic outlook, noting that recent trade tariff measures have amplified uncertainties and pose new challenges to worldwide growth and inflation. In this turbulent environment, the US dollar has weakened, bond yields have softened, equity markets are experiencing corrections, and crude oil prices have fallen to their lowest levels in over three years. Central banks across the globe are responding cautiously, with diverging policy approaches reflecting their individual domestic priorities. Domestically, the Indian economy has demonstrated steady progress in achieving price stability and sustained growth. The MPC noted the significant decline in food inflation, which has provided a degree of comfort, while emphasizing the need to remain vigilant against potential risks arising from global uncertainties and weather-related disruptions.
Looking ahead, the RBI projects a real GDP growth of 6.5 percent for the fiscal year 2025-26, with quarterly growth estimates ranging from 6.3 percent to 6.7 percent. This projection, however, marks a slight downward revision of 20 basis points from the February policy assessment, primarily reflecting the anticipated impact of global trade and policy uncertainties on exports. On the inflation front, the central bank forecasts CPI inflation for FY26 at 4.0 percent, with quarterly figures ranging from 3.6 percent to 4.4 percent, assuming a normal monsoon. The positive outlook for food inflation, driven by strong Rabi crop prospects and declining inflation expectations, has played a key role in this projection. The MPC emphasized that the current benign inflation outlook and moderate growth necessitate continued support for economic expansion.
In addition to the rate cut, the RBI announced several developmental and regulatory policy measures. These include enabling the securitization of stressed assets through a market-based mechanism, expanding the scope of co-lending arrangements to all regulated entities and loan types, harmonizing guidelines for lending against gold jewelry across different financial institutions, and streamlining regulations for non-fund-based facilities to potentially broaden funding sources for infrastructure projects. Draft guidelines for these measures have been released for public consultation. Furthermore, the RBI will allow the National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) to determine transaction limits for person-to-merchant UPI transactions in consultation with banks and stakeholders, and will make the Regulatory Sandbox theme-neutral and an ongoing process to foster continuous innovation in the fintech sector. The RBI underscored its commitment to providing sufficient system liquidity and ensuring financial stability within the banking and NBFC sectors, which currently exhibit robust financial soundness parameters.
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA
April 09, 2025
Governor’s Statement: April 9, 2025
This was the 54th meeting overall and the first meeting in the financial year 202526 of the MPC. The year has begun on an anxious note for the global economy. Some of the concerns on trade frictions are coming true, unsettling the global community. We, at the Reserve Bank, while remaining alert to these global developments, began the year celebrating the completion of 90 years of this august institution since its establishment on 1st April, 1935. The Reserve Bank’s journey over the last nine decades is closely intertwined with the nation’s development and progress. As a custodian of monetary and financial stability, the Reserve Bank has evolved over the years into a full-service central bank with varied functions facilitating a market economy.
2. The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) met on the 7th, 8th and 9th of April to deliberate and decide on the policy repo rate in the backdrop of a challenging global environment1. The global economic outlook is fast changing. The recent trade tariff related measures have exacerbated uncertainties clouding the economic outlook across regions, posing new headwinds for global growth and inflation. Amidst this turbulence, the US dollar has weakened appreciably; bond yields have softened significantly; equity markets are correcting; and crude oil prices have fallen to their lowest in over three years. Under these circumstances, central banks are navigating cautiously, with signs of policy divergence across jurisdictions, reflecting their own domestic priorities.
3. The Indian economy has made steady progress towards the goals of price stability and sustained growth. On the inflation front, while the sharper-than-expected decline in food inflation has given us comfort and confidence, we remain vigilant to the possible risks from global uncertainties and weather disturbances. Growth is improving after a weak performance in the first half of the financial year 2024-25, although it still remains lower than what we aspire for.
