Introduction
Exports have been the area of focus in all policy initiatives of the Government for more than 30 years. Now with the Make in India initiative, exports continue to enjoy this special treatment because exports should not be burdened with domestic taxes. On the other hand, GST demands that the input-output chain not be broken and exemptions have a tendency to break this chain. Zero-rated supply is the method by which the Government has approached to address all these important considerations.
In this article, I have tried to explain the basic provision, rules as well as notification which are very important to understand the GST on the export of Goods as well as services.
What is Export of Goods under GST?
As per IGST Act Section 2(5) Export of goods with its grammatical variations and cognate expressions, means taking goods out of India to a place outside India. Export means trading or supplying of goods and services outside the domestic territory of a country.
What is Export of Services under GST?
As per IGST Act Section 2(6) “Export of services” means the supply of any service when, –
(i) the supplier of service is located in India;
(ii) the recipient of service is located outside India;
(iii) the place of supply of service is outside India;
(iv) the payment for such service has been received by the supplier of service in convertible foreign exchange; or in Indian rupees wherever permitted by RBI, [inserted vide IGST (Amendment) Act, 2018, w.e.f. 1-2-2019 and
(v) the supplier of service and the recipient of service are not merely establishments of a distinct person. if place of supply is out of India (Notification No. 9/2017-IT (Rate) both dated 28-6-2017 as inserted w.e.f. 27-7-2018.)
Supply of services having place of supply in Nepal or Bhutan, against payment in Indian Rupees is exempted even if the payment is received in Indian Currency looking at the business practices and trends.
Notification No. 42/2017-Integrated Tax (Rate) 27th October 2017
Case Law : The Administrative and support services supplied to foreign client, where payment is received in foreign exchange, is export of service and is zero rated.( New Global Specialist Engineering Services P Ltd. In re (2019) (AAR-Maharashtra),
Bank Remittance Certificate(BRC) or Foreign Exchange Remittance Certificate (FIRC) is required only in case of export of services and not in case of export of goods ( clarified vide CBI&C circular No. 37/11/2018-GST dated 15-3-2018)
Exports of goods and services to Nepal and Bhutan and supplies to SEZ is ‘export’ even if payment is received in Indian rupees – MF(DR) circular No. 5/5/2017-GST dated 11-8-2017 and CBI&C circular No. 8/8/2017-GST dated 4-10-2017, as amended by CBI&C circular No. 88/07/2019-GST dated 1-2-2019.
How are Exports treated under GST Law?
Under the GST Law, export of goods or services has been treated as:
- Inter-State supply (7(5) IGST act) and covered under the IGST Act. Export is treated as Inter-state supply under GST and IGST is charge on export.
- ‘zero rated supply’ (Sec.16 (1) IGST act) i.e. the goods or services exported shall be relieved of GST levied upon them either at the input stage or at the final product stage.
GST will not be levied in any Kind of Exports of Goods or Services.
What is Zero rated Supply? – Sec.16 (1) IGST ACT
(1) “zero rated supply” means any of the following supplies of goods or services or both, namely:––
(a) Export of goods or services or both; or
(b) Supply of goods or services or both to a Special Economic Zone developer or a Special Economic Zone
Zero-rated supply does not mean that the goods and services have a tariff rate of ‘0%’ but the recipient to whom the supply is made is entitled to pay ‘0%’ GST to the supplier.
In other words, as it has been well discussed in section 17(2) of the CGST Act that input tax credit will not be available in respect of supplies that have a ‘0%’ rate of tax. However, this disqualification does not apply to zero-rated supplies covered by this section.
These provisions of zero-rated supplies are introduced in the statute on the basis of the prevalent Central Excise and Service Tax laws. It is widely believed that introduction of this provision will alleviate the difficulty of a supplier who exempts goods or services or both in terms of export competitiveness.
This provision also specifically expresses that taxes are not exported. Care must be exercised that while paying taxes, such taxes are not collected from the recipient of goods or services or both. This would result in unjust enrichment.
The exporter may utilize such credits for discharge of other output taxes or alternatively, the exporter may claim a refund of such taxes as per section 54 of CGST or Rules made there under. .
Person making zero rated supply requires GST registration (except in case of service providers having turnover less than Rs 20 lakhs)
Exporters can claim refund of GST Compensation Cess & Compensation Cess will not be charged on goods exported under bond or LUT (CBE&C circular No. 1/1/2017-Compensation Cess dated 26-7-2017.)
