Updated as on 15th December, 2018
Q.1 What is GSTN?
Ans. Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) is a not-for-profit, non-government company under Section-8 of the Companies Act-2013, promoted jointly by the Central and State Governments, to provide shared IT infrastructure and services, t o both central and state governments including tax payers and other stakeholders. The Front end services of Registration, Returns, Payments, etc. to all taxpayers will be provided by GSTN. It will be the interface between the government and the taxpayers. Further, GSTN also provides the Back-End Services to tax officers of the Model 2 states.
Considering the nature of function performed by GSTN, GST Council has taken a decision that GSTN be converted into a fully owned government Company. For this, the entire 51% equity holding held by the Non-Governmental Institutions in GSTN shall be acquired equally by the Centre and the States governments.
The existing financial commitments given by Centre and States to GSTN to share the capital and O&M cost of the IT Systems shall continue.
Q.2 What was need to create GSTN?
Ans. The GST System Project is a unique and complex IT initiative. Before GST, since, the Centre and State indirect tax administrations worked under different laws, regulations, procedures and formats, there IT infrastructure and systems were also independent of each other. Integrating them for GST implementation would have been complex since it would have required integrating the entire indirect tax ecosystem so as to bring all the tax administrations (Centre, State and Union Territories) to the same level of IT maturity with uniform formats and interfaces for taxpayers and other external stakeholders. Besides, GST being a destination based tax, the inter-state trade of goods and services (IGST) would have needed a robust settlement mechanism amongst the States and the Centre. Meeting these objectives were only possible only when there is a strong IT Infrastructure and Service back bone which would have enabled capturing, processing and exchange of information amongst the stakeholders (including taxpayers, States and Central Government, Bank and RBI). To achieve these objectives of establishing a uniform interface for the tax payer and a common and shared IT infrastructure between the Centre and States, the SPV namely GSTN was created.
Q.3 What is the genesis of GSTN?
The requirement of a strong IT Infrastructure was discussed in the 4th meeting of 2010 of the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers (referred to as the EC) held on 21/7/2010. In the said meeting, the EC approved the creation of an ‘Empowered Group on IT Infrastructure for GST’ (referred to as the EG) under the chairmanship of Dr. Nandan Nilekani with Additional Secretary (Rev), Member (B&C) CBIC, DG (Systems), CBIC, FA Ministry of Finance, Member Secretary EC and five state commissioners of Trade Taxes (Maharashtra, Assam, Karnataka, West Bengal and Gujarat) as its Members. The Group was mandated to suggest, inter alia, the modalities for setting up a National Information Utility (NIU/ SPV) for implementing the Common Portal to be called GST Network (GSTN) and recommend the structure and terms of reference for the NIU/ SPV, detailed implementation strategy and the road map for its creation in addition to other items like training, outreach etc.
In March 2010, TAGUP constituted by the Ministry of Finance had recommended that National Information Utilities should be set up as private companies with a public purpose for implementation of large and complex Government IT projects including GST. Mandate of TAGUP was to examine the technological and systemic issues relating to the various IT projects such as GST, TIN, NPS, etc.
The EG had seven meetings between 2nd August 2010 and 8th August 2011 to discuss the modalities. After due deliberations, the EG recommended creation of a Special Purpose Vehicle for implementing the GST System Project. To enable efficient and reliable provision of services in a demanding environment, the EG recommended a non-Government structure for the SPV called GSTN with Government equity of 49% (Centre – 24.5% and States – 24.5%) after considering key parameters such as independence of management, strategic control of Government(s), flexibility in its organizational structure, agility in decision making and ability to hire and retain competent human resources from both, government and private sector.
In view of the sensitivity of the role of GSTN and the information that would be available with it, the EG also considered the issue of strategic control of Government over GSTN. The Group recommended that strategic control of the Government over the SPV should be ensured through measures such as composition of the Board of Directors (also referred to as the Board), mechanisms of Special Resolution and Shareholders Agreement, induction of Government officers on deputation, and agreements between GSTN SPV and the Government(s). Also, the said shareholding pattern ensured that the Centre individually and States collectively are the largest stakeholders at 24.5% each. In combination, the Government shareholding at 49% would far exceed that of any single private institution.
