MESSAGE
“By common endeavor we can raise the country to a new greatness, while a lack of unity will expose us to fresh calamities”
-Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
The Country celebrates Samvidhan Diwas (Constitution Day) every year on 26th November to commemorate the adoption of the Constitution of India and to honor the contribution of founding fathers of the Constitution. The Constitution Day was celebrated with much fervor in the GST Council Secretariat this year and on this occasion, we must reflect on the Or Amendment to the Constitution which paved the way for GST Council. This watershed moment translated into reality the spirit of co-operative federalism enshrined in our Constitution. The coming together of Center and States to jointly discuss and decide the levy of tax on goods and services and is a perfect system for enabling the federal framework.
Over the past 5 years, the GST Council through its various meetings have furthered the cause of co-operative federalism by addressing a number of GST related issues through dialogue. During this period tax related issues pertaining to Central levy and States levy were treated uniformly and resolutions were agreed upon only after extensive deliberations and discourse amongst the members. Further, depicting the true federal spirit, the Council also on various occasions have constituted Group of Ministers and Committees involving representations from different States in order to assist the Council in addressing the said issues. The Council has so far met for 47 times and all decisions except one have been taken by consensus. This is a clear demonstration of co-operative federalism.
It has been a journey of great significance. We have come a long way in making improvements to GST regime. Compliances have been strengthened, IT system has become more robust and the GST regime is on a robust path. Introduction of key initiatives such as the e-waybill mechanism, e-invoicing and auto-population of returns has helped in reducing the compliance burden on taxpayers.
The upcoming 48th GST Council meeting is scheduled to be held on 17th December, 2022 in New Delhi through video conferencing and it shall discuss important matters pertaining to law and rate rationalization. The GoM on GSTAT has submitted its report to the Union Finance Minister thus paving the way for formation of GSTAT, which has been a long standing demand for a proper Appellate mechanism.
Pankaj Kumar Singh
Additional Secretary
GST Revenue Collection
Rs. 1,45,867 crore gross GST revenue collected for November, 2022, records increase of 11% Year-on-Year
The gross GST revenue collected in the month of November, 2022 is Rs. 1,45,867 crore of which CGST is Rs. 25,681 crore, SGST is Rs. 32,651 crore, LOST is Rs. 77,103 crore (including Rs. 38,635 crore collected on import of goods) and Cess is Rs. 10,433 crore (including Rs. 817 crore collected on import of goods)
The government has settled Rs. 33,997 crore to CGST & Rs. 28,538 crore to SGST from LOST as regular settlement.
The total revenue of Centre and the States after regular settlements in the month of November, 2022 is Rs. 59678 crore for CGST and Rs. 61189 crore for the SGST. In addition, Centre had also released Rs. 17,000 crore as GST compensation to States/UTs in November, 2022.
The revenues for the month of November, 2022 are 11% higher than the GST revenues in the same month last year, which itself was ? 1.31,526 crore.
During the month, revenues from import of goods are 20% higher and the revenues from domestic transaction (including import of services) are 8% higher than the revenues from these sources during the same month last year.
The chart below shows trends in monthly gross GST revenues during the current year.
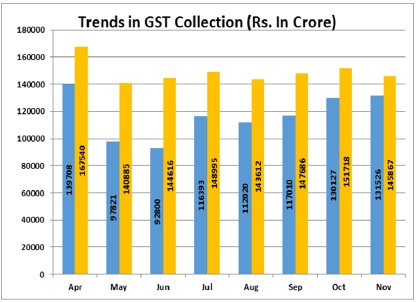
Source: PIE Press release deed 01.12.2022
Centre releases Rs. 17,000 crore of GST compensation to States/UTs
The Central Government released an amount of Rs. 17,000 crore to States/UTs on 24.11/022 towards the balance GST compensation for the period April to June, 2022 (State-wise details as per Table below). The total amount of compensation released to the States/UTs so far, including the aforesaid amount, during the year 2022-23 is Rs. 1,15,662 crore.
