1. Introduction
1.1 Background
The GST Council has approved introduction of ‘E-invoicing’ or ‘electronic invoicing’ in a phased manner for reporting of business to business (B2B) invoices to GST System, starting from 1st January 2020 on voluntary basis.
Since there was no standard for e-invoice existing in the country, standard for the same has been finalized after consultation with trade/industry bodies as well as ICAI after keeping the draft in public place. Having a standard is a must to ensure complete inter-operability of e-invoices across the entire GST eco-system so that e-invoices generated by one software can be read by any other software, thereby eliminating the need of fresh data entry – which is a norm and standard expectation today. The machine readability and uniform interpretation is the key objective. This is also important for reporting the details to GST System as part of Return. Apart from the GST System, adoption of a standard will also ensure that an e-invoice shared by a seller with his buyer or bank or agent or any other player in the whole business eco-system can be read by machines and obviate and hence eliminate data entry errors.
The GST Council approved the standard of e-invoice in its 37th meeting held on 20th Sept 2019 and the same along with schema has been published on GST portal. Standards are generally abstruse and thus an explanation document is required to present the same in common man’s language. Also, there are lot of myth or misconception about e-Invoice. The present document is an attempt to explain the concept of e-invoice, how it operates and basics of standards.
E-invoicing in India will be a big move, due to the volume of business transactions undertaken every day, as well as the plethora of different, non-standardised formats used in invoice generation. The main objective is to enable interoperability across the entire GST eco-system i.e. an e-invoice generated by one software should be capable of being read by any other software. Basically, through machine readability, an invoice can be uniformly-interpreted.
In addition to the above, this new system of e-invoicing aims to make invoice reporting an integral part of a business process and remove the tedious task of invoice-compilation at the end of a return period. Claiming fictitious Input Tax Credit (ITC) by raising fake invoices is also one of the biggest challenges currently faced by tax authorities.
The e-invoice system will help to curb the actions of unscrupulous taxpayers and reduce the number of fraud cases as the tax authorities will have access to data in real-time. The basic aim behind adoption of e-invoice system by tax departments is ability to pre-populate the return and to reduce the reconciliation problems.
1.2 Purpose and Intended Audience
This document aims to explain the operational procedure on how to use offline and online tool to generate the e-invoices. This document is intended for registered taxpayers under GST, who are the main stakeholders of e-invoice system under GST.
The present document is an attempt to explain the concept of e-invoice, how it operates and basics of standards. It is expected that the document will be useful for the taxpayers, tax consultants and the software companies to adopt the designed standard.
1.3 Scope
The scope of this document covers:
- Explaining the features of the e-invoice system.
- Activities of various stake holders.
- Registration for the e-invoice system.
- Processes involved in generation of web based e-invoices.
- Enabling the various modes of the e-invoice generation.
- Managing the sub-users by the stake holders.
- Using online tool to generate e-invoices
- Process of uploading the generation of e-invoices.
1.4 URL or Web site address
IRP PORTAL
2. E-Invoice System
2.1 What is E-invoice?
If an invoice is generated by software on the computer or a machine then does it become an e-invoice? Is e-invoice as a system where taxpayers can generate the invoices centrally? Many such questions are raised when e-invoice gets discussed.
E-invoice does not mean generation of invoices from a central portal of tax department, as any such centralization will bring unnecessary restriction on the way trade is conducted. In fact, taxpayers have different requirements and expectation, which can’t be met from one software generating e-invoices from a portal for the whole country. Invoice generated by every software may look more or less same; however, they can’t be understood by another computer system even though business users understand them fully. There are hundreds of accounting/billing software which generate invoices but they all use their own formats to store information electronically and data on such invoices can’t be understood by the GST System if reported in their respective formats.
