In the modern business environment, all companies strive for efficiency, accuracy, and agility in their business operations. In this race, the Order to Cash (O2C) process plays a vital role in the business cycle, which involves all activities from receiving an order from a customer to payment collection and subsequent accounting entries.
This critical process serves as the lifeblood of a business, directly influencing cash flow, customer satisfaction, and overall financial well-being. It represents the seamless flow of transactions, encompassing order processing, fulfilment, invoicing, and payment receipt. As the backbone of operational efficiency, a streamlined O2C cycle ensures timely delivery, accurate billing, and prompt payment reconciliation, fostering sustainable growth and profitability.
SAP S/4HANA, with its advanced capabilities, revolutionizes the O2C process by integrating various functions and providing real-time insights, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and optimizing revenue streams.
The Process flow start from:
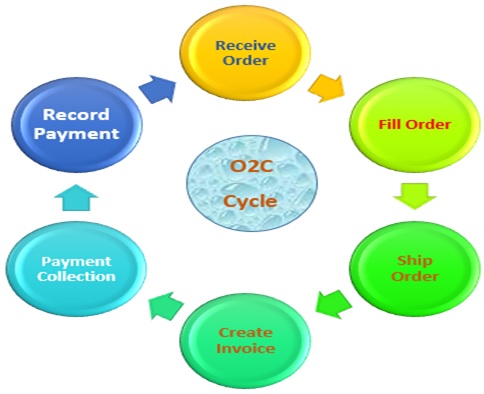
1. Order Management:
√ The O2C process begins with order management, where customer orders are received through various channels such as online platforms, sales representatives, or through Electronic Data Interchange mode.
√ With SAP S/4HANA, the order capturing process is streamlined, facilitating real-time visibility into customer`s demand patterns and current inventory levels. This means that as soon as an order is placed by a customer, it is instantly captured within the system. Consequently, businesses gain immediate insights into customer demands and can accurately assess their inventory levels. This real-time visibility enables organizations to make informed decisions regarding order fulfilment, inventory management, and resource allocation, ultimately enhancing operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
√ Advanced features like order promising and inventory availability checks ensure accurate order fulfilment and optimal allocation of resources.
2. Credit Management:
√ Effective credit management is crucial to mitigate risks and ensure timely payments. SAP S/4HANA offers sophisticated credit management tools that assess customer creditworthiness based on historical data, credit limits, and risk factors.
√ Automated credit checks streamline the process, allowing businesses to make informed decisions while minimizing bad debt exposures.
3. Order Fulfilment:
√ Order fulfilment involves picking, packing, and shipping of goods to customers. With SAP S/4HANA’s integrated logistics and warehouse management capabilities, businesses can optimize their fulfilment processes.
√ Advanced features such as wave picking, automated packing, and real-time inventory tracking enhance efficiency and accuracy, reducing order cycle times and improving customer satisfaction.
4. Invoicing and Billing:
√ Invoicing and billing processes are streamlined with SAP S/4HANA’s invoicing capabilities, which generate accurate invoices based on order details, pricing agreements, and billing schedules.
√ Integration with financial systems ensures seamless accounting entries and compliance with regulatory requirements.
5. Payment Processing:
√ Integration with payment gateways and banking systems enables real-time payment processing, reducing payment delays and enhancing cash flow management.
√ SAP S/4HANA facilitates flexible payment processing options, including electronic payments, credit cards, and invoicing.
6. Collections and Accounts Receivable:
√ Efficient collections management is essential for optimizing cash flow and reducing overdue receivables. SAP S/4HANA provides comprehensive collections management tools that streamline communication with customers, automate follow-up processes, and prioritize collection activities based on payment behaviour and credit risk.
7. Reporting and Analytics:
√ SAP S/4HANA’s advanced analytics capabilities offer real-time insights into O2C performance metrics, including order cycle times, fulfilment rates, cash conversion cycles, and customer payment trends.
√ Interactive dashboards and customizable reports empower decision-makers to identify bottlenecks, optimize processes, and drive continuous improvement initiatives.
B. Order to Cash Cycle Summary Sheet in SAP SD Module
SAP Order-to-Cash (OTC) cycle is a streamlined process that efficiently manages the entire lifecycle of customer orders within the SAP ecosystem.