This is despite the fact that total Cess collection till October, 2022 was only Rs. 72,147 crore and the balance of Rs. 43,515 crore has been released by the Centre from its own resources. With this release, the Centre has released, in advance, the entire amount of Cess estimated to be collected this year till March-end available for payment of compensation to States. This decision was taken to assist the States in managing their resources and for ensuring that their programmes especially the expenditure on capital is carried out successfully during the Financial Year.
Even in May this year, the Central Government had released Rs. 86,912 crore as provisional GST compensation to States for the period Feb-May’2022 despite the fact that there was only about Rs. 25,000 crore in the GST Compensation Fund, by making arrangement of finds of around Rs. 62,000 crore from its own resources.
| Name of the State/UT | (Rs. is crones) |
| Andhra Pradesh | 682 |
| Assam | 192 |
| Bihar | 91 |
| Chhattisgarh | 500 |
| Delhi | 1.200 |
| Goa | 119 |
| Gujarat | 856 |
| Haryana | 622 |
| Himachal Pradesh | 226 |
| Jammu and Kashmir | 208 |
| Jharkhand | 338 |
| Kamataka | 1.915 |
| Kerala | 773 |
| Madhya Pradesh | 722 |
| Maharashtra | 2,081 |
| Odisha | 524 |
| Puducherry | 73 |
| Punjab | 984 |
| Rajasthan | 806 |
| Tamil Nadu | 1,188 |
| Telangana | 542 |
| Uttar Pradesh | 1,202 |
| Uttarakhand | 342 |
| West Bengal | 814 |
| Total | 17,000 |
Source: PIB Press release dated 25.11.2022
Notifications
> Notification No. 22/2022-Central Tax dated 15.11.2022 regarding notifying amendments to the CGST Rules, 2017(Third Amendment, 2022).
The Government vide the said Notification has amended the instructions at Paragraph 7 of Form GSTR-9 in order to give effect to the change of time limit for claiming ITC, issuing credit or debit notes & making amendments in outward supplies for the previous year. The words ‘April 2022 to September 2022’ have now been substituted with ‘April 2022 to October 2022 filed up to 30th November, 2022’ in the relevant places in order to provide increased time limit to taxpayers for claiming Input Tax Credit.
> Notification No. 24/2022-Central Tax dated 23.11.2022 regarding notifying amendments to the CGST Rules, 2017 (Fourth Amendment, 2022).
The Government vide the said Notification has omitted Rules 122,124,125,134 and 137 from the CGST Rules, 2017. Vide the said Notification changes have been introduced via substitution in Rule 127 and in the Explanation after Rule 137. These Rules pertain to Anti Profiteering provisions.
These amendments have come into effect from 01.12.2022.
> Notification No. 23/2022-Central Tax dated 23.11.2022
The Government vide the said Notification has empowered the Competition Commission of India to handle Anti-profiteering cases under CGST Act, 2017 with effect from 01.12.2022.
Circulars
> Circular No. 182/14/2022-GST dated 10.11.2022 regarding Guidelines for verifying the Transitional Credit.
Vide the said Circular the Central government has provided detailed Guidelines for verifying the Transitional Credit in light of the Order of the Hon’ble Supreme Court in the case of Union of India vs. M/s Filco Trade Centre Pvt. Ltd., SLP(C) No. 32709-32710/2018, Order dated 22.07.2022 & 02.09.2022.
The detailed guidelines can be accessed by clicking on
Guidance Note for Verification of CGST Transitional Credit Claimed In TRAN-1/TRAN-2
> Circular No. 181/13/2022-GST dated 10.11.2022 regarding Clarification on refund related issues.
The Central Government vide Notification No. 14/2022-Central Tax dated 05.07.2022, had amended the formula prescribed for refund on account of Inverted Duty Structure (IDS) under Rule 89(5) of Central Goods and Services Tax Rules, 2017 (CGST Rules). Further, vide Notification No. 9/2022- Central Tax (Rate) dated 13.07.2022, effective from 18.07.2022, the Central Government had placed restriction on Input Tax Credit on account of Inverted Duty Structure in case of supply of certain goods falling under Chapter 15 and Chapter 27.