Hence a need was felt to standardize the format in which electronic data of an Invoice will be shared with others to ensure there is interoperability of the data. The adoption of standards will in no way impact the way user would see the physical (printed) invoice or electronic (ex pdf version) invoice. All these software would adopt the new e-Invoice standard wherein they would re-align their data access and retrieval in the standard format. However, users of the software would not find any change since they would continue to see the physical or electronic (PDF/Excel) output of the invoices in the same manner as it existed before incorporation of e-Invoice standard in the software. Thus the taxpayer would continue to use his accounting system/ERP or excel based tools or any such tool for creating the electronic invoice as she is using today.
Taxpayer can enter the invoice details in bulk generation tool available on e-invoice portal which in turn will create JSON file for uploading on the e-invoice system.
2.2 E-Invoice and Tax Department
The e-invoice system being implemented by tax departments across the globe consists of two important parts namely,
a) Generation of invoice in a standard format so that invoice generated on one system can be read by another system.
b) Reporting of e-invoice to a central system.
The basic aim behind adoption of e-invoice system by tax departments is ability to pre-populate the return and to reduce the reconciliation problems. Huge increase in technology sophistication, increased penetration of Internet along with availability of computer systems at reasonable cost has made this journey possible and hence more than 60 countries are in the process of adopting the e-invoice.
GST Council has given the responsibility to design the standard of e-invoice and update the same from time to time to GSTN which is the custodian of Returns and invoices contained in the same. Adoption of e-invoice by GST System is not only part of Tax reform but also a Business reform as it makes the e-invoices completely inter-operable eliminating transcription and other errors.
2.3 Invoice Reference Number (IRN)
The Invoice Reference Number (IRN) is a unique number (also known as hash) generated by the e-invoice system using a hash generation algorithm. For every document such as an invoice or debit or credit note to be submitted on the e-invoice system, a unique 64 character invoice reference number shall be generated.
The unique IRN will be based on the computation of hash of GSTIN of generator of document (invoice or credit note etc.), Year and Document number like invoice number. The hash could also be generated by the taxpayers based on above algorithm. This shall be unique to each invoice and hence be the unique identity for each invoice for the entire financial year in the entire GST System for a taxpayer.
2.4 QR Code
E-invoice system will generate a unique 64 character length Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and digitally sign the e-invoice and the QR code (Quick response Code). The QR code will enable quick view, validation and access of the invoices from the GST system from hand held devices.
The QR code will consist of the following e-invoice parameters:
- GSTIN of supplier
- GSTIN of Recipient
- Invoice number as given by Supplier
- Date of generation of invoice
- Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
- Number of line items.
- HSN Code of main item (the line item having highest taxable value)
- Unique Invoice Reference Number (hash)
The digitally sign QR code will have a unique IRN (hash) which can be verified on the central portal as well as by an Offline App by officer. This will be helpful for tax officers checking the invoice on the roadside where Internet may not be available all the time
2.5 E-invoicing System under GST
The move will help in curbing Goods and Services Tax (GST) evasion through issue of fake invoices. Besides, it would make the returns filing process simpler for businesses as invoice data would already be captured by a centralised portal. The proposed ‘e-invoice’ is part of the exercise to check GST evasion. With almost two years into GST implementation, the government is now focussing on anti-evasion measures to shore up revenue and increase compliance.
There are over 1.21 crore registered businesses under the GST, of which 20 lakh are under the composition scheme. In order to ensure no duplication, e-invoice system will be closely connected to the GST system, which will be the central repository for all IRN generated. Given that GST system already has IRN data, populating of ANX 1 for the supplier will be possible.
2.6 Objective
E-invoicing in India will be a big move, due to the volume of business transactions undertaken every day, as well as the plethora of different, non-standardised formats used in invoice generation. The new e-invoicing system aims to make invoice reporting an integral part of a business process and to remove the tedious task of invoice-compilation at the end of a return period. Claiming fictitious Input Tax Credit (ITC) by raising fake invoices is also one of the biggest challenges currently faced by tax-authorities. The e-invoice system will help to curb the actions of unscrupulous taxpayers and reduce the number of fraud cases as the tax authorities will have access to data in real-time.