The process starts from:
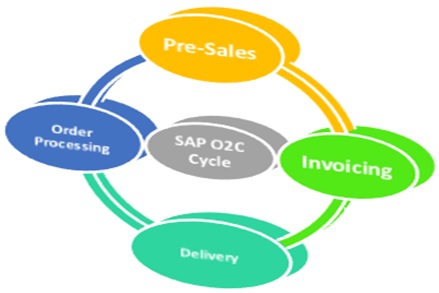
1. Pre-Sales:
The presales process involves activities such as customer inquiries, creating quotations, and establishing initial contact with potential customers. In SAP, the Sales and Distribution (SD) module is extensively used to manage these presales activities. Here’s an overview of the presales process in SAP:
a) Inquiry: This step typically involves handling customer inquiries and creating inquiry documents to track and manage these inquiries. No account entry will be generated during this step.
Transaction code — VA11
b) Quotation: Once a potential opportunity is identified, a sales representative can create a quotation in SAP. The quotation contains details such as the products or services offered, pricing, and validity period. Quotations help in presenting a formal offer to the customer.
Transaction code — VA21
c) Sales Contract: A sales contract is a legal agreement between a company and a customer that outlines the terms and conditions of their business relationship over a specified period. It differs from a standard sales order or quotation in that it represents a longer-term commitment between the parties.
Transaction code — VA41
2. Order Processing
a) Create Sales Document: In SAP, the creation of a sales order is done using transaction code VA01. This transaction code allows users to enter the necessary details such as customer information, material details, quantity, pricing conditions, and delivery dates. The information entered here is stored in the Sales Order (SO) document.
There are other transactions in SAP to change and display Sales orders, which can be useful in the overall process.
VA02 — Change Sales Document
VA03 — Display Sales Document
3. Delivery
a) After the sales order has been created, users initiate the delivery process by creating an outbound delivery. The outbound delivery specifies the items to be delivered, the shipping point, and other relevant details. The delivery document is linked to the sales order and contains information on the ordered items, quantities, and shipping information. During the creation of the outbound delivery, users may perform actions such as picking (selecting items from the warehouse) and packing (organizing items for shipment).
Transaction Code: VL01N
b) Post Goods Issue (PGI): Once the items are picked, packed, and ready for shipment, the next step is to post the goods issue. This step signifies the physical or logical transfer of goods from the seller to the buyer. Within the delivery document, they navigate to the “Goods Movement Data” tab and post the goods issue. This action updates the stock levels in the system.
Transaction Code: VL02N
c) Shipment: The shipment process involves grouping multiple outbound deliveries into a single shipment for transportation efficiency. Users create a shipment document and link multiple outbound deliveries to it. This helps in managing the transportation of goods more effectively. Shipment documents include information about carriers, transportation modes, and routes. They serve as a central point for monitoring and managing the transportation of goods.
Transaction Code: VT01N
4. Invoicing
a) Create Billing Document: After successful delivery, the invoicing process is started in SAP. The invoicing document contains information about the products delivered, prices, and any applicable taxes. This document is used for invoicing to the customer.
Transaction Code: VF01
b) Customize Billing Document: In SAP, different billing document types may be defined based on business requirements. Common billing document types include invoices, credit memos, and debit memos etc.
Transaction Code: VOK0
c) Payment Processing: SAP supports various payment methods, and once the customer makes the payment, it is recorded in the system. This step involves updating the Accounts Receivable and General Ledger modules.
Transaction codes: F-28: for Incoming Payments, FBL5N:for Customer Account Display, FBE1: for Payment Advice
Once the payment is received and all financial transactions are reconciled, the sales order is considered complete. SAP updates relevant records and allows for reporting and analysis of the OTC process.
Moreover,
The Order to Cash process is the lifeline of every business. By seamlessly integrating order management, credit management, Order fulfilment, invoicing, payment processing, collections, and analytics, SAP S/4HANA enables organizations to enhance operational efficiency, optimize cash flow, and deliver superior customer experiences in today’s digital economy.
*****
Author: CMA Pradyumna Kumar Dash | Internal Control, Risk Assurance &Corporate Services Professional | Mob:+91-7894805771