Pursuant to the applicability of the said amendments, the Government vide the aforesaid Circular has clarified that the amended formula under sub-rule (5) of Rule 89 of the CGST Rules, 2017 for calculation of refund of input tax credit on account of inverted duty structure would be applicable only in respect of refund applications filed on or after 05.07.2022. The refund applications filed before 05.07.2022 will be dealt as per the formula as it existed before the amendment.
The Central Government further clarified that the restrictions imposed on Refund of unutilized Input Tax Credit on account of inverted duty structure in case of specified goods falling under chapter 15 and 27 would apply prospectively i.e., the said restrictions would apply to all refund applications filed on or after 18.07.2022, i.e. the date from which Notification No. 9/2022- Central Tax (Rate) was made effective and would not apply to the refund applications filed before 18.07.2022.
Instruction
> Instruction No 04/2022 Central Tax dated 28.11.2022 regarding manner of processing and sanction of IGST refunds in terms of Rule 96(4)(c) of the CGST Rules, 2017 The Central Government vide the said instruction has issued detailed guidelines regarding manner of processing and sanction of IGST refunds, withheld in terms of clause (c) of sub-rule (4) of Rule 96 and transmitted to the jurisdictional GST authorities under sub-rule (5A) of Rule 96 of the CGST Rules, 2017.
GST Outreach Programmes
> Hon’ble Union Finance Minister Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman’s visit to Thiruvananthapuram, Kerala
Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman, Hon’ble Union Finance Minister on her one-day visit to Kerala on 05.11.2022 inaugurated the Balaramapuram Handloom Producer Company and Common Facility Centre at Pallichal, Tiruvanthpuram for giving a boost to Handloom Sector.
to coordinate and work in sync with the cyber security department of Home Ministry in the wake of increase in financial frauds & cybercrimes.
Hon’ble Finance Minister also held discussions with various industry associations, including Trivandrum Chamber of Commerce and Industry, Kerala Gramin Bank Association and All Kerala Fresh Vegetables & Fruits Exporters Association.
In Pictures above: Hon’ble Union Finance Minister, Smt. Nirmala Sitharaman with Members of various Industry Associations.
> Maharashtra’s Deputy Chief Minister & Finance Minister conducted meeting on 07.11.2022 with officials of GST department
Shri Devendra Fadnavis, Hon’ble Deputy Chief Minister and Finance Minister of Maharashtra chaired a GST Department Review Meeting on 07.11.2022 with ACS (Finance), GST Commissioner and other senior officials of State GST Department. During the meeting he reviewed the working of GST department, achievements and growth made in GST collection, reforms in system and GAIN – GST Analysis & Intelligence Network. He further, directed the GST department
In pictures above: Sh. Devendra Fadnavis, Hon’ble Deputy Chief Minister & Finance Minister of Maharashtra during the review meeting with officers of State GST Department.
> Robust & User-friendly Website ICEGATE 2.0 launched by CBIC
Chairman CBIC Sh. Vivek Johri virtually launched the robust, multifunctional and user-friendly website ICEGATE 2.0 on 16.11.2022. The other dignitaries present during the website launch were Member (IT) Sh. Alok Shukla, Member (GST) V. Rama Mathew, Pr. DG Systems and other senior officers.
The website has been launched with a motive to improve user experience and to provide various additional EXIM services to stakeholders for enhancing the Ease of Doing Business and for minimizing the grievances.
In pictures above: Sh. Vivek Johri, Chairman, CBIC launching ICEGATE 2.0 website
> Outreach programme on “Recent changes in GST Law & Practices” at Central GST Pune-II Commissionerate
An outreach programme on “Recent changes in GST Law and Practices” was organised by Central GST Pune-II Commissionerate at Solapur especially for MSMEs along with GST Practitioners and Trade bodies of Solapur, Pandharpur and Barshi. The programme was organized both in Marathi and Hindi language in order to ensure maximum outreach.