2.7 Stakeholders
The objective behind introducing e-invoice is to effectively address the expectations and concerns of the stakeholders by leveraging the use of ITC (Input Tax Credit).
2.8 Benefits of E-invoice System
The major benefits of e-invoice system are as follows:
- Standardization: One time reporting on B2B, B2G and export invoice data in the form it is generated to reduce reporting in multiple formats.
- Seamless Reconciliation: Reconciliation and data verification between suppliers and recipient will be seamless and thus provide better control over input tax credit computation and claim.
- Lesser Compliance: Reduction in overall compliance burden. Substantial reduction in input credit verification issues as same data will get reported to tax department as well to buyer in his inward supply (purchase) register.
- Automation: Auto-generation of Sales and Purchase Registers (ANX-1 and ANX-2). To generate Sales and purchase register (ANX-1 and ANX-2) from this data to keep the Return (RET-1 etc.) ready for filing under New Return.
- Elimination of fake invoices: Reduction of tax evasion, System level matching of input credit and output tax.
- Information Availability: Near real-time availability of information to all the relevant participants in the supply chain.
- On receipt of info thru GST System as buyer can do reconciliation with his Purchase Order and accept/reject in time under New Return
- Environment friendly – The need of the paper form of the multiple copies of way bill is eliminated. Hence, the tons of paper are saved per day.
- Officials saved of monotonous work collecting and matching the manual work with the returns of the taxpayers.
2.9 How E-invoice will be beneficial to taxpayers:
- Save time: With e-invoicing, many unnecessary steps are cut out of the invoicing process. Both you and your customer will be saving time using e-invoicing system.
- Reduce costs: With paperless invoicing, you do not have to pay for paper or for postal fees. Further, by saving time with e-invoicing instead of using templates and emailing PDFs, you save working time. Concentrate on other value-adding tasks instead. We all know time is money!
- Reduce mistakes: By minimizing manual input and increasing automation, mistakes and typos are reduced.
- Offer better customer service: It is more convenient for customer to get an e-invoice to their desired platform receiving an e-invoice instead of a paper invoice saves up to 90% on processing costs.
- Easier to keep track of invoices: Know when an invoice has been sent, viewed, and paid when using e-invoicing system. You will know for sure that the invoice is sent and received.
- A higher degree of control and insight into the invoicing process: If you use online invoicing software, everything is saved on one platform which is accessible from anywhere on any device.
2.10 Features of the E-invoice system
- User friendly System – The system is user friendly with lots of easy to use operations by the users.
- Easy and quick generation of methods – There are a number of methods are provided using which the users can easily and quickly generate the e-invoices.
- Multiple modes for e-invoice generation – This system support different modes of e-invoice generation. The user can register the mode of e-invoice generation and use them for invoice generation.
- Creating own masters – The user has a provision to create his own masters like customers, suppliers, products and transporters. The system facilitates to use them while generating the e-invoice.
- Managing sub-users – The taxpayer or registered person can create, modify and freeze the sub-users for generation of the e-invoice and assign them to his employees or branches as per need. This system also facilitates him to assign the roles/activities to be played by the sub-user on the system.
- Monitoring the IRN generated– The system facilitates the registered person to know the number of INR, generated by them on a specific date
- Generating the GSTR-1 from the e-invoices – Based on the e-invoice generated, the system pulls the GSTR-1 related information and pushes it to the taxpayers GSTR-1 returns. This avoids the taxpayers in uploading these transaction details.
- QR bar code on the e-invoice – The QR code on the e-invoice helps for easier and faster verification of the e-invoices.
3. Registering for e-invoice System
3.1 Registering by Taxpayers on the E-invoice System
The registration mechanism for the GST taxpayers for the e-invoice system is a simple process. If a taxpayer is already registered on the e-way bill portal, he/she can use the same login credentials to Log-in to E-Invoice system. If a taxpayer is not registered in the EWB portal then he/she can register to register on the e-invoice system, taxpayer needs to have the GSTIN issued under the GST system and mobile number registered with the GST system with him. Once a user enters the URL address of the E-invoice System in his browser, the below screen will be displayed. The taxpayer is already registered to e-waybill system he/she can use his same login credentials of E-waybill to access the e-invoice system.