Decisions of the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)
4. After a detailed assessment of the evolving macroeconomic and financial conditions and outlook, the MPC voted unanimously to reduce the policy repo rate by 25 basis points to 6.00 per cent with immediate effect; consequently, the standing deposit facility (SDF) rate under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) shall stand adjusted to 5.75 per cent and the marginal standing facility (MSF) rate and the Bank Rate to 6.25 per cent.
5. I shall now briefly set out the rationale for these decisions. The MPC noted that inflation is currently below the target, supported by a sharp fall in food inflation. Moreover, there is a decisive improvement in the inflation outlook. As per projections, there is now a greater confidence of a durable alignment of headline inflation with the target of 4 per cent over a 12-month horizon. On the other hand, impeded by a challenging global environment, growth is still on a recovery path after an underwhelming performance in the first half of 2024-25. In such challenging global economic conditions, the benign inflation outlook and moderate growth demand that the MPC continues to support growth. Accordingly, the MPC unanimously voted to reduce the policy repo rate by 25 basis points to 6.0 per cent. Moreover, it also decided to change the stance from neutral to accommodative. It also noted that the rapidly evolving situation requires continuous monitoring and assessment of the economic outlook.
6. Let me dwell a little on the monetary policy stance. From a cross-country perspective, monetary policy stance is typically characterised as accommodative, neutral or tightening. While an accommodative stance entails easy monetary policy that is geared towards stimulating the economy through softer interest rates; tightening refers to contractionary monetary policy whereby interest rates are hiked to restrain spending and curb economic activity, all with the objective of reining in inflation. A neutral stance is typically associated with a state of economy which neither calls for stimulating economic activity nor calls for controlling inflation by curtailing demand and provides flexibility to move in either direction on the basis of evolving economic conditions.
7. In our context, the stance of monetary policy signals the intended direction of policy rates going forward. Accordingly, with respect to the policy rate, which is the mandate of the MPC, today’s change in stance from ‘neutral’ to ‘accommodative’ means that going forward, absent any shocks, the MPC is considering only two options – status quo or a rate cut. Let me also clarify that the stance should not be directly associated with liquidity conditions. While liquidity management is important for monetary policy including decisions related to policy rate, it is an operating tool with the RBI for various purposes including monetary policy transmission. Monetary policy decisions to change policy rates do however have implications for liquidity management, being the operational tool to carry out the policy changes. To summarise, our stance provides policy rate guidance, without any direct guidance on liquidity management. I will discuss our approach to management of liquidity a little later.
Assessment of Growth and Inflation
Impact of Global Trade and Policy Uncertainties on Growth and Inflation
8. Before I share our assessment of growth and inflation, a few words on the implications of the recent global trade and related policy uncertainties are in order. Let me first highlight the possible implications for growth. First and foremost, uncertainty in itself dampens growth by affecting investment and spending decisions of businesses and households. Second, the dent on global growth due to trade frictions will impede domestic growth. Third, higher tariffs shall have a negative impact on net exports. There are, however, several known unknowns – the impact of relative tariffs, the elasticities of our export and import demand; and the policy measures adopted by the Government including the proposed Foreign Trade Agreement with the USA, to name a few. These make the quantification of the adverse impact difficult.
9. The risks to inflation, on the other hand, are two sided. On the upside, uncertainties may lead to possible currency pressures and imported inflation. On the downside, slowdown in global growth could entail further softening in commodity and crude oil prices, putting downward pressure on inflation. Overall, while global trade and policy uncertainties shall impede growth, its impact on domestic inflation, while requiring us to be vigilant, is not expected to be of high concern.
Growth
10. Real GDP is estimated to grow at 6.5 per cent in 2024-25 on top of a 9.2 per cent growth rate observed in the previous year.2 In 2025-26, prospects of agriculture sector remain bright on the back of healthy reservoir levels and robust crop production.3 Manufacturing activity is showing signs of revival4 with business expectations remaining robust5, while services sector activity continues to be resilient6.