In pictures above: Sh. S.M. Tata, Chief Commissioner, Pune Zone during the outreach programme with traders
> GST awareness programme for traders and hoteliers of Pahalgam district, J&K
As part of Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav’s public outreach campaign, the State Taxes Department, J&K conducted a GST awareness session on 16.11.2022. The interactive session was moderated by Dr Rashmi Singh, IAS Commissioner, State Taxes Department, J&K and was specifically conducted for traders and hoteliers of Pahalgam district.
In pictures above: Dr Rashmi Singh, IAS Commissioner, State Taxes Department, J&K during the outreach programme with traders and hoteliers of Pahalgam district.
> Instructions issued by Tamil Nadu Government for Initiating Action against Non-Filers of GST Returns
Vide Circular no. 14-2022-TNGST dt. 12.11.2022 the Tamil Nadu Commercial Taxes department has issued detailed instructions with respect to the procedure to be followed in respect of non-filers of GST Returns under the Tamil Nadu Goods and Service Tax Act, 2017.
Instructions issued by Kerala State GST Department on mandatory furnishing of proper information of ineligible / blocked Input Tax Credit and reversal thereof in FORM GSTR-3B
Vide Trade Circular No.1/2022 dated 21.11.2022 the Kerala State GST Department has issued detailed instructions regarding mandatory furnishing of correct and proper information of ineligible / blocked Input Tax Credit (“ITC”) and reversal thereof in FORM GSTR-3B in view of the recent changes made in FORM GSTR-3B. The Circular has detailed out the procedure to be followed for furnishing of information regarding Input Tax Credit availed, reversal thereof and ineligible Input Tax Credit in Table 4 of FORM GSTR-3B.
The Trade notice can be accessed clicking on
Mandatory furnishing of ineligible / blocked ITC & reversal thereof in Form GSTR-3B – instructions
> National Seminar on “Recent Developments under GST Regime -Challenges & Way forward” organized by ASSOCHAM
A National Seminar on “Recent Developments under GST Regime -Challenges & Way forward” was organised in New Delhi under the aegis of ASSOCHAM on 25.11.2022. The objective of the program was to update the industry on the recent developments made under GST regime and to obtain the feedback from the trade about their experience while dealing with revenue authorities with respect to dispute, audit, refund, compliance, etc.
The seminar was attended by Sh. Sanjay Mangal IRS, Principal Commissioner, GST Policy wing, CBIC, Ministry of Finance, Ms. Ashima Bansal IRS, Joint Secretary, GST Council Secretariat and Mr. Vishal Pal Singh, Sr. Vice President, Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) along with other eminent stakeholders from the industry.
In pictures above : Sh. Sanjay Mangal IRS, Principal Commissioner, GST Policy Wing & Ms. Ashima Bansal IRS, Joint Secretary, GST Council Secretariat being felicitated by ASSOCHAM
Portal Updates
> Webinar on ‘Filing of an Appeal by Taxpayers on GST Portal’
For creating awareness amongst all the stakeholders, GSTN conducted webinars on ‘Filing of an Appeal by Taxpayers on GST Portal’, as per the details given below:
| Webinar Topic | Webinar on Filing of an Appeal by Taxpayers on GST Portal | |||
| Language of webinar | Hindi | English | Marathi | Tamil |
| Date | 29.11.2022 Tuesday |
30.11.2022 Wednesday |
01.12.2022 Thursday |
05.12.2022 Monday |
| Time | 11:00 AM | 12:00 NOON | 12:30 PM | 12:00 NOON |
| Speaker | Ms. Ankita Assistant Manager, GSTN |
Sh. Sanjay Kumar Sharma AVP, GSTN |
Sh. Bhagwan Patil
VP, GSTN |
Sh. Rafi Ahmed Kidwai Manager, GSTN |
| YouTube Link for Webinar |
https://yout u.be/1cui RZacHz0 |
https://youtu. be/O_3j5 AdQBrs |
https://you tu.be/8xpr5 OT0ccE |
https://youtu. be/isEdP NtIWI0 |
Recording of these sessions is available on GSTNs dedicated YouTube channel, at https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCFYpOk92qurlO5t-Z_y-bOQ.