If GST compensation Cess is payable on inputs but not on output supply of goods exported, refund of ITC of GST Compensation Cess can be claimed ( CBI&C circular No. 45/19/2018-GST dated 30-5-2018.)
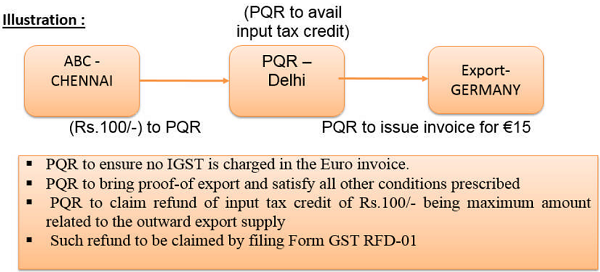
How Exporter can claim refund for Zero rated supply?
A guidance note relating was released by the Indian government which has helped in clearing doubts regarding the claim of input tax credit on zero-rated exports. An exporter dealing in zero-rated goods under GST can claim a refund for zero-rated supplies as per the following options:
The requirement of bond has been mostly dispensed with. Thus, all direct exporters are required to execute only LUT w.e.f. 4-10-2017. Now, bond and guarantee is required in very few cases.
How Exporter can claim refund under Option -1 LUT Method?
He may export the Goods/services under a Letter of Undertaking, without payment of IGST and claim refund of unutilized input tax credit; (Rule 96A of CGST Rules)
(1) Any registered person availing the option to supply goods or services for export without payment of integrated tax shall furnish, prior to export, a bond or a Letter of Undertaking in FORM GST RFD-11 Bond and LUT Format to the jurisdictional Commissioner, binding himself to pay the tax due along with the interest specified under sub-section (1) of section 50 within a period of—
Who can export without payment of IGST by furnishing only Letter of Undertaking (LUT) in place of Bond?
(a) fifteen days after the expiry of three months from the date of issue of the invoice for export, if the goods are not exported out of India; or
(b) fifteen days after the expiry of one year, or such further period as may be allowed by the Commissioner, from the date of issue of the invoice for export, if the payment of such services is not received by the exporter in convertible foreign
(2) The details of the export invoices contained in FORM GSTR-1 furnished on the common portal shall be electronically transmitted to the system designated by Customs and a confirmation that the goods covered by the said invoices have been exported out of India shall be electronically transmitted to the common portal from the said
All exporters registered under GST can export goods or services without payment of IGST, on execution of LUT, except those who have been prosecuted for offence under any law where tax evade exceeds Rs 250 lakhs. The LUT is valid for whole financial year.
LUT/bond is to be submitted to concerned Central/State tax authority having jurisdiction over the taxable person will be accepted by Deputy/Assistant Commissioner within three working days. If the LUT/bond is not accepted within three working days, it will be deemed to have been accepted.
Running bond is required to maintained. The bond amount should cover amount of self assessed estimated tax liability on export. If bond amount is not sufficient, fresh bond should be executed
LUT can be on letter head of exporter with signature and seal of authorised person. LUT shall be valid for twelve months. If the exporter fails to comply with the conditions of the LUT he may be asked to furnish a bond.
The Bond/LUT shall be accepted by the jurisdictional Deputy/Assistant Commissioner having jurisdiction over the principal place of business of the exporter. The exporter is at liberty to furnish the bond/LUT before Central Tax Authority or State Tax Authority. However, if in a State, the Commissioner of State Tax so directs, by general instruction, to exporter, the Bond/LUT in all cases be accepted by Central tax officer till such time the said administrative mechanism is implemented. Bond or LUT should be accepted in maximum three working days.
Declaration about non-prosecution is already filed with LUT. Hence, further Self-Declaration about non-prosecution is not required with every refund claim ( CBI&C circular No. 37/11/2018-GST dated 15-3-2018.)
The exporter is required to execute a bond or Letter of Undertaking, prior to exports, binding him to (a) pay tax with interest, within 15 days after three months from date of issue of invoice, if goods are not exported. This period can be extended by Commissioner. (b) 15 days after expiry of one year or such further period as may be allowed by Commissioner, from date of issue of invoice for export, if payment is not received by the exporter or in convertible foreign exchange or in Indian Rupees, where permitted by RBI – (rule 96A(1) of CGST Rules, as amended w.e.f. 1-2-2019.)
