Article explains Important Changes in GST effective from 1st Jan, 2022 related to Changes in GST impacting On E-Commerce Operators i.e. Zomato, Swiggy etc., Recovery of Self-assessment tax without Opportunity of Difference between GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B, ITC availability on filing of GSTR-1 by supplier, Blocking of GSTR-1 for non-filing of GSTR 3B, Mandatory Aadhaar authentication for GST Revocation & Refund application, Empowerment of GST Commissioner to attach provisionally, any property, including bank account, Amendments in Section 129 & 130 of CGST Act, 2017., Pre-Condition of Payment of a a sum equal to 25% of the penalty for filing of Appeal against section 129(3) order, Changes in GST rate on footwear from 5% to 12%, GST rate on Works Contract Services for specified Contracts to Government Authority and Government Entity and GST on services provided by Club or Association to its members retrospectively w.e.f. July 01 2017.
Page Contents
- 1. Changes in GST impacting On E-Commerce Operators i.e.Zomato, Swiggy etc.
- 2. Recovery of Self-assessment tax without Opportunity of Difference between GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B
- 3. ITC available only When Supplier files his GSTR-1 and makes payment
- 4. Blocking of GSTR-1 for non-filing of GSTR 3B.
- 5. Mandatory Aadhaar authentication for GST Revocation & Refund application.
- 6. Commissioner empowered to attach provisionally, any property, including bank account.
- 7. Amendments in Sec. 129 & 130 of CGST Act, 2017
- 8. No appeal to be filed against section 129(3) order, unless a sum equal to 25% of the penalty is paid.
- 9. Changes in GST rate on footwear from 5% to 12%.
- 10. GST rate on Works Contract Services for specified Contracts to Government Authority and Government Entity
- 11. GST on services provided by Club or Association to its members retrospectively w.e.f. July 01 2017
1. Changes in GST impacting On E-Commerce Operators i.e.Zomato, Swiggy etc.
On September 17, it was decided at the Goods and Services Tax Council meeting that e-commerce operators be made liable to pay tax on services provided through them namely transport of passengers, by any type of motor vehicles- restaurant services provided, with some exceptions. This will become effective January 1, 2022, said a statement issued by the Finance Ministry after the GST Council meeting.
> You might already be aware that the government has given a directive via issued NN. 17/2021- Central Tax (Rate) dated 18th November 2021 wherein E-commerce platforms (“ECO”) like Zomato, Swiggy are liable to pay tax on the restaurant services effective 1st January, 2022. The liability to pay taxes on the non-restaurant services as per this directive still lies with the restaurants themselves.
> Further Circular No. 167/23/2021-GST dated 17.11.2021 issued for clarification regarding modalities of compliance to the GST laws in respect of supply of restaurant service through ECO.
> ECO is now made liable to pay GST on “restaurant services” provided through the e-commerce platform.
> This change is not applicable for restaurant services provided from a premise with declared tariff of Rs. 7,500/- or above per day.
> Swiggy, Zomato qualifies etc is qualify as an “e-commerce operator” under Section 2(45) of CGST Act, 2017.
What is Restaurant and Non-Restaurant Services?
As per NN.11/2017 – CTR, “Restaurant service means supply, by way of or as part of any service, of goods, being food or any other article for human consumption or any drink, provided by a restaurant, eating joint including mess, canteen, whether for consumption on or away from the premises where such food or any other article for human consumption or drink is supplied”.
A restaurant is a place which is in the business of preparing and serving food in the premises or as takeaway.
An illustration under this category is provided below:
a) Restaurants located in a premise where declared tariff is not exceeding Rs. 7,500 per day and providing restaurant services.
b) Food and beverage sold as a part of restaurant services and which qualifies as restaurant services.
c) Cloud kitchens providing restaurant services etc.
d) Stand-alone restaurants which are not ice cream parlors or bakeries.
As per NN. 17/2021, Zomato, Swiggy shall be responsible for charging, collecting and paying GST @ 5% on supply of “restaurant services” made by such restaurant thru the ECO platform.
For Restaurant with No GSTIN, ECO will be responsible for charging, collecting, paying GST @5% on total order value.

Section 9(5) The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, specify categories of services the tax on intra-State supplies of which shall be paid by the electronic commerce operator if such services are supplied through it, and all the provisions of this Act shall apply to such electronic commerce operator as if he is the supplier liable for paying the tax in relation to the supply of such services.