EG also brought out the need to have technology specification to run this company so that there is 100 percent matching of returns. The business knowledge resides with the officials of Government of India and the States/Union Territories. However, the professionals with knowledge pertaining to technology will also be required as equally important stakeholders to run this company independently, on the lines of NSDL which is working professionally, as well as independently. EG also recommended a non-government company as that will have operational freedom.
These recommendations were presented before the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers in its 3rd meeting of 2011 held on 19th August 2011 and in the 4th meeting of 2011 of the EC held on 14th Oct 2011. The proposal of the EG on IT infrastructure for GST regarding GSTN and formation of a not-for-profit section 25 company with the strategic control of the Government were approved by the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers (EC) in its meeting held on 14.10.11.
The note of Department of Revenue for setting up a Special Purpose Vehicle to be called Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN-SPV) on the lines mentioned above was considered by the Union Cabinet on 12th April 2012 and approved. The Union cabinet also approved the following:
i. Suitable and willing non-government institutions will be identified and firmed up by the Ministry of Finance to invest in GSTN-SPV prior to its incorporation.
ii. The strategic control of the Government over the SPV would be ensured through measures such as composition of the Board, mechanisms of Special Resolution and Shareholders Agreement, induction of Government officers on deputation, and agreements between GSTN SPV and Governments.
iii. The Board of Directors of GSTN SPV would comprise 14 Directors with 3 Directors from the Centre, 3 from the States, a Chairman of the Board of Directors appointed through a joint approval mechanism of Centre and States, 3 Directors from private equity stake holders, 3 independent Directors who would be persons of eminence and a CEO of the GSTN SPV selected through an open selection process.
iv. Relaxation in relevant rules to enable deputation of Government officers to the GSTN SPV for exercise of strategic control and for bringing in necessary domain expertise.
v. GSTN SPV would have a self- sustaining revenue model, where it would be able to levy user charges on the tax payers and the tax authorities availing services.
vi. GSTN SPV to be the exclusive national agency responsible for delivering integrated indirect Tax related services involving multiple tax authorities. Accordingly, any other service provider seeking to deliver similar integrated services would be required to enter into a formal arrangement with GSTN SPV for the services.
vii. A one- time non- recurring Grant- in aid of Rs. 315 crores from the Central Government towards functioning of the SPV for a three-year period after incorporation.
Considering the nature of function performed by GSTN, GST Council has taken a decision that GSTN be converted into a fully owned government Company. For this, the entire 51% equity holding held by the Non-Governmental Institutions in GSTN shall be acquired equally by the Centre and the States governments.
Q.4 What is the equity structure and Revenue Model of GSTN?
Ans. (a) Equity Structure: – In compliance of the Cabinet decision, GST Network was registered as a not-for-profit, non-Government, private limited company under section 8 of the Companies Act, 1956 with the following equity structure:
| Central Govt | 2 |
| State Govts | 2 |
| HDFC | 1 |
| HDFC Bank | 1 |
| ICICI Bank | 1 |
| NSE Strategic Investment Co | 1 |
| LIC Housing Finance Ltd | 1 |
The GSTN in its current form was created after taking % approval of the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers and Union Government after due deliberations over a long period of time.
(b) Revenue Model: An amount of 315 Cr. was approved by the Govt. of India as Grants-in-Aid for initial setting up of the GSTN-SPV in 2013. During the period 31.03.2013 to 31.03.2016, an amount of Rs 143.96 Crores was released as Grant-In-Aid to GSTN out of Rs 315 Crores approved by Govt of India. Out of the grant-in-aid received, only Rs. 62.11 Cr was spent during this period in setting of the Company and making it functional. The balance grant was returned to Govt. of India. During FY 2016-17, GSTN has got loan sanctioned from a commercial bank to meet expenditure over setting up the IT Platform to provide services to the Center and States through GST portal and developing the backend for 27 States and Union Territories. The Revenue model for GSTN has been approved by the Empowered Committee of State Finance Ministers under which user charges will be paid by the Centre and States/UTs equally on behalf of taxpayers and other stakeholders for availing services from the GST Portal. The user charges will be shared equally by the Centre and the States. The user charges for States will be apportioned amongst them based on number of registered taxpayers.
Q.5 What services are being rendered by GSTN?