On the e-invoice portal, a first time GSTIN can register by clicking on the ‘e-invoice Registration’ link under registration option. Then the user will be redirected to the ‘e-invoice registration form’.
The registration form is shown below.

The user needs to enter his/her GSTIN number along with the displayed captcha and shall click ‘Go’ to submit the request. Once the request is submitted the user will be redirected to the following page with GSTIN details.
Figure 3: e-invoice Registration, form2.
In the above mentioned form, Applicant name, Trade name, Address, Mail ID and Mobile Number are auto populated once the user enters his/her GSTIN number along with displayed captcha. If the details have been changed or are incorrect, the user needs to click ‘Update from GST Common Portal’ to pull the latest data from the GST Common Portal. User needs to click on ‘Send OTP’ to get the OTP. Once OTP is received on the registered mobile number, user needs to enter the OTP and click on ‘verify OTP’ to verify the same and validate.
Next, the user needs to provide his choice of User ID or username, which he/she plans to use to operate his account on this system. Username should be about 6 to 15 alphanumeric characters and can include special characters. A Unique username should be given by the user, which is not there in the system. Once a request for registration is submitted, the system validates the entered values and pops up the appropriate message if there is any error. Otherwise the username with password is created and registered with e-invoice System. The tax payer can use this registered username and password to access the e-invoice system.
3.2 Forgot Password
If the e-invoice system user forgets his password for his username, he needs to enter e-invoice system username, GSTIN and register mobile no. On successful verification, user can reset his password and can again access the e-invoice system.
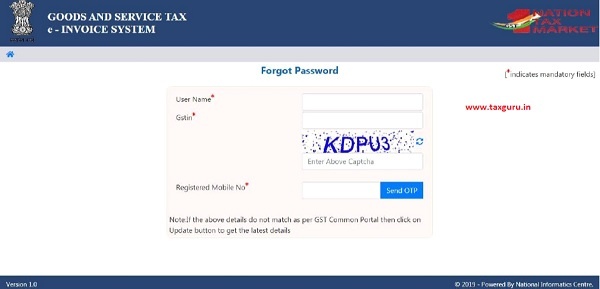
Figure 5: Forgot Password.
If the details entered are not matching with the GSTIN data available in the system, the system pops up message saying invalid details. If the tax payer has updated his details in GST Common Portal, but is not being reflected in the e-invoice system, he can select ‘Update details from GST common portal. Now, the system pulls the latest data from the Common Portal and updates and he can try again the same so that he can get the OTP to his updated mobile.
3.3 Forgot User Name
If the user of the e-invoice system has forgotten his/her username, they needs to enter the GSTIN and registered mobile number. On entry of his GSTIN and registered mobile number, the system will send the username to his mobile number through SMS.
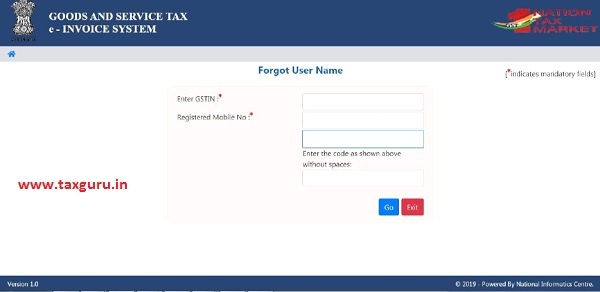
Figure 6: Forgot Username.
If the details entered are not matching with the GSTIN data available in the system, the system pops up error message. If the tax payer has updated his details in GST Common Portal, but is not being reflected in the e-invoice system, he can select ‘Update details from GST CP’. Now, the system pulls the latest data from the Common Portal and updates and he can try again the same so that he can get the SMS to his updated mobile.