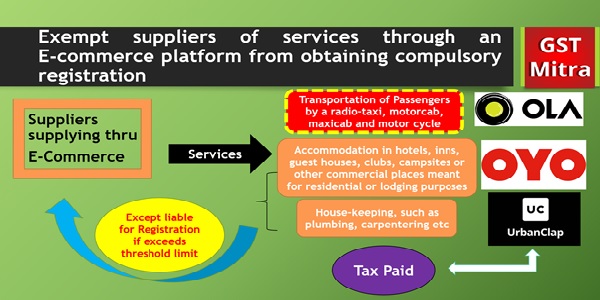
(iv) supply of restaurant service other than the services supplied by restaurant, eating joints etc. located at specified premises.
(c) specified premises means premises providing hotel accommodation service having declared tariff of any unit of accommodation above seven thousand five hundred rupees per unit per day or equivalent.”
Schedule II of CGST Act, 2017- Clause 6 – Composite Supply
The following composite supplies shall be treated as a supply of services, namely:—
(a) works contract as defined in clause (119) of section 2; and
(b) supply, by way of or as part of any service or in any other manner whatsoever, of goods, being food or any other article for human consumption or any drink (other than alcoholic liquor for human consumption), where such supply or service is for cash, deferred payment or other valuable consideration.
1. If you operate or manage E-Commerce Platform, Whether TCS would be applicable? YES
2. If Suppliers making taxable supplies thru E-Commerce Operator, Whether TCS would be applicable? YES
3. Suppliers supplies Transportation of Passengers, housekeeping, and hotel accommodation services thru ECO, Whether TCS would be applicable? NO
4. Restaurant Service is provided from Specified Premises, Whether ECO would be liable for charging of tax? NO
5. Restaurant Service is provided from location other than Specified Premises, Whether ECO would be liable for charging of tax? YES
| GST Categories | Tax Charged by Restaurants | Current Tax Treatment | New Tax Treatment (w.e.f. 1-Jan-22) | |||
| Registered under GST | ECO collects & pay GST | Restaurant pays to Govt. | ECO collects & pay GST | Restaurant pays to Govt. | ||
| Restaurant | 5% | 1% | 4% | 5% | Nil | |
| Non-Restaurant | 5/12/18/28 | 1% | Balance amount | 1% TCS | Balance amount | |
| Hybrid | 5/12/18/28 | 1% | Balance amount | 5% on Restaurant Services | Nil | |
| 1% TCS on non-restaurant services | Balance amount | |||||
| Unregistered under GST | Restaurant | No tax | No tax | |||
| Non-Restaurant | No tax | No tax | ||||
| Hybrid | No tax | No tax | ||||
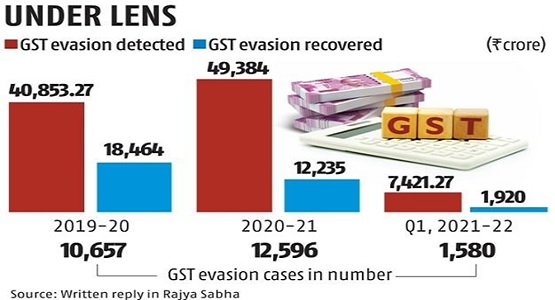
2. Recovery of Self-assessment tax without Opportunity of Difference between GSTR-1 and GSTR-3B
> Section 75 (12) states that “Notwithstanding anything contained in section 73 or section 74, where any amount of self-assessed tax in accordance with a return furnished under section 39 remains unpaid, either wholly or partly, or any amount of interest payable on such tax remains unpaid, the same shall be recovered under the provisions of section 79.”
> Explanation For the purposes of this sub section, the expression “self-assessed tax” shall include the tax payable in respect of details of outward supplies furnished under section 37 but not included in the return furnished under section 39.
> Earlier, Self-assessed tax were to be determined on the basis of liabilities declared in Section 39.
> In pursuance of above, the tax payable in respect of invoices reported in GSTR-1 but not covered in GSTR 3B could not be recovered because it could not be considered as self-assessed tax.
> With this amendment, Difference between GSTR-3B and GSTR-1 may be recovered u/s 79 without any SCN u/s 74/75.
3. ITC available only When Supplier files his GSTR-1 and makes payment
> Section 16 (aa) the details of the invoice or debit note referred to in clause (a) has been furnished by the supplier in the statement of outward supplies and such details have been communicated to the recipient of such invoice or debit note in the manner specified under section 37.