Ans. GSTN renders the following services through the Common GST Portal:
(a) Registration (including existing taxpayer migration);
(b) Payment management including payment Gateways and integration with banking systems;
(c) Return filing and processing;
(d) Taxpayer management, including account management, notifications, information, and status tracking;
(e) Tax authority account and ledger Management;
(f) Computation of settlement (including IGST Settlement) between the Centre and States; Clearing house for IGST;
(g) Processing and reconciliation of GST on import and integration with EDI systems of Customs;
(h) MIS including need based information and business intelligence;
(i) Maintenance of interfaces between the Common GST Portal and tax administration systems;
(j) Provide training to stakeholders;
(k) Provide Analytics and Business Intelligence to tax authorities; and
(l) Carry out research and study best practices.
(m) E-way bill generation by the stake holders
Q.6 What is the interface system between GSTN and the States/CBIC?
Ans. It was decided that in th e GST regime, while taxpayer facing core services of applying for registration, uploading of invoices, filing of return, making tax payments shall be hosted by GST System, all the statutory functions (such as approval of registration, assessment of return, conducting investigation and audit etc.) shall be conducted by the tax authorities of States and Central governments.
Thus, it was decided that the Front-End (GST Portal services) shall be provided by GSTN and the Back-End modules shall be developed by states and Central Government themselves. However, 27 states (termed as Model-2 states) asked GSTN to develop their Back-End interface also. The CBIC and 9 states (Model 1) decided to develop and host the Back-End modules themselves. For Model 1 states/ CBIC full data (registration, return, payment etc.) submitted by taxpayers is being shared with them for information and analysis as deemed fit by them.
Q.7 What is the role of GSTN in registration?
Ans. The application for Registration is made Online on GST Portal. Some of the key data like PAN, Business Constitution, Aadhaar, CIN/DIN etc. (as applicable) is validated by the GST Portal online with the respective agency i.e. CBDT, UID, MCA etc., thereby ensuring minimum need for submission of documentation. The application data along with supporting scanned documents is being sent by GSTN to states/Centre, which in turn processed that application and sends the query, if any, o r approval or rejection intimation and digitally signed registration to GSTN for eventual download by the taxpayer.
Q.8 What is the role of Infosys in GSTN?
Ans. GSTN has engaged M/s Infosys as a single Managed Service Provider (MSP) for the design, development and deployment of GST system, including all application software, tools and Infrastructure and for operating & maintaining the system for a period of 5 years from the Go-Live date.
Q.9 What are the basic features of GST common portal?
Ans. The GST portal (www.gst.gov.in ) is accessible over Internet (by Taxpayers and their CAs/Tax Advocates etc.) and Intranet by Tax Officials etc. The portal is going to be one single common portal for all GST related services e.g.–
i. Tax payer registration (New, surrender, cancelation, amendment etc.);
ii. Invoice upload, auto-drafting of Purchase register of buyer, GST Returns filing on stipulated dates for each type of return (GSTR [1, 2, 3, 5, 9.etc];
iii. Tax payment by creation o f Challan and integration with agency Banks;
iv. ITC and Cash Ledger and Liability Register;
v. MIS reporting for tax payers, tax officials and other stakeholders;
vi. BI/Analytics for Tax officials.
Q.10 What is the concept of GST Eco-system?
Ans. A common GST system will provide linkage to all State/UT Commercial Tax departments, Central Tax authorities, Taxpayers, Banks and other stakeholders. The eco-system consists of all stakeholders starting from taxpayer to tax professional to tax officials to GST portal to Banks to accounting authorities. The diagram given below depicts the whole GST eco-system.
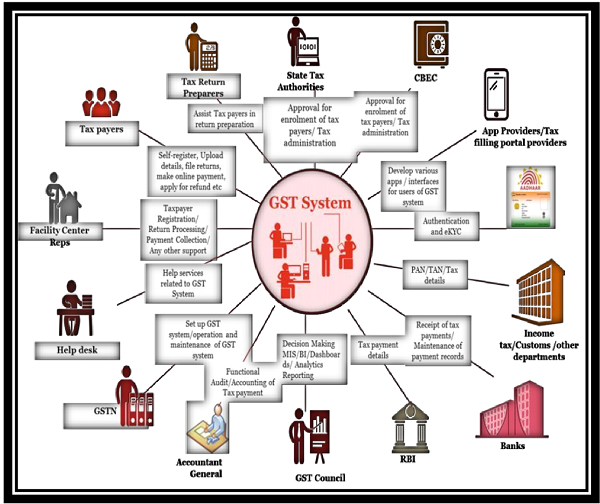
Q.11 What is GSP (GST Suvidha Provider)?