11. On the demand side, bright prospects of the agriculture sector bode well for rural demand which continues to be healthy, while urban consumption is gradually picking up with an uptick in discretionary spending.7 Investment activity has gained traction8 and it is expected to improve further on the back of sustained higher capacity utilisation, 9 government’s continued thrust on infrastructure spending,10 healthy balance sheets of banks and corporates, along with the easing of financial conditions. Merchandise exports will be weighed down by global uncertainties, while services exports are expected to remain resilient.11 Headwinds from global trade disruptions continue to pose downward risks.
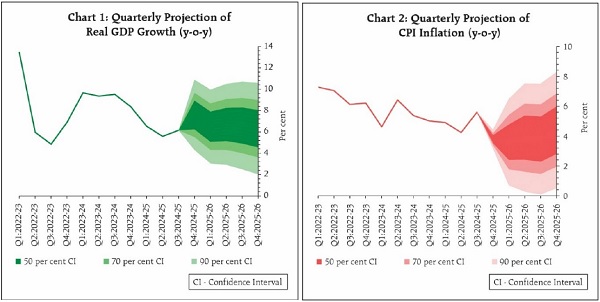
12. Taking all these factors into consideration, real GDP growth for 2025-26 is now projected at 6.5 per cent, with Q1 at 6.5 per cent; Q2 at 6.7 per cent; Q3 at 6.6 per cent; and Q4 at 6.3 per cent. While the risks are evenly balanced around these baseline projections, uncertainties remain high in the wake of the recent spike in global volatility. It may be noted that the growth projection for the current year has been marked down by 20 basis points relative to our earlier assessment of 6.7 per cent in the February policy. This downward revision essentially reflects the impact of global trade and policy uncertainties, which I had highlighted earlier.
Inflation
13. Headline inflation moderated during January-February 2025 following a sharp correction in food inflation.12 The outlook for food inflation has turned decisively positive. The uncertainties regarding rabi crops have abated considerably and the second advance estimates point to a record wheat production and higher production of key pulses over that last year.13 Along with robust kharif arrivals, this is expected to set the stage for a durable softening of food inflation. Sharp decline in inflation expectations in our latest survey for three months and one year ahead would also help anchor inflation expectations, going ahead.14 Furthermore, the fall in crude oil prices augurs well for the inflation outlook. Concerns on lingering global market uncertainties and recurrence of adverse weather-related supply disruptions, however, pose upside risks to the inflation trajectory.
14. Taking all these factors into consideration, and assuming a normal monsoon, CPI inflation for the financial year 2025-26 is projected at 4.0 per cent, with Q1 at 3.6 per cent; Q2 at 3.9 per cent; Q3 at 3.8 per cent; and Q4 at 4.4 per cent. The risks are evenly balanced.
External Sector
15. India’s services exports remained resilient in January-February 2025, driven by software, business and transportation services.15 Going forward, net services and remittance receipts are expected to remain in large surplus, partly offsetting the trade deficit. The CAD for 2024-25 and 2025-26 are expected to remain well within the sustainable level.
16. On the financing side, gross foreign direct investment (FDI) remained strong during the period of April 24 to January 25 in 2024-25 reflecting India’s strong macroeconomic fundamentals. Net FDI however moderated sharply during this period due to higher repatriations and outward FDI.16 Net FPI inflows to India stood at 1.7 billion US dollars during 2024-25, supported by debt inflows as the equity segment recorded net outflows. External commercial borrowings and non-resident deposits, on the other hand, witnessed higher net inflows compared to that last year.17
17. As on 4th April, 2025, India’s foreign exchange reserves stood at 676.3 billion US dollars, providing an import cover of about 11 months.18 Overall, India’s external sector remains resilient as key indicators stay robust.19
Liquidity and Financial Market Conditions
18. System liquidity was in deficit in January 2025 with net injection under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) scaling a peak of ₹3.1 lakh crore on 23rd January 2025. However, as a result of a slew of measures injecting liquidity of about 6.9 lakh crore20 rupees, the system liquidity deficit tapered during February-March 2025 and further turned into surplus on 29th March 2025. Coupled with government spending picking up pace during the latter half of March, system liquidity further improved and it stood at a surplus of ₹1.5 lakh crore as on 7th April, 2025.