> Section 16 of the CGST Act provides for conditions and restrictions subject to which the input tax credit shall be credited to the electronic credit ledger. It would be logical to complete this linkage of outward supplies declared by the supplier with the tax liability, by also limiting the credit availed in Form GSTR 3B to that reflected in GSTR 2A of the recipient, subject to additional amount available under the rule 36(4).
> 39/2021–Central Tax notified the amendment made vide Section 109 of the Finance Act, 2021 to insert the new clause ‘(aa)’ in Section 16(2) of the CGST Act, 2017, that provides an additional condition to claim ITC based on GSTR-2A and newly introduced GSTR-2B, i.e., ITC on invoice or debit note can be availed only when details of such invoice/debit note have been furnished by the supplier in his outward supplies (GSTR-1) and such details have been communicated to the recipient of such invoice or debit note.
> Consequently, there would be no relevance of 5% limit mentioned in Rule 36(4), as the recipient would not be able to take any ITC if the same is not coming in recipients GSTR-2A and/or 2B.
4. Blocking of GSTR-1 for non-filing of GSTR 3B.
> NN 35/2021-Central Tax amended rule 59 of the CGST Rules, 2017 to provide that a registered person shall not be allowed to furnish form GSTR-1, if has not furnished the return in Form GSTR-3B for the preceding month.
> It means w.e.f. 1st January, 2022, the GSTR-1 return filing facility will be blocked if you have not submitted the return in FORM GSTR-3B for the preceding month.
> For example, if a taxpayer has not filed GSTR-3B for November 2021, the GSTR-1 filing facility will be blocked from the 1st January 2022.
5. Mandatory Aadhaar authentication for GST Revocation & Refund application.
> NN 38/2021-CT has notified January 1, 2022 as the implementation date for Rule 10B of CGST Rules, 2017.
> Mandatory for the registered person to undergo Aadhaar authentication for the below purposes:
1. Filing of application for revocation of cancellation of registration in FORM GST REG-21 under Rule 23 of CGST Rules, 2017.
2. Filing of refund application in FORM RFD-01 under Rule 89 of CGST Rules, 2017.
3. Refund of the IGST paid on goods exported out of India under Rule 96 of CGST Rules, 2017.
> The taxable person, who have not yet authenticated their Aadhaar, may like to go through this authentication process before filing the above two applications and enabling GST system to validate and transmit the IGST refund data from GST system to ICEGATE system.
> If Aadhaar number has not been assigned to the concern person for Aadhaar authentication as specified above, such person may undergo e-KYC verification by furnishing the following:
(a) She/he will feed Aadhaar Enrolment ID and upload the acknowledgement; and
(b) She/he shall also upload any one of the following documents:
(i) Bank passbook with photograph; or
(ii) Voter identity card issued by the Election Commission of India; or
(iii) Passport; or
(iv) Driving license issued by the Licensing Authority under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 (59 of 1988):
Provided further that such person shall undergo the Aadhaar authentication within a period of thirty days from allotment of the Aadhaar number.
Aadhaar authentication or e-KYC verification before filing of refund may be completed by navigating to “Dashboard > My Profile > Aadhaar Authentication Status”
6. Commissioner empowered to attach provisionally, any property, including bank account.
> Section 115 of the Finance Act, 2021 seeks to Amend section 83, for sub-section (1), the sub-section shall be substituted, namely
> “(1) Where, after the initiation of any proceeding under Chapter XII, Chapter XIV or Chapter XV, the Commissioner is of the opinion that for the purpose of protecting the interest of the Government revenue it is necessary so to do, he may, by order in writing, attach provisionally, any property, including bank account, belonging to the taxable person or any person specified in sub-section (1A) of section 122, in such manner as may be prescribed.
> To empower officers to provisionally attach after the initiation of proceedings and property of taxable person or any other person who is a beneficiary of the transaction.
7. Amendments in Sec. 129 & 130 of CGST Act, 2017
> Section 129(1) – 200% Penalty is required to be paid to release the goods which are seized for violation of E-way Bill provsions.
> Section 129(2) – Omitted à The goods so seized under sub-section shall be released, on a provisional basis, upon execution of a bond and furnishing of a security, in such manner and of such quantum, respectively, as may be prescribed or on payment of applicable tax, interest and penalty payable, as the case may be.
