A company from time to time required funding from outside like from banks of any other public financial institutions.
These banks of any other public financial institutions after checking the company’s credentials and other norms and aspects lends monetary help to companies by creating charge on the assets of the company.
Let’s understand the charge and its various other aspects in simple question answer way.
What is Charge?
As per the provision of The Companies Act, 2013, charge” means an interest or lien created on the property or assets of a company or any of its undertakings or both as security and includes a mortgage.
In normal language, a Charge confers a right on the secured party to look to a particular asset in the event of the debtor’s default. It gives creditor a right to recover their dues from borrower.
What provision governs the charge?
As per The Companies Act, 2013 section 77 to 87 governs the charges of company read with rules The Companies (Registration of Charges) Rules, 2014.
The Companies Act, 2013 these section deals with registration of charges, satisfaction of charges, modification of charges, punishment for non-compliance, etc.
Who is charge holder?
A charge holder is owner of a legal interest in a particular asset, especially one used as a guarantee to secure payment, e.g. of a mortgage or other form of loan or debt.
For example, ABC Private Limited Company took a loan from XYZ Bank. In this case XYZ bank created charge on assets of ABC Private Limited and is Charge holder.
What is the time limit to register charge?
As per the Provisions of The Companies Act, 2013, from the date of creation of charge once executed and signed by both the parties, the charge should be filled to Registrar of Companies within (30) thirty days.
What are different kind of charges?
There are two (2) kinds of charges:-
1. Fixed charge
2. Floating Charge
Fixed charge in which the assets/ property is defined and specific on whom the charge is created. No other assets other than on whom charge is created are covered.
Floating charge in which there is no specific/ fixed assets or property, however, they cover enough assets/property which will be enough to make the payment in case default, if any arises.
What are the forms required to register Charge?
As per The Companies Act, 2013 and rules, E-Form CHG-1 – for other than Debentures and E-Form CHG-9 – for Debentures are filled within thirty (30) days from date of creation of charges registration.
Can charges be modified?
Yes, the Companies Act, 2013 has these provisions, a company can modify its charge using the same forms i.e. E-Form CHG-1 – for other than Debentures and E-Form CHG-9 – for Debentures. For modification also forms should be fille within thirty (30) days from modification.
What if charge is satisfied?
Once a charge is satisfied, the company shall file E-form CHG-4 within thirty (30) days from the satisfaction of charge. The registrar shall also take note of satisfaction of charge shall issue certificate of registration of satisfaction of charge.
What is Register of Charges?
Every company who creates charge as per the Companies Act, 2013 shall maintain, update and keep register of charges at company’s registered office. Entries in the register shall be authenticated by a director or the secretary of the company or any other person authorised by the Board for the purpose.
The register of charges shall be preserved permanently and the instrument creating a charge or modification thereon shall be preserved for a period of eight years from the date of satisfaction of charge by the company.
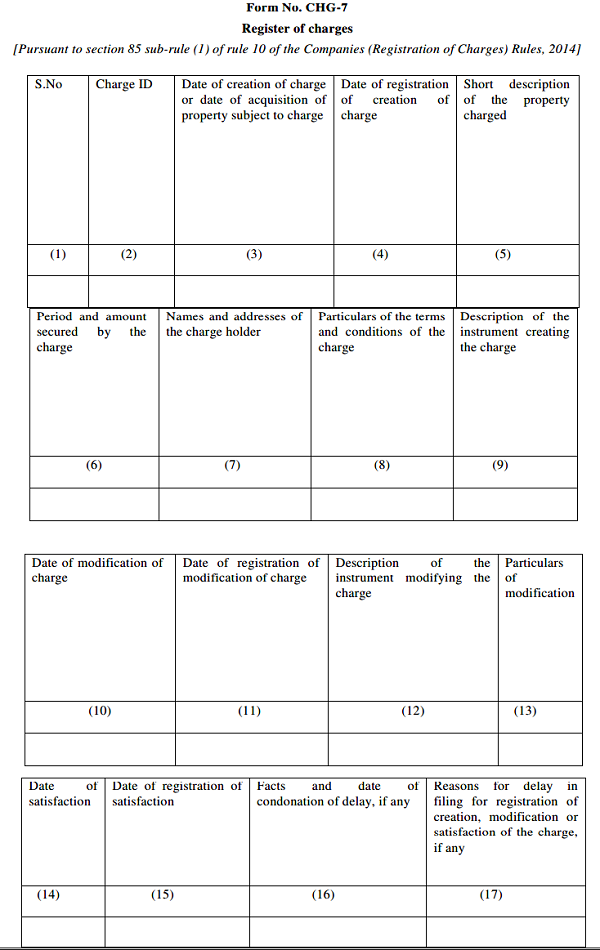
The register of charges shall in form CHG-7 is appended below.
What is company or charge holder fails to register the form on time?
If any company is in default in complying with any of the provisions of this Chapter, the company shall be liable to a penalty of five lakh rupees and every officer of the company who is in default shall be liable to a penalty of fifty thousand rupees.
Apart from this if charge created by a company shall be not be taken into account by the liquidator appointed under this Act or the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, as the case may be, or any other creditor unless it is registered with Registrar of Companies.
Form No. CHG-7 Register of charges
[Pursuant to section 85 sub-rule (1) of rule 10 of the Companies (Registration of Charges) Rules, 2014]
Disclaimer: – The above article is prepared keeping in mind various provisions relating to transfer of shares under the Companies Act, 2013 and rules made thereunder. The author has tried to cover all the important and basic question registration of charge thereunder. Under no circumstance, the author shall be liable for any direct, indirect, special or incidental damage resulting from, arising out of or in connection with the use of the information.
(The Author is Corporate Consultant and provides varied array of services including Start-ups mentor, Secretarial, Legal, Trademark, taxation, Audit, GST, Book keeping and other ancillary advisory service in Delhi, Chandigarh as well as The National Capital Region (NCR) and can be contacted through email id:- triptishakyacs2017@gmail.com and Contact Number: 91-8178515005).