19. Reflecting these developments, the weighted average call rate (WACR) softened and remained near the repo rate since the last policy meeting.21 The spreads of 3-month CP and 3-month CD rates over 91-day Treasury bill rate have also softened since the second half of March, suggesting improvement in liquidity conditions.22
20. The Reserve Bank is committed to provide sufficient system liquidity. We will continue to monitor the evolving liquidity and financial market conditions and proactively take appropriate measures to ensure adequate liquidity.
Financial Stability
21. Financial soundness parameters of the banking sector continue to be robust.23 The liquidity buffer in the banking system is well above the regulatory threshold.24 Profitability indicators are also healthy reflecting robust operational efficiency of the system. 25 Similarly, the system-level parameters of NBFCs too are sound.26
Additional Measures
22. I shall now announce six additional measures related to banking regulation, fintech and payment systems.
23. First, it is proposed to enable securitisation of stressed assets through market-based mechanism. This is in addition to the existing ARC route under the Securitisation and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
24. Second, the extant guidelines on co-lending are presently applicable only to arrangements between banks and NBFCs. Moreover, they are restricted to priority sector loans. To exploit the huge potential of such lending arrangements, it is proposed to extend them to all regulated entities and to all loans – priority sector or otherwise.
25. Third, loans against the collateral of gold jewellery and ornaments, commonly known as gold loans, are extended by regulated entities for both consumption and income-generation purposes. In order to harmonise guidelines across various types of regulated entities, to the extent possible, keeping in view their differential risk-bearing capabilities, we shall issue comprehensive regulations on prudential norms and conduct related aspects for such loans.
26. Fourth, to harmonise the regulations governing non-fund-based facilities across regulated entities, we propose to issue comprehensive guidelines. Instructions related to partial credit enhancement (PCE) by regulated entities are also proposed to be revised. This is expected to broaden the funding sources for infrastructure financing.
27. The draft of these four guidelines and regulations are being published today for public consultation. We shall finalise these guidelines based on the feedback received.
28. The other two announcements relate to enabling NPCI to decide, in consultation with the banks and other stakeholders, the transaction limits in UPI for person to merchant transactions; and making the Regulatory Sandbox theme-neutral and ‘on-tap’. Necessary directions for the implementation of these two measures shall be issued separately.
Concluding Remarks
29. The global economy is going through a period of exceptional uncertainties. The difficulty to extract signal from a noisy and uncertain environment poses challenges for policy making. Nevertheless, monetary policy can play a vital anchoring role in ensuring that the economy remains on an even keel.
30. In our context, as I mentioned earlier, the domestic growth-inflation trajectory
demands monetary policy to be growth supportive, while being watchful on the inflation front. We are aiming for a non-inflationary growth that is built on the foundations of an improved demand and supply response and sustained macroeconomic balance. As before, we shall remain agile and decisive in our response and put in place policies that are clear, consistent, credible and in the best interest of the economy.
Thank you. Namaskar and Jai Hind.
(Puneet Pancholy)
Chief General Manager
Press Release: 2025-2026/62
Statement on Developmental and Regulatory Policies
This Statement sets out various developmental and regulatory policy measures relating to (i) Regulations; (ii) Payment Systems; and (iii) Fintech.
I. Regulations
1. Securitisation of Stressed Assets Framework
A prudentially structured securitisation transaction can be an enabler for resolution of stressed assets as it is expected to improve risk distribution and provide an exit route from such exposures for lenders. With this objective, RBI had released a discussion paper on Securitisation of Stressed Assets Framework in January 2023, to seek comments from market participants on various aspects of the framework. After factoring in the suggestions received from the stakeholders on the discussion paper, the draft framework for securitisation of stressed assets is being issued for public comments. The framework intends to enable securitisation of stressed assets through a market-based mechanism, in addition to the existing ARC route under SARFAESI Act, 2002.