4. Opening the E-invoice System
4.1 Logging into E-invoice System
To open or login to the e-invoice system, user should have registered in the e-invoice system or e-Way Bill system. The user can read the chapter 3 to know how to register into the e-invoice system.
The user has to open the e-invoice portal and enter his username and password along with the displayed captcha. On successful authentication, the system shows him the main menu of the e-invoice System.
4.2 Main Menu
The main menu, lists the options available to a user to operate on the e-invoice system.

Figure 7: Main Menu screen.
In the middle, the system shows the dash board for different activities pertaining to the user on e-invoice system.
On the left hand side, the system shows the main menu options which are explained in detail in subsequent sections.
5. Options under E-invoice
Figure 8: Options under e-invoice menu.
5.1 Generate IRN
This option is used to generate the 64 character length Invoice reference number (IRN).
When the user clicks the ‘Generate New’ sub-option under ‘e-invoice’ option, the following e-invoice Entry Form will be displayed, allowing the user to enter the invoice details.
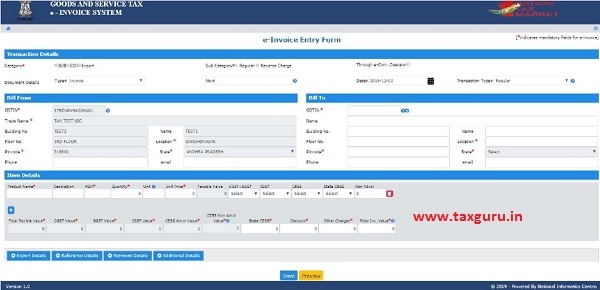
Figure 9: Generating New invoice.
Before initiating a new Invoice reference number generation, the user should have the Invoice/Debit Note/Credit Note’ in his hand.
In the e-invoice Entry Form, first the user needs to select the type of Category i.e. B2B, B2G or Export. The B2B transactions are the invoice that is exchanged in the private sector between a client and the provider of goods or services and Business-to-government (B2G) is a business model that refers to businesses selling products, services or information to governments or government agencies. Export Transaction in e-invoice means any transaction involving export of goods out of the India. Depending upon the type of category selected, the system will show the sub-category of transactions. The user needs to select the sub-Category accordingly.
Once the user selects the Category and Sub Category in ‘Transaction Details’ section, system will display only the relevant document types in ‘Document Type’ dropdown pertaining to the selected sub category as shown in below tables.
Case I: For B2B
| S No. | Sub category -Type | Document Type | Original Inv. No. | To GSTIN |
| 1. | Regular | Invoice | Other GSTIN | |
| Debit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| Credit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| 2. | Reverse Charge | Invoice | Other GSTIN | |
| Debit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| Credit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN |
Case II: B2G
| S No. | Sub category -Type | Document Type | Original Inv. No. | To GSTIN |
| 1. | Regular | Invoice | Other GSTIN | |
| Debit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| Credit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN |
Case III: Export
| S No. | Sub category -Type | Document Type | Original Inv. No. | To GSTIN |
| 1. | Direct | Invoice | URP | |
| Debit Note | Invoice number | URP | ||
| Credit Note | Invoice number | URP | ||
| 3. | Invoice | Other GSTIN | ||
| Debit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| Credit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| 4. | SEZ | Invoice | Other GSTIN | |
| Debit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| Credit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| 5. | SEZ developer | Invoice | Other GSTIN | |
| Debit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN | ||
| Credit Note | Invoice number | Other GSTIN |
Now the user has to select the type of document from the drop down menu as per the document in his hand. The user will enter the document number and select the date of document as given on the document (invoice, credit note debit note etc.) he is holding. The Document No. should be unique for all Invoice reference number supposed to be generated by a user. Document Date should be less than or equal to current date.
Tax payer needs to enter the “Transactions Type” i.e “Bill To” & “Ship To” and “Bill From” & “Dispatch From” details of the goods that in the document.