> Section 129(3) – Specified period of issuance of notice (7 days) and passing of order(7 days) under Section 129(3) of the CGST Act, 2017.
> No penalty shall be determined without giving opportunity of hearing as per amended Section 129(4) of the CGST Act, 2017.
> Specified time limit for selling/ disposing seized goods or conveyance under Section 129(6) of the CGST Act, 2017
8. No appeal to be filed against section 129(3) order, unless a sum equal to 25% of the penalty is paid.
> Section 116 of the Finance Act, 2021 seeks to Amend section 107, in sub-section (6), the proviso shall be inserted, namely “Provided that no appeal shall be filed against an order under sub-section (3) of section 129, unless a sum equal to twenty-five percent of the penalty has been paid by the appellant.”
> Where proceedings against main person liable to pay tax have been concluded under Section 74, proceedings against co-noticee are also deemed to be concluded as provided under Explanation 1(ii) to Section 74. However, now, such benefit will not be available to co-noticee for proceedings initiated to impose penalties for violation of E-way bill.
9. Changes in GST rate on footwear from 5% to 12%.
10. GST rate on Works Contract Services for specified Contracts to Government Authority and Government Entity
> Works contract services provided for specified contracts to Government Authority or Government Entity have been excluded from the reduced tax rate entry of GST @5%/12% w.e.f 01.01.2022 vide NN 15/2021-CTR.
> Those specified works contract services will be taxable at residual tax rate @18% under entry 3 (xii) of tax rate notification no 11/2017- CT(R) w.e.f 01.01.2022.
> The contractor and the sub-contractor (providing services to main contractor) providing works contract services to the Government Authority or Government Entity must revisit their contracts to check the implications in their ongoing projects and to ensure the compliance with the said amendment effective from 01.01.2022.
11. GST on services provided by Club or Association to its members retrospectively w.e.f. July 01 2017
> NN 39/2021-CT notified Section 108 (Section 7(1)(aa) of CGST Act, 2017) and Section 122 (Omitted para 7 of Schedule II of the CGST Act, 2017) of the Finance Act, 2021.
> The Scope of term Supply by including therein activities or transactions of supply of goods or services or both between any person (other than individual) to its members or constituents or vice versa for cash, deferred payment or other valuable consideration.
> The supply of goods or services by an incorporated or unincorporated club or association, has in view of the Supreme Court judgment in Calcutta Club case, completely gone out of tax net.
> Under GST regime the Appellants in various Advance Rulings had contended that services by clubs, associations etc to its members are not taxable for the reason of principle of mutuality determined by the Hon’ble Apex Court in the case of Calcutta Club Limited.
Now, through this amendment, all such contentions has been set aside.
******
Disclaimer: The contents of this article are for information and strictly for educative purposes only and does not constitute an advice or a legal opinion and are personal views of the author. It is based upon relevant law and/or facts available at that point of time and prepared with due accuracy &reliability. Readers are requested to check and refer relevant provisions of statute, latest judicial pronouncements, circulars, clarifications etc before acting on the basis of the above write up. The possibility of other views on the subject matter cannot be ruled out. By the use of the said information, you agree that Author is not responsible or liable in any manner for the authenticity, accuracy, completeness, errors or any kind of omissions in this piece of information for any action taken thereof. This is not any kind of advertisement or solicitation of work by a professional.
About the Author : CA. Praveen Sharma, is a Fellow Member of The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India. He has rich qualification of B.Com, M.Com, LL.B., Diploma in IFRS from ACCA UK, Certified Fraud and Forensic Auditor, Certified Anti-Money Laundering Specialist, Certified Independent Director. He has contributed a knowledge sharing platform to the professionals and on public domain in the name of “GST Mitra”. He is a recognized Faculty of The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India for Indirect Taxes. He addressed Certificate and Advance Courses of ICAI and Other Institutes on GST, besides addressing Study Circles and other forums of trade and professionals. He has provided GST training to Officers of 32 States and Union Territories and to CBIC Officers.






As a restaurant under the 5% gst slab, we manufacture sweets as part of services in the restaurant (with accommodation below 7500 tariff) are we liable to pay gst separately for the orders placed through ECO (zomato) ? or all orders in restaurants are considered part of services and require eco to pay the entire gst amount?
I think these NEW era of GST will need GST service as while running a business its hard to keep up with GST filling dates so I think it is important to Get GST filing Service.