Portal update on 25.11.2022
Legal Corner
> Noscitur a Sociis
The Principle of Noscitur a Sociis is one of the rules of interpretation relied on by courts while interpreting the meaning of any legislation. The term Noscitur a Sociis is derived from Latin, with noscitur meaning knowing and socii meaning association. It is relied on by the Courts of law for interpreting those provisions of law which contains a word or phrase that is capable of bearing more than one meaning. The rule implies that the meaning of an unclear word or phrase must be determined by the words that surround it i.e. the meaning of a word is to be judged by the company it keeps.
| Speaker | Ms. Ankita Assistant Manager, GSTN |
Sh. Sanjay Kumar Sharma AVP, GSTN |
Sh. Bhagwan Patil
VP, GSTN |
Sh. Rafi Ahmed Kidwai Manager, GSTN |
| YouTube Link for Webinar |
https://yout u.be/1cui RZacHz0 |
https://youtu. be/O_3j5 AdQBrs |
https://you tu.be/8xpr5 OT0ccE |
https://youtu. be/isEdP NtIWI0 |
This rule of interpretation is well explained by Maxwell in his book interpretation of statutes and he states that when two or more words susceptible of analogous meaning are coupled together, they are understood to be used in their cognate sense. The words take their colour from and are quantified by each other, the meaning of the general words being restricted to a sense analogous to that of the less general.
Pertinently, the scope of this rule of interpretation is limited, for it can only be applied in the circumstances where the law is either not clear or it is ambiguous. The doctrine of ejusdem generis discussed in the October edition of the Newsletter is a facet of Noscitur a sociis. The rule of ejusdem generis is an offshoot of noscitur a socii. It is considered that the rule of noscitur a socii is broader in understanding as compared to the rule of ejusdem generis.
> Doctrine of Promissory Estoppel
The doctrine of promissory estoppel is an equitable doctrine evolved by courts of equity to prevent miscarriage of justice. It is based on the principles of justice, fair play, and good conscience. Like all equitable remedies, it is discretionary in nature, in contrast to the rights available under Common law.
The doctrine of promissory estoppel states that when one individual with the intention of creating or affecting lawful relationship makes a promise with another individual and that individual acts on it, then that promise must be binding for the individual who is making it. He/she would not be allowed to go back from their words. Because reverting from the words shall be against equity.
In Union of India & Anr vs Wing Commander R.R. Hingorani the Apex court laid down that to invoke the doctrine of estoppels, there are three conditions which must be satisfied:
1. That there was a representation or promise.
2. The other should have acted upon the said representation &
3. Such action should have been detrimental to the interests of the person to whom the representation has been made.
In-House Activities
The Constitution Day – or ‘Samvidhan Divas’ – was celebrated on 26th November at GST Council Secretariat to commemorate the adoption of the Constitution of India. To mark the celebration an event was organized for the staff on Constitution of India for better understanding of the basic tenets of law. Presentations made by the in-house team elaborated on the Preamble of the Constitution, the Basic Structure Doctrine and the 101st Constitutional Amendment by which GST Council Secretariat had come into existence.
The aim of the event was to make the officers understand and appreciate the nuances of the Constitution and as to how it has undergone amendments over the years. The presentations made during the event were an attempt to simplify and familiarize everyone with the basic tenets of constitutional law. The underlying theme was to emphasize B R Ambedkar’s reminder that “the spirit of the Constitution is the spirit of the age”.
Joint Secretary concluded the meeting stating that the Constitution of India and its makers need to be revered for endowing its citizens with such exhaustive and elaborate set of rights.
The presentation on the 101st Constitutional Amendment delivered during the said event is annexed herewith as Annexure 1
Portal update on 25.11.2022
Farewell
The GST Council Secretariat staff bid farewell to Sh. Manish Wadhwa, Superintendent on his superannuation. He had successfully completed 34 years of his dedicated services in CBIC, Ministry of Finance and had worked in GST Council Secretariat for close to 2 years. GST Council Secretariat also bid farewell to Sh. Sanjay Kumar Bansal, Superintendent who was relieved after a long tenure close to 3 years.