2. Framework on Co-lending arrangements (CLA)
The extant guidelines on co-lending are applicable only to arrangements between banks and NBFCs for priority sector loans. In light of the evolution of such lending practices, and the potential of such lending arrangements in catering to the credit needs of a wider segment in a sustainable manner, it has been decided to expand the scope for co-lending and issue a generic regulatory framework for all forms of co-lending arrangements among REs. The draft guidelines are being issued for public comments.
3. Review of Guidelines for Lending against Gold Jewellery
Loans against the collateral of gold jewellery and ornaments are extended by regulated entities (REs) for both consumption and income-generation purposes. Prudential and conduct related regulations for such loans have been issued from time to time and they vary for different categories of REs. With a view to harmonizing such regulations across REs while keeping in view their risk-taking capabilities, and also to address a few concerns that have been observed, it has been decided to issue comprehensive regulations, on prudential norms and conduct related aspects, for such loans. The draft guidelines in this regard are being issued for public comments.
4. Review of Non-Fund Based Facilities
Non-fund based (NFB) facilities like Guarantees, Letters of Credit, Co-Acceptances etc. play a significant role in facilitating effective credit intermediation, besides enabling seamless business transactions, including trade transactions. It has now been decided to harmonize and consolidate guidelines covering these facilities across all REs. The revised guidelines include a review of instructions on issuance of partial credit enhancement by REs, with a view to, inter alia, broadening funding sources for infrastructure financing. Draft guidelines in this regard are being issued for public comments.
II. Payment Systems
5. Enhancing transaction limits in UPI
At present, the transaction amount for UPI, covering both Person to Person (P2P) and Person to Merchant payments (P2M), is capped at ₹1 lakh except for specific use cases of P2M payments which have higher limits, some at ₹2 lakh and others at ₹5 lakh.
To enable the ecosystem to respond efficiently to new use cases, it is proposed that NPCI, in consultation with banks and other stakeholders of the UPI ecosystem, may announce and revise such limits based on evolving user needs. Appropriate safeguards will be put in place to mitigate risks associated with higher limits. Banks shall continue to have the discretion to decide their own internal limits within the limits announced by NPCI.
P2P transactions on UPI shall continue to be capped at ₹1 lakh, as hitherto. NPCI will be advised accordingly.
III. Fintech
6. ‘On Tap’ application facility under theme neutral Regulatory Sandbox
The Reserve Bank has been operating the Regulatory Sandbox (RS) framework since 2019, and four specific thematic cohorts have been announced and completed till date. An ‘On Tap’ application facility for themes of closed cohorts was announced in October 2021. A fifth ‘Theme Neutral’ cohort with a specified time window for receiving applications was also announced in October 2023, which will close in May 2025. Under this cohort, any innovative product or solution within the regulatory ambit of RBI could be tested if found eligible. Based on the experience gained and feedback received from stakeholders, it is now proposed to make the Regulatory Sandbox ‘Theme Neutral’ and ‘On Tap’.
This initiative is expected to foster continuous innovation and keep pace with the rapidly evolving FinTech / regulatory landscape. Additional details in this regard will be communicated separately.
(Puneet Pancholy)
Chief General Manager
Press Release: 2025-2026/63
Monetary Policy Statement, 2025-26
Resolution of the Monetary Policy Committee
April 7 to 9, 2025
Monetary Policy Decisions
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) held its 54th meeting from April 7 to 9, 2025 under the chairmanship of Shri Sanjay Malhotra, Governor, Reserve Bank of India. The MPC members Dr. Nagesh Kumar, Shri Saugata Bhattacharya, Prof. Ram Singh, Dr. Rajiv Ranjan, and Shri M. Rajeshwar Rao attended the meeting.