Ans. GST System will provide a GST portal for taxpayers to access the GST System and do all the GST compliance activities. But there will be wide variety of tax payers (SME, Large Enterprise, Micro Enterprise etc.) which may require different kind of facilities like converting their purchase/sales register data in GST compliant format, Integration of their Accounting Packages/ERP with GST System etc., various kind of dashboards to view Matched/Mismatched ITC claims, Tax liability, Filing status etc. As invoice level filing is required, so large organizations may require an automated way to interact with GST system as it may be practically impossible for them to upload large number of invoices through a web portal. So an eco- system is required, which can help such taxpayers in GST compliance.
As Tax payer convenience will be the key to success of GST regime, this eco-system also provides tax payer options of using third party applications, which can provide different kind of interfaces on desktop/mobile for them to be GST compliant.
All above reasons require an eco-system of third party service providers, who have access to GST System and capability to develop such applications. These service providers have been given a generic name, GST Suvidha Providers or GSP.
Q.12 What is the role of GST Suvidha Providers (GSP)?
Ans. GSP develops applications having features like return filing, reconciliation of purchase register data with auto populated data for acceptance/rejection/Modification, dashboards for taxpayers for quick monitoring of GST compliance activities. They may also provide role based access to divide various GST related activities like uploading invoice, filing returns etc., among different set of users inside a company (medium or large companies will need it), Applications for Tax Professional to manage their client’s GST compliance activities, Integration of existing accounting packages/ERP with GST System, etc.
Q.13 What are the benefits to taxpayers in using the GSPs?
Ans. At the outset it is clarified that all required functions under GST can be performed by a taxpayer at the GST portal. GSP is an additional channel being made available for facilitating the taxpayers for performing some of the functions and use of their services is optional. Some of the specific solution(s) which could be offered by the GSPs to meet specific requirements of Taxpayers for GST compliance are given below:
1. Conversion of their current invoice format generated by their existing accounting software, which could be in csv, pdf, excel, word format, into GST compliant format.
2. Reconciliation of auto populated data from GST portal with their purchase register data, where purchase register data can be on excel, csv or in any proprietary database and uploaded data from GST format could be in json/csv.
3. Organization having various branches will need a way to upload branch wise invoices, as GST System will only provide one user-id/password for GST system access. An application having role based access and different view for different branches will be needed.
4. A company registered in multiple States may require unified view of all branches in one screen,
5. GST professionals will need some specific applications to manage and undertake GST compliance activities for their client Tax payers from one dashboard, etc.
Above are just a few illustrations. There will be many more requirements of different sets of Tax payers. These requirements of taxpayers can be met by GSPs.
Q.14 What are the functions which a taxpayer performs at the GST Common Portal being developed and maintained by GSTN for the taxpayers?
Ans. GST Common Portal is envisaged as one-stop-shop for all requirements under GST for the taxpayers. Illustrative list of functions that can be performed by taxpayers through GST Portal managed by GSTN are:
- Application for registration as well as amendment in registration, cancellation of registration and profile management;
- Payment of taxes, including penalties, fines, interest, etc. (in terms of creation of Challan as payment will take place at bank’s portal or inside a bank premises);
- Change of status of a taxpayer from normal to Compounding and vice-versa;
- Uploading of Invoice data & filing of various statutory returns/Annual statements;
- Track status of return/tax ledger/cash ledger etc. using unique Application Reference Number (ARN) generated on GST Portal.
- File application for refund, appeal, advance ruling etc.
- Status review of return/tax ledger/cash ledger
- Generation of E-way bill
Q.15 What is the role of tax officers from State and Central Govt in respect of the GST system being developed by GSTN?
Ans. The officers use information/ application submitted by taxpayer on GST Portal for following statutory functions:
- Approval/rejection for enrollment/registration of taxpayers;
- Tax administration (Assessment/Audit /Refund/Appeal/Investigation etc.);
- Business Analytics, MIS and other statutory functions.