There are four types of transactions:
- Regular: This is a regular or normal transaction, where Billing is happening between two parties – consignor and consignee. That is, the invoicing and the movement of goods from consignor to consignee have taken place directly.
- Bill To – Ship To: In this type of transaction, three parties are involved. Billing has taken places between consignor and consignee, but the goods are moved from the consignor to the third party as per the request of the consignee.
- Bill From – Dispatch From: In this type of transaction also, three parties are involved. Billing has taken place between consignor and consignee, but the goods were moved by the consignor from the third party to the consignee.
- Combination of both: This is the combination of above two transactions and involves four parties. Billing has taken place between consignor and consignee, but the goods were moved by the consignor from the third party to the fourth party, as per the consignee’s request.
Taxpayer enters the Bill To details like GSTIN, Trade Name, Location, Pincode, State etc.
Now, the user needs to enter the details of products as per the invoice in the “Item Details” section.
- Taxpayer enters “Product Name’ “Description”, “HSN Code”, “Unit” and “Tax Rates” details are auto populated. These details will come from Products Masters’ entry.
- Tax payer needs to enter “Quantity” and “Value/Taxable Value (Rs)” as written in the Document declared in the Document declared above.
- Next, System will auto-populate the standard rate of tax (%) in the dropdown while entering the HSN code. Tax payer has to select the applicable tax rate slab (in %) from the dropdown and based on this, the system calculates and auto-populates the CGST, SGST, IGST & CESS amount etc.
- Tax Payer can enter any additional charges or any discount applicable on the Invoice in “CESS Non-Advol” & “Other Amount (+/-) so that “Total invoice value” can match to the Invoice value. The system calculates and displays the Total Inv. Value.
Tax payer can add multiple products by clicking (+) on button.
It may be noted that the system will show the CGST and SGST tax rate for intra-state movement and IGST tax rate for inter-state movement.
Once a request for E-invoice is submitted, the system validates the entered mandatory values and pops up appropriate message if there is any error. Otherwise the system will generate a 64 character length Invoice reference number and will add digital signature on the Invoice and to QR code.

QR Code: The QR code will enable quick view, validation and access of the invoices from the GST system from hand held devices.
The QR code will consist of the following e-invoice parameters:
- GSTIN of supplier
- GSTIN of Recipient
- Invoice number as given by Supplier
- Date of generation of invoice
- Invoice value (taxable value and gross tax)
- Number of line items.
- HSN Code of main item (the line item having highest taxable value)
- Unique Invoice Reference Number (hash)
The digitally sign QR code will have a unique IRN (hash) which can be verified on the central portal as well as by an Offline App by officer.
IRN: IRN shall be unique to the digitally signed invoice and hence be the unique identity for each invoice for the entire financial year in the entire GST System for a taxpayer. E-Invoice will be valid only if it has IRN of 64 Character length.

Figure 10: Generated E-invoice
The user can take the print out of the E-invoice using the ‘Print’ option provided.
Tips for easy and quick generation of e-invoice number
1. Mandatory fields are indicated by.
2. Please ensure that you have the document details of the goods, in hand before starting the data entry.
3. Please ensure that document number is entered with alphanumeric value as mentioned in the document.
5.2 Generate Bulk IRN
This is simple method for generation of multiple Invoice reference numbers (IRN) in one go. Here, the tax payer has to prepare the JSON file request for IRN and upload into the common portal.
For generating a Bulk IRN the user needs to have the bulk convertor or the excel file, which helps the user to convert the multiple invoices excel file into a single JSON file. The Excel to JSON file converter has been provided on the portal. The JSON must conform to the e-invoice schema (standards) that is published and have the mandatory parameters. The optional parameters can be according to the business need of the supplier.
Taxpayer will be required to upload the JSON to the e-invoice system, which in turn will generate a unique Invoice Reference Number (IRN) and digitally sign the e-invoice and also generate a QR code. The QR Code will contain vital parameters of the e-invoice and return the same to the taxpayer who generated the document in first place.