2. After assessing the current and evolving macroeconomic situation, the MPC unanimously voted to reduce the policy repo rate by 25 basis points to 6.00 per cent with immediate effect. Consequently, the standing deposit facility (SDF) rate under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) shall stand adjusted to 5.75 per cent and the marginal standing facility (MSF) rate and the Bank Rate to 6.25 per cent. This decision is in consonance with the objective of achieving the medium-term target for consumer price index (CPI) inflation of 4 per cent within a band of +/- 2 per cent, while supporting growth.
Growth and Inflation Outlook
3. The global economic outlook is fast changing. The recent trade tariff related measures have exacerbated uncertainties clouding the economic outlook across regions, posing new headwinds for global growth and inflation. Financial markets have responded through sharp fall in dollar index and equity sell-offs with significant softening in bond yields and crude oil prices.
4. The National Statistics Office (NSO) has estimated real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth at 6.5 per cent for 2024-25, on top of 9.2 per cent in 2023-24. Going forward, sustained demand from rural areas, an anticipated revival in urban consumption, expected recovery of fixed capital formation supported by increased government capital expenditure, higher capacity utilisation, and healthy balance sheets of corporates and banks are expected to support growth. Merchandise exports would be weighed down by the evolving global economic landscape which appears to be uncertain at the current juncture, while services exports are expected to sustain the resilience. On the supply side, while agricultural prospects appear bright, industrial activity continues to recover, and services sector is expected to be resilient. Headwinds from global trade disruptions continue to pose downward risks. Taking all these factors into consideration, real GDP growth for 2025-26 is now projected at 6.5 per cent, with Q1 at 6.5 per cent; Q2 at 6.7 per cent; Q3 at 6.6 per cent; and Q4 at 6.3 per cent. (Chart 1). The risks are evenly balanced.
5. CPI headline inflation declined by a cumulative 1.6 percentage points during January-February 2025, from 5.2 per cent in December 2024 to a low of 3.6 per cent in February 2025. On the back of a strong seasonal correction in vegetable prices this year, food inflation dropped to a 21-month low of 3.8 per cent in February. Fuel group continued to remain in deflation. Core inflation, after remaining steady in December 2024-January 2025, inched up to 4.1 per cent in February 2025, driven primarily by a sharp pick-up in gold prices.
6. The outlook for food inflation has turned decisively positive. There has been a substantial and broad-based seasonal correction in vegetable prices. The uncertainties on rabi crops have abated considerably and the second advance estimates point to a record wheat production and higher production of key pulses over last year. Along with robust kharif arrivals, this is expected to set the stage for a durable softening in food inflation. Sharp decline in inflation expectations for three months and one year ahead period would help anchor inflation expectations going ahead. Furthermore, the fall in crude oil prices augurs well for the inflation outlook. Concerns on lingering global market uncertainties and recurrence of adverse weather-related supply disruptions pose upside risks to the inflation trajectory. Taking all these factors into consideration, and assuming a normal monsoon, CPI inflation for the financial year 2025-26 is projected at 4.0 per cent, with Q1 at 3.6 per cent; Q2 at 3.9 per cent; Q3 at 3.8 per cent; and Q4 at 4.4 per cent. The risks are evenly balanced.
Rationale for Monetary Policy Decisions
7. The MPC noted that inflation is currently below the target, supported by a sharp fall in food inflation. Moreover, there is a decisive improvement in the inflation outlook. As per projections, there is now a greater confidence of a durable alignment of headline inflation with the target of 4 per cent over a 12-month horizon. On the other hand, impeded by a challenging global environment, growth is still on a recovery path after an underwhelming performance in the first half of 2024-25. While the risks are evenly balanced around the baseline projections of growth, uncertainties remain high in the wake of the recent spurt in global volatility. In such challenging global economic conditions, the benign inflation and moderate growth outlook demands that the MPC continues to support growth. Accordingly, the MPC unanimously voted to reduce the policy repo rate by 25 basis points to 6.00 per cent. Moreover, it also decided to change the stance from neutral to accommodative. However, it noted that the rapidly evolving situation requires continuous monitoring and assessment of the economic outlook.