Refund of input tax credit will be permissible even if export is made after three months. It is not necessary to pay IGST and claim refund of IGST. Extension of three months period can be given by jurisdictional Commissioner on ex post facto basis keeping in view the facts and circumstances of each case. This principle applies in case of export of service also – (CBI&C circular No. 37/11/2018-GST, dated 15-3-2018.)
The LUT shall be deemed to have been accepted as soon as an acknowledgement reference number (ARN) is generated online. Any physical document is not required to be submitted. If it is later found that the exporter was not eligible to submit LUT, the LUT shall be deemed to have been rejected ab initio – CBI&C circular No. 40/14/2018-GST, dated 6-4-2018.
Procedural Requirement for LUT Method:
| Format of Letter of Undertaking in |
: | FORM GST RFD-11 (as per Rule 96A CGST Rule) |
| Submission to | : | The jurisdictional Commissioner, |
| Validity Period | : | Financial Year |
| How | : | On letter head of the registered person |
| Executed by | : | Working partner, Managing Director or the Company Secretary, Proprietor, A person duly authorized by such working partner or Board of Directors of such company or proprietor. |
How Exporter can claim refund under Option -2 Refund of IGST?
 Refund of integrated tax paid on goods or services exported out of India. – Rule 96 CGST Rules.
Refund of integrated tax paid on goods or services exported out of India. – Rule 96 CGST Rules.
(1) The shipping bill filed by an exporter of goods shall be deemed to be an application for refund of integrated tax paid on the goods exported out of India and such application shall be deemed to have been filed only when:-
(a) the person in charge of the conveyance carrying the export goods duly files an export manifest or an export report covering the number and the date of shipping bills or bills of export; and
(b) The applicant has furnished a valid return in FORM GSTR-3 or FORM GSTR-3B, as the case may be;
(2) The details of the relevant export invoices in respect of export of goods 48 contained in FORM GSTR-1 shall be transmitted electronically by the common portal to the system designated by the Customs and the said system shall electronically transmit to the common portal, a confirmation that the goods covered by the said invoices have been exported out of
ATTENTION EXPORTERS ;
GSTIN / PAN and Invoice information in Shipping Bill:
(a) Quoting GSTIN in Shipping bill is mandatory if the export product attracts GST for domestic clearance.
(b) Quoting PAN (Permanent Account Number), which is authorized as Import Export code by DGFT, would suffice if the exporter exclusively deals with products which are either wholly exempt from GST or out of GST regime.
(c) In case of exports by specialized agencies such as United Nations Organization or notified Multilateral Financial Institutions, Embassies and Consulates, the exporter can quote Unique Identity Number, instead of GSTIN, in the Shipping bill.
(d) Without GSTIN or PAN or UIN, the Shipping bill cannot be filed.
(e) The claim for refund of IGST paid or Input Tax Credit on inputs consumed in goods exported cannot be processed without GSTIN and GST Invoice details in Shipping Bill.
(f) Commercial Invoice information should be provided in the Shipping Bill. Wherever Commercial Invoice is different from Tax Invoice, details of both have to be provided in the Shipping Bill.
(g) Taxable value and Tax amount should be mentioned against each item in the Shipping bill for processing the refund amount. Multiple tax invoices issued by same GSTIN holder are allowed in one Shipping bill for the same consignee.
(h) State code is part of GSTIN numbering scheme. However, in the Shipping Bill for the field “State of origin” declare the State code from where export goods originated as it was being done before.
Changes in Export Procedures:
Electronic as well as manual Shipping Bill formats including Courier Shipping Bill are being amended to include GSTIN and IGST related information so as to ensure that the export benefits like refund of IGST paid as well as accumulated input tax credit can be processed seamlessly. For the benefit of the trade, modified Forms have been hosted on the departmental website, www.cbec.gov.in. Further, suitable notifications shall be issued to amend the relevant regulations and introduce modified Forms.
Export under factory stuffing procedures:
In the context of GST, taking into account the obligation of filing GSTR1 and GSTR2 by exporters who are registered under GST, Board intends to simplify the procedure relating to factory stuffing hitherto carried out under the supervision of Central Excise officers. It is the Endeavour of the Board to create a trust based environment where compliance in accordance with the extant laws is ensured 64
How tax will be charged when sold to merchant Exporter or in the course of Penultimate Sale.