Step by Step Process to Generate Invoice reference number
For generating a Bulk Invoice reference numbers, user needs to have the EINV bulk convertor or the excel file, which helps the user to convert the multiple invoices excel file into a single JSON file.
Step 1: To generate a Bulk Invoice reference numbers, user needs to select the sub option ‘Bulk Upload’ option under ‘e-invoice. On clicking this option, the following screen will be displayed.

Figure 11: Figure 12: Generating and Uploading Bulk Update IRN form 1
Step 2: Upload JSON: User has to upload the JSON file (maximum allowed file size for upload is 2 MB along with the hash, if generated) to the e-invoice system.

Figure 12: Generating and Uploading Bulk Update IRN form 2
Step 3: Generation of IRN: After processing the JSON file, the system generates the e-invoices and shows the 64 character length Invoice reference number for each request. If it is not possible it will show the appropriate error for each request.

Figure 12: Generating and Uploading Bulk Update IRN form 3
The user can export the e-invoices in excel file by clicking on ‘Export to Excel”.
Note: Please refer Bulk E-Invoice generation manual for detailed.
The hash computed by e-invoice system will become the IRN (Invoice Reference Number of 64 character length) of the e-invoice. This shall be unique to each invoice and hence be the unique identity for each invoice for the entire financial year in the entire GST System for a taxpayer.
System will also update the invoice details to E-Waybill system. E-Way bill system will create Part-A of e-way bill using this data to which only vehicle number will have to be attached in Part-B of the e-way bill.
Tips for easy and quick generation of e-invoice number
1. The hash computed by e-invoice system will become the IRN (Invoice Reference Number of 64 character length) of the e-invoice.
2. The JSON must conform to the e-invoice schema (standards) that is published and have the mandatory parameters. The optional parameters can be according to the business need of the supplier.
5.3 Cancel IRN
The provision has been provided to the taxpayer to cancel the invoice reference number for various reasons like incorrect entry, duplicate entry etc.
To cancel IRN user selects the ‘Cancel’ sub-option under ‘E-invoice option’ then the following screen will be displayed.
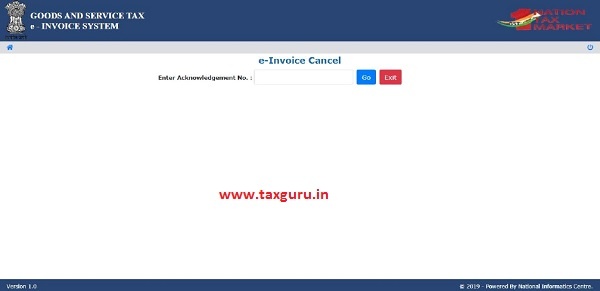
Figure 26: Cancelling IRN.
Before going for IRN Cancellation, the user should have the IRN in hand which he intends to cancel.
Next, the user needs to enter the 64 character length invoice reference number and select go. That particular e-invoice will be displayed, system will prompt user to select the reason of cancellation and enter remark and clicks Go.
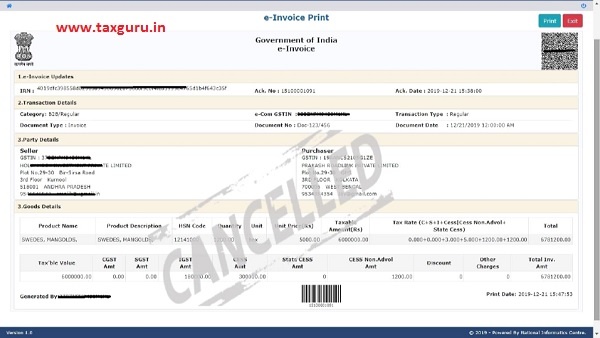
System will give a message stating that “e-invoice Cancelled successfully!!” and the cancelled e-invoice is displayed with a “Cancelled” watermark.