8. The minutes of the MPC’s meeting will be published on April 23, 2025.
9. The next meeting of the MPC is scheduled from June 4 to 6, 2025.
(Puneet Pancholy)
Chief General Manager
Press Release: 2025-2026/61
Notes:-
1 As per the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) Economic Outlook Interim Report, March 2025, global GDP growth is projected to moderate from 3.2 per cent in 2024 to 3.1 per cent in 2025 and 3.0 per cent in 2026, a downward revision of 20 bps and 30 bps respectively vis-à-vis its previous release of December 2024.
2 As per the Second Advance Estimates (SAE) released by National Statistics Office (NSO), GDP growth in 2024-25 is estimated at 6.5 per cent as against 9.2 per cent in 2023-24. Private final consumption expenditure (PFCE) and gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) posted a growth of 7.6 per cent and 6.1 per cent, respectively. Government consumption expenditure (GFCE) increased by 3.8 per cent over the previous year. Gross value added (GVA) at basic prices (y-o-y) is expected to grow by 6.4 per cent. Agriculture and allied activities witnessed a significant improvement in growth at 4.6 per cent in 2024-25 while industrial growth moderated to 4.3 per cent even as services grew by 7.5 per cent.
3 All-India water storage in 155 major reservoirs stands at 40 per cent of the total capacity as of April 3, 2025, as against 35 per cent a year ago and decadal average of 34 per cent. (As per the second advance estimate (SAE) for 2024-25, total foodgrain production is estimated to grow by 4.8 per cent y-o-y.
4 Industry sector picked up modestly by 3.5 per cent in Q3:2024-25 from 2.0 per cent in Q2:2024-25 following the recovery in manufacturing GVA by 3.5 per cent during Q3 after a weak 2.1 per cent growth in Q2.
5 PMI manufacturing Future Output Index in March 2025 was placed at 64.4. Future Output Index has hovered above 60.0 since April 2023.
6 E-way bills increased by a robust 19.4 per cent in Q4:2024-25. Gross GST revenues rose by 9.9 per cent and toll collections expanded by 11.9 per cent during March 2025. Consumption of finished steel grew by 10.9 per cent and cement production increased by 10.5 per cent in February 2025. On the other hand, petroleum products consumption contracted by 5.4 per cent in February 2025. PMI services for March 2025 moderated to 58.5 from 59.0 in February 2025.
7 IIP consumer durables expanded 7.2 per cent in January 2025. Domestic air passenger traffic expanded by 12.1 per cent in February 2025 and 10.1 per cent in March.
8 Indicators of investment are recording healthy growth. IIP capital goods expanded by 7.8 per cent in January 2025, import of capital goods increased by 7.5 per cent during January-February 2025, consumption of finished steel and cement production during January-February 2025 grew by 10.9 per cent, and 12.5 per cent, respectively.
9 As per the order books, inventories, and capacity utilisation survey (OBICUS), seasonally adjusted capacity utilisation in manufacturing sector in Q3:2024-25 at 75.3 per cent was well above the long-term average.
10 As per the Union Budget 2025-26, the central government’s effective capital expenditure (including grants-in-aid to state governments for capital expenditure) is budgeted to grow by 17.4 per cent.
11 Services exports increased by 11.8 per cent during January-February 2025, on the back of robust software and business exports.
12 CPI headline inflation declined by a cumulative 1.6 percentage points during January-February 2025, from 5.2 per cent in December 2024 to a low of 3.6 per cent in February 2025. Buoyed by a strong seasonal correction in vegetable prices this year, food inflation dropped to a 21-month low of 3.8 per cent in February from 5.7 per cent in January 2025. Deflation in fuel group, year-on-year, was at (-) 1.3 per cent in December 2024, (-) 1.5 per cent in January 2025 and (-) 1.3 per cent in February 2025. However, CPI excluding food and fuel inflation after remaining steady at 3.6 per cent, year-on-year, during December 2024-January 2025 inched up to 4.1 per cent in February 2025.