Notification No. 41/2017-Integrated Tax (Rate) 23rd October 2017
Exempts the inter-State supply of taxable goods (hereafter in this notification referred to as “the said goods”) by a registered supplier to a registered recipient for export, from so much of the integrated tax leviable thereon under section 5 of the Integrated Good and Services Tax Act, 2017 (13 of 2017), as is in excess of the amount calculated a t the rate of 0.1 per cent. Subject to fulfillment of the following conditions, namely –
Important Condition for the above notification are as follows:
(i) The registered supplier shall supply the goods to the registered recipient on a tax invoice;
(ii) The registered recipient shall export the said goods within a period of ninety days from the date of issue of a tax invoice by the registered supplier;
(iii) The registered recipient shall indicate the Goods and Services Tax Identification Number of the registered supplier and the tax invoice number issued by the registered supplier in respect of the said goods in the shipping bill or bill of export, as the case may be.
The manufacturer supplier should supply goods to merchant exporter The merchant exporter should be registered under GSTIN and Export Promotion Council or Commodity Board recognized by Department of Commerce.
The merchant exporter should place an order of manufacturer exporter and its copy shall be provided to jurisdictional tax officer of registered supplier.
The manufacturer exporter shall clear goods on payment of 0.1% IGST (or 0.05% of CGST plus 0.5% of SGST/UTGST).
Goods should be dispatched directly from place of manufacturer to port, ICD, Airport of Land customs station from where goods are to be exported.
Goods can also be sent to a registered warehouse from where goods can be sent to port, ICD, Airport of Land customs station from where goods are to be exported.
The goods can be aggregated at the registered warehouse and then sent to port, ICD, Airport of Land customs station from where goods are to be exported. In such case, the merchant exporter shall endorse receipt of goods on the tax invoice and also acknowledgement of receipt of goods in the registered warehouse. These should be provided to the registered supplier as well as to jurisdictional tax officer of such supplier.
After export, the merchant exporter shall provide copy of shipping bill or bill of export containing details of GSTIN of supplier and his tax invoice of manufacturer with proof of filing of export general manifest (EGM) or export report.
Export through post by e-commerce operators ; E-commerce operators can export goods through Foreign Post Office (FPO). These exports will be zero rated. Declaration is to be filed in PBE-1. Exports by e-commerce operators can be from any foreign post office. However, exports under MEIS can be only from Foreign Post Offices at Delhi, Mumbai and Chennai. (CBI&C circular No. 14/2018-Cus dated 4-6-2018.)
What is Deemed Export?
The Government may, on the recommendations of the Council, notify certain supplies of goods as deemed exports, where goods supplied do not leave India, and payment for such supplies is received either in Indian rupees or in convertible foreign exchange, if such goods are manufactured in India.
Notification No. 48/2017-Central Tax
Some supplies have been notified as deemed export vide above notification as below:
| 1. | Supply of goods by a registered person against Advance Authorization |
| 2. | Supply of capital goods by a registered person against Export Promotion Capital Goods Authorization |
| 3. | Supply of goods by a registered person to Export Oriented Unit |
| 4. | Supply of gold by a bank or Public Sector Undertaking specified in the notification No. 50/2017-Customs, dated the 30th June, 2017 (as amended) against Advance Authorization. |
(Author is chartered accountant from Raipur, Chhattisgarh practicing in indirect tax and is national empanelled faculty of indirect tax committee of ICAI, New Delhi. Author may be contacted at caramandeep.bhatia@gmail.com or on + 91 9827152729)
(Republished with Amendments. Amendments been made by CA Anita Bhadra)









SIR, IF THE PAYMENT RECEIVED THROUGH STRIPE PAYMENT GETWAY FROM OTHER COUNTRY FOR SERVICE PROVIDED BY INDIA GST HOLDER THEN THE GST LIABLE ON THAT SERVICE IS 18% OR 0 RATED SUPLY IN GST?
Can we procure material with less or zero rated GST as we are exporter . Lot of cash gets blocked in GST as well as old Excise refund is also transfer to CGST is there any way to get exemption on purchase of raw material
sir , we want clarification and your opinion of this our issue