In pictures above:
Left to right (Sitting): Mrs. Ashima Bansal Joint Secretary, Sh. Pankaj Kumar Singh Additional Secretary with the superannuated officer Sh. Manish Wadhwa & his wife Smt. Sumita Wadhawa.
Left to right (Standing): Mrs. Reshma R. Kurup Under Secretary, Sh. Harish Kumar Deputy Secretary, Sh. Kshitendra Verma Director & Sh. Joginder Singh Mor Under Secretary.
Right Picture: (Left to Right) Director Sh. Kshitendra Verma felicitating Sh. Manish Wadhwa.
In pictures above (Right to Left): Sh. Pankaj Kumar Singh Additional Secretary bidding farewell to Sh. Sanjay Kumar Bansal on his transfer.
ANNEXURE 1
Framework of Constitution of India
Article 245. Extent of laws made by Parliament and by the Legislatures of States
(1) Subject to the provisions of this Constitution, Parliament may make laws for the whole or any part of the territory of India, and the Legislature of a State may make laws for the whole or any part of the State
(2) No law made by Parliament shall be deemed to be invalid on the ground that it would have extra territorial operation
246. Subject matter of laws made by Parliament and by the Legislatures of States
(1) Notwithstanding anything in clauses (2) and (3), Parliament has exclusive power to make laws with respect to any of the matters enumerated in List I in the Seventh Schedule (referred to as the Union List)
(2) Notwithstanding anything in clause ( 3 ), Parliament, and, subject to clause ( 1 ), the Legislature of any State also, have power to make laws with respect to any of the matters enumerated in List III in the Seventh Schedule (in this Constitution referred to as the Concurrent List)
(4) Parliament has power to make laws with respect to any matter for any part of the territory of India not included (in a State) notwithstanding that such matter is a matter enumerated in the State List
Schedule VII of the Constitution consist of following three list:-
- List I (Union List) contains entries over which the Parliament has power to legislate
- List II (State List) contains entries over which the State Assembly has power to legislate, and
- List III (Concurrent List) contains entries over which both the Central Govt. & the State Govt. has power.
Article of Indian Constitution for GST
Special Provision for GST in Indian Constitution –
Insertion of new Article 246A- Simultaneous power to levy GST –
Article 246A has been inserted in the constitution to confer simultaneous power to the Union & state legislature to legislate upon the GST. Both Center & State can simultaneously levy GST.
246A.
(1) Notwithstanding anything contained in articles 246 and 254, Parliament, and, subject to clause (2), the Legislature of every State, have power to make laws with respect to goods and services tax imposed by the Union or by such State
(2) Parliament has exclusive power to make laws with respect to goods and services tax where the supply of goods, or of services, or both takes place in the course of inter-State trade or commerce.
Explanation.—The provisions of this article, shall, in respect of goods and services tax referred to in clause (5) of article 279A, take effect from the date recommended by the Goods and Services Tax Council.
GST
India has adopted the Dual GST model in which both States and Central levies tax on Goods or Services
or both.
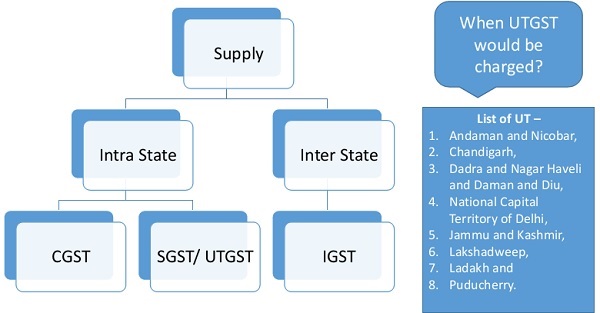
Article 269A
(1) Goods and services tax on supplies in the course of inter-State trade or commerce shall be levied and collected by the Government of India and such tax shall be apportioned between the Union and the States in the manner as may be provided by Parliament by law on the recommendations of the GST Council.