13 As per the Second Advance Estimates of agricultural production (kharif and rabi) for the year 2024-25, released in March 2025, the wheat production has been estimated at a record 115.4 million tonnes for 2024-25, which is 1.9 per cent higher than the final estimates of 2023-24. The production of pulses (kharif and rabi) in 2024-25 is estimated to be 3.8 per cent higher than the final estimates of 2023-24. The production of key rabi season pulses, such as gram and lentil is estimated to increase by 4.5 per cent and 1.5 per cent, respectively.
14 In the latest round of survey, households’ perception of the current median inflation declined by 50 basis points (bps) and reached 7.8 per cent. Households’ inflation expectations for the next three months and one year ahead also came down by 40 bps and 50 bps, reaching 8.9 per cent and 9.7 per cent, respectively.
15 India’s services exports grew by 11.8 per cent on a y-o-y basis during January-February 2025.
16 Gross FDI inflows grew by 15.3 per cent to US$ 69.4 billion in April-January 2024-25 from US$ 60.2 billion during the same period a year ago. Net FDI inflows declined to US$ 2.5 billion in April-January 2024-25 from US$ 11.5 billion a year ago.
17 Net inflows under external commercial borrowings to India increased to US$ 15.2 billion during April-February 2024-25 as compared with US$ 2.8 billion a year ago. Non-resident deposits recorded a net inflow of US$ 14.3 billion in April-January 202425, higher than US$ 10.2 billion in the same period last year. Net FPI outflows during January 2025 and February 2025 were US$ 6.7 billion and US$ 4.0 billion, respectively. However, net FPI inflows stood at US$ 3.8 billion in March 2025.
18 Based on actual merchandise imports (on a BoP basis) during the four quarters (Q4:2023-24 to Q3:2024-25).
19 India’s external debt to GDP ratio stood at 19.1 per cent at end-December 2024 (18.5 per cent at end-March 2024), while the net international investment position (IIP) moderated to (-) 9.8 per cent of GDP at end-December 2024 from (-) 10.1 per cent of GDP at end-March 2024.
20 The Reserve Bank conducted 8 OMO purchase auctions injecting liquidity amounting to ₹2.85 lakh crore. 3 term VRR auctions injected liquidity to the tune of ₹1.83 lakh crore. 3 USD/INR Buy/Sell swaps auctions injected liquidity to the tune of ₹2.18 lakh crore so far. 2 OMO purchase auctions for an amount of ₹40,000 crore are scheduled later in April 2025..
21 Average spread of WACR over the policy repo rate was 6 bps during February-March 2025 compared to 13 bps during December-January.
22 CD and CP spreads averaged 88 bps and 113 bps respectively since mid-March 2025 as compared to 143 bps and 112 bps, respectively during the first half of March.
23 The system-level Capital to Risk Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR) of 16.43 per cent in December 2024 was well above the regulatory minimum level. Gross non-performing asset (GNPA) ratio at 2.42 per cent in December 2024 improved by 54 bps over December 2023. Special Mention Account (SMA)-2 ratio was 0.90 per cent in December 2024
24 Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) was 130 per cent as of December 2024.
25 As on December 2024, system level return on asset (RoA), return on equity (RoE), and net interest margin (NIM) were at 1.37 per cent, 14.14 per cent, and 3.49 per cent, respectively.
26 Total CRAR of NBFCs was 26.22 per cent and Tier I CRAR was 24.13 per cent in December 2024. GNPA ratio improved from 2.70 per cent in December 2023 to 2.53 per cent in December 2024. The RoA decreased from 3.11 per cent in December 2023 to 2.86 per cent in December 2024.




