Taarakesh, Priyacharan

Electoral Bond is a financial instrument for making donations to political parties. These are issued by Scheduled Commercial Banks upon authorization from the Central Government (“the CG”) to the intending donors, but only against cheque and other digital payments (in other words, it cannot be purchased using cash). These bonds shall be redeemable in the designated account of a registered political party prior to the expiry of the life of the bonds.
Page Contents
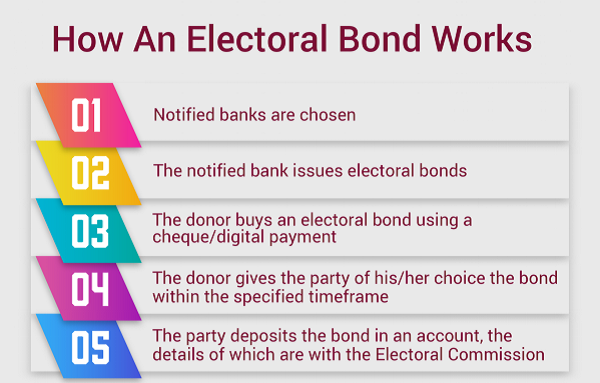
The process of how electoral bonds are proposed to be rolled out:-
1) Selection of notified banks–
The CG after precise review selects a panel of scheduled banks which shall be eligible to issue such electoral bonds in consultation with the respective bank’s management.
2) Issue of bonds–
The banks once notified shall be permitted to issue electoral bonds in specified denominations to the intended parties / customers (“the donor”).
3) Subscription–
The donor buys electoral bonds using cheque or through digital banking channel.
4) Tenure –
The donor gives such bonds to the party of his / her choice within the specified time during which the bond shall be valid. However, it is proposed to choose 30 days as the tenure of the bond by the CG.
5) Encashment–
On receipt of electoral bond from the donor, the party deposits the bond into an account, the details of which are with the Electoral Commission.
Role of Reserve Bank of India
Required amendments to the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 (“the RBI Act”), specifically to Section 31(3) and the Representation of People Act, 1951 were made through Section 133 to 136 of Finance Bill, 2017.
CG is in the process of framing a Scheme in this regard. Section 31 of the RBI Act gives power to issue bearer bonds to RBI and government. The bearer bond has the characteristic of a currency.
The RBI Act states that other than the Central Bank and the CG, nobody can issue notes which have the characteristic of a banknote or a currency note. Hence, the government’s move to amend the Act to allow commercial banks to issue such bonds is leading to some discomfort among RBI officials who feel it will erode some of the Central Bank’s authority.
Description of the scheme
In an effort downsize the malpractices prevailing in political funding in India, the Government has taken this step to streamline Electoral Funding. This scheme enables the donor’s identity to remain anonymous as these bonds are intended to be rolled out as bearer bonds. Hence, the donors concern of remaining anonymous to the general public or to the political parties is addressed in this form of funding.
Further, in accordance with the suggestion made by the Election Commission, the maximum amount of cash donation that a political party can receive is stipulated at Rs. 2,000/- from one person, pursuant to the announcement in Union Budget 2017-18. However, Political parties will be entitled to receive donations by cheque or digital mode from their donors. Every political party would have to file its return within the time prescribed in accordance with the provision of the Income-tax Act. Existing exemption to the political parties from payment of Income-tax would be available only subject to the fulfilment of these conditions.
As per Section 29C(1) of The Representation of People Act, 1951, a political party needs to disclose the details of non-governmental corporations and persons who donate more than Rs. 10,000 to it in a Financial Year (“FY”). Vide Finance Bill 2017, it has been specified that no report needs to be prepared in respect of the contributions received by way of an Electoral Bond.
This reform is expected to bring about greater transparency and accountability in political funding, while preventing future generation of black money. Similar amendments to the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881 is also proposed to be made.
Advantages of Electoral Bond
1. It is an effort directed to reduce cash funding for funding of political parties. Hence, it helps the political parties to operate in a more transparent manner with the election commission, regulatory authorities and the general public at large.
2. The identity of the person who has made the donation shall remain confidential as the political parties would not have the details of the original subscriber to these bonds, as these instruments are issued in bearer form.
3. The Government is planning to peg the tenure of the bond at 30 days. Hence, this ensures early encashment of the bonds by the political parties.
4. As encashment of all the donations are through banking channels, every political party shall be obliged to explain how the entire sum of money received has been expended with necessary supportings. Hence, alleged practices such as note for vote and other illicit spending shall be downsized significantly.
5. It channelizes the donations to be more accountable and the political party to be more vigilant on its monetary spends/activities performed.
6. It instils a sense of certainty, trust and belief in the donor’s mind that the amount donated by the donor is used for legitimate purposes. Thus, it gives the psychological push in the donor’s mind to start giving higher sums as donation to political parties as the funds utilization is more transparent in this form of funding.
Disadvantages of Electoral Bond
1) Though it is proposed that the scheme of electoral funding shall keep the identity of donor to remain confidential from the political parties, corporate entities may not enjoy this benefit. As the corporate entities may have to declare the amount of electoral bonds purchased by them to Registrar of Companies.
2) There is a counter argument that a bearer bond assumes the character of cash. Hence, it is can be argued that there is no difference if political parties are funded by cash or through Electoral Bonds. According to certain section of critics, it doesn’t result in improvement of the transparency of the funding process.
3) This is not the first time that the Government has issued such bearer bonds. In the year 1987, the then Government floated a Development Bond called Indira Vikas Patra, which was issued through post offices. Since this had the characteristic of a bearer bond, it conferred anonymity to the holders of this bond. However, it was finally discontinued after it was suspected that these bonds were used as a conduit for laundering black money. As the electoral bonds are also in bearer form the above example can be cited to allegedly prove the intended measure by the government to be wrong.
Finally, none of us can question this measure of the Government to cleanse the political funding of our country through introduction of Electoral Bonds. However, the success of this scheme lies in its implementation and the integrity in which the system functions. So, we hope that the move produces the intended results as expected.
Disclaimer: The best efforts have gone into compiling the above information. However the author/s are neither responsible for any consequences occurring directly / indirectly based on decisions taken from the above information published.
Republished with amendments





Dear Author ,
Both the measures taken in Budget viz reduction in cash donation to Rs.2000 and funding through Electoral boards donot help at all in curbing black money generation nor corruption . Why the identity of the donor should not be disclosed ?Pl. read my article on the issue published a few days ago in tax guru.in for understanding thee issue in right perspective .