Explanation.—For the purposes of this clause, supply of goods, or of services, or both in the course of import into the territory of India shall be deemed to be supply of goods, or of services, or both in the course of inter- State trade or commerce.
(2) The amount apportioned to a State under clause (1) shall not form part of the Consolidated Fund of India.
Article 286 – Restrictions on the States to impose tax
→ Prior to amendment, the clause restricted the states to impose taxes on sale or purchase of goods.
→ Now it has been amended to provide that the state shall not impose any tax on the supply of the goods or services or both, where such supply takes place:
a. Outside the State
b. in the course of the import of the goods into, or export of the goods out of, the territory of India
→ Further, the Parliament will formulate the principals for determining when a supply constitutes a supply as mentioned in the point above.
Definition of GST
Meaning of GST Article 366(12A)- ‘GST’ means any tax on supply of goods , or services or both except taxes on the supply of the alcoholic liquor for human consumption.
Amendment of Seventh Schedule
|
Entry No. 84 of Union List prior to 101 CAA |
Entry No. 84 post to 101 CAA |
| Excise duty on tobacco & goods manufactured or produced in India Except:- | Duties on excise on the following goods manufactured or produced in India, namely:- |
| (a) Alcoholic liquor for human consumption,
(b) Opium, Indian hemp & other narcotic drug but including medicinal & toilet preparation containing alcohol or any substance in (b) |
(a) Petroleum crude;
(b) High speed diesel; (c) Motor spirit (commonly known as petrol; (d) natural gas; (e) aviation turbine fuel; and (f) Tobacco & tobacco products |
Tobacco & Tobacco products under GST regime
Tobacco & tobacco products would be subject to GST. In addition, to the Centre would have the power to levy Central Excise Duty on these products.
| Entry No. 92 of Union List prior to 101 CAA | Entry No. 92 post to 101 CAA |
| Taxes on sale or purchase of newspaper and advertisements published therein | Omitted |
–
| Entry No. 92C of Union List prior to 101 CAA | Entry No. 92C post to 101 CAA |
| Tax on services | Omitted |
–
| Entry No. 52 of State List prior to 101 CAA | Entry No. 92 post to 101 CAA |
| Taxes on the entry of goods into a local area for consumption, use or sale therein. (Octroi / Entry Tax) | Omitted |
–
| Entry No. 92C of Union List prior to 101 CAA | Entry No. 92C post to 101 CAA |
| Tax on services | Omitted |
GST Council & Its Function Article 279A of the Constitution of India
| Union Finance Minister | Chairperson |
| Union Minister of State in charge of Revenue or Finance | Member |
| The minister in charge of Finance or Taxation or any other minister nominated by each State Govt. | Member |
- GST council is a joint forum of the Center & State
- It was to be constituted within 60 days of commencement of the Constitution (101st amendment) Act 2016
- It would be function under the Chairmanship of Union F.M.
- 50% of the members of GST Council shall constitute the quorum.
- Its decision needs to be approved by a 3/4th majority.
- The vote of the Central Govt. shall have a weightage of 1/3rd of the total votes cast, and
- The votes of all the State Govt. taken together shall have a weightage of 2/3rd of the total votes casts, in that meeting
- It shall recommended the date from when Petroleum Products shall be taxed under the GST.
Function of GST Council- Article 279A(4)
GST Council shall make recommendation to the Union & States on :-
✓ Taxes, cesses and surcharges levied by the Union, States and local bodies which may be subsumed in the GST;
✓ Goods and services that may be subject to, or exempted from the GST;
✓ Model GST Laws, principal of levy, apportionment of GST levied on applies in the course of inter-State trade or commerce under Article 269A;
✓ Threshold limit of turnover below which goods and services may be exempted from the GST;
✓ Rates including floor rates of GST;
✓ Any special rate or rates for a specified period, to raise additional resources during any natural calamity or disaster;
✓ Special provisions with respect to the States of Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, J&K, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Sikkim, Tripura, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand;
✓ any other matter relating to the GST, as the council may decide.





Thanks for your wonderful analysis from IT angle.
Thank You Sir