Q.16 Can invoice data be uploaded on day to day basis?
Ans. Yes, GST Portal will have functionality for taxpayers to upload invoice data on any time basis. Early upload of invoices by supplier taxpayer will help receiver taxpayer in early reconciliation of data in Invoices as well as help supplier taxpayer in avoiding last minute rush of uploading returns on the last day.
Q.17 Does GSTN provide tools for uploading invoice data on GST portal?
Ans. Yes, GSTN has provided spreadsheet like tools (such as Microsoft Excel), Offline Utilities, free of cost, to taxpayers to enable them to compile invoice data in the same and generate files which can then be uploaded on GST portal. This are offline tools which can be used to input/capture invoice data without being online and then generate final files in compatible format for uploading to GST portal. These can be accessed at Download section of GST Portal.
Q.18 Does GSTN be provide mobile based Apps to view ledgers and other accounts?
Ans. The GST portal is being designed in such a way that it can be seen on any smart phone. Thus ledgers like cash ledger, liability ledger, ITC ledger etc. can be seen on a mobile phone using compatible browsers.
Q.19 Does GSTN provide separate user ID and password for GST Practitioner to enable them to work on behalf of their customers (Taxpayers) without requiring user ID and password of taxpayers, as happens today?
Ans. Yes, GSTN has provided a separate user ID and Password to GST Practitioner to enable them to work on behalf of their clients without asking for their user ID and passwords. They will be able to do all the work on behalf of taxpayers as allowed under GST Law.
Q.20 Could the tax payer change the GST Practitioner once chosen in above mentioned facility?
Ans. Yes, a taxpayer may choose a different GST Practitioner by simply unselecting the previous one and then choosing a new GST Practitioner on the GST portal.
Q.21 What material has been provided by GSTN, on various aspects of working on GST portal, for the benefit of taxpayers?
Ans. GSTN has prepared Computer Based Training materials (CBT’s), which have videos embedded into them, for each process to be performed on the GST portal. These have been put on the GST portal as well as on the website of all tax authorities. Apart from CBT’s, Various User Manuals, FAQ’s etc., have also be placed on GST Portal for education of the taxpayers. Apart from it, an interactive Self Help Grievance Redressal Portal has been set up for the taxpayers for logging of their tickets (https://selfservice.gstsystem.in/) or phone (0124-4688999). CBT, FAQ and User Manuals for enrolment process are readily available at https://www.gst.gov.in/help.
GSTN conducts webinars on various topics related to GST Portal and same can be seen in GSTN you tube channel (https://www.youtube.com/c/GoodsandServicesTaxNetwo rk ).
Apart from sending bulk mails to the taxpayers regarding new functionalities and advisories , GSTN connects with the taxpayers and other stakeholders through its social media channel i.e facebook https://www.facebook.com/gstsystemsindia/ and twitter handle (@askGSTech) https://www.facebook.com/gstsystemsindia/ and through regular updates on new functionalities /advisories and troubleshooting tips.
Q.22 Does the return and registration data furnished by the taxpayers on the GST Common Portal remain Confidential? How does GSTN ensure the same?
Ans. Yes, all steps are being taken by GSTN to ensure the confidentiality of personal and business information furnished by the taxpayers on GST Common Portal. This is being done by ensuring Role Based Access Control (RBAC) and encryption of critical data of taxpayers both during transit and in storage. The access to the taxpayer data is given only to the jurisdictional officers, and strictly on a need to know basis, with ensuring due checks and balances.
Q.23 What are the security measures being taken by GSTN to ensure security of the GST system?
Ans. GST Systems project has incorporated state of art security framework for data and service security. Besides high end firewalls, intrusion detection, data encryption at rest as well as in motion, complete audit trail, tamper proofing using consistent hashing algorithms, OS and host hardening etc. has been done. GSTN has also established a primary and secondary Security Operations Command & Control center, which proactively monitors and protect malicious attack on a real-time basis. GSTN is also ensuring secure coding practices through continuous scanning of source code & libraries being used in GST system to protect against commonly known and unknown threats.
Source- FAQs on GST updated till 15th December 2018
INDEX OF ALL FAQs ON GOODS AND SERVICE TAX