Note: The invoice reference number once generated cannot be deleted. However, it can be cancelled by the generator within 24 hours of generation.
5.4 Print E-Invoice
When the user selects the ‘Print’ sub option under ‘e-invoice’ option, the following screen will be displayed.

Figure 27: Print E-Invoice, Form 1.
After entering the 64 character length invoice reference number, the below mentioned form will be displayed. The system shows the e-invoice with an option to take the print.

Figure 28: Print E-Invoice, Form 2.
User can take a print by clicking “Print” option.
6. MIS Reports
There is an option for the taxpayer to generate reports on list of all invoices generated by him on a particular date to manage his business.
6.1 Generated IRN
Using this option user can view the list all the Invoice reference numbers generated by the user on a selected date along with relevant parameters.
IMAGE
User navigates to Generate IRN option under MIS reports and selects the date. System will generate list of invoice reference numbers generated by the user for a particular date. The user can export the report in excel by clicking on ‘Export to Excel” tab as shown in below figure.
IMAGE
7. User Management
Some of the users or taxpayers need to generate the Invoice reference numbers from multiple business places or in 2-3 shifts or many numbers of Invoice reference numbers under his account. Also, some of the users do not want to manage all the activities under one username or account. Under these circumstances, he/she may not be able to manage this with one user name and such tax payers can use the user management option to create multiple sub-users and assign them different roles. The following sub-options help the user to manage the sub-users.

Figure 56: Options under User Management.
7.1 Create Sub-User
The system enables the user to create a sub user. Once the user clicks on the sub option ‘Create Sub user’ under the option user management, the system asks the user to enter the mobile number and validates the same via the OTP. Once correct OTP is entered the following screen is displayed.

Figure 57: Creating Sub-User.
In this form, the user can create the sub-user by entering a ‘suffix user id’ for the sub user and shall check the availability of the user id. That is, if the tax payer’s username is ‘abcdef’ and he is giving suffix as ‘rvk’, then the sub user id will be ‘abcdef_rvk’ is created.
Then the user needs to enter the name, destination, and mobile number, email id, enabling the user to generate the Invoice reference number for all the offices or for a particular office.
The user can authorise the sub user to generate Invoice reference number, cancel invoice reference number and report generation of IRN. The system will pop up an error if the entered fields are incorrect otherwise the system will create a sub-user and send SMS pop up a message with password to the sub-user.
7.2 Freeze Sub-User
The system gives an option to the user to freeze the sub user so that he cannot login in the e-invoice system. Once the user selects ‘Freeze sub-user’ under the option user management the following screen is displayed.

Figure 58: Freezing Sub-User.
The user shall select the freeze button to freeze a sub user. Once a sub-user is frozen, he/she won’t be able to login E-invoice system.
7.3 Update Sub-User
In the same manner explained under chapter 7.1 create sub user, a user can update a sub-user after successful validation of the OTP sent on users mobile by the system.
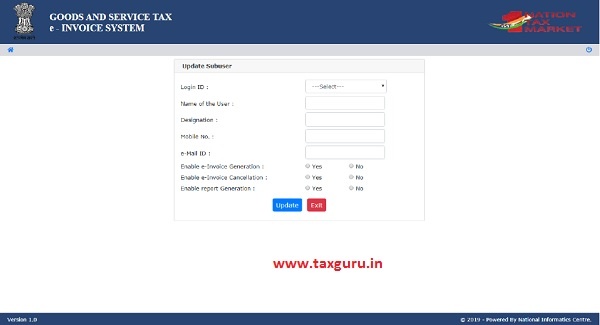
Figure 58: Update Sub-User.
8. Change Password
User can change his login password using this option. Once the user clicks on ‘Change Password’ under the menu, the following screen is displayed.

Figure 59: Change password.
In this form the user needs to first enter his existing password and then the new password which he wants to use and click ‘Submit’. The system will then validate the entered details and change the login password of the user with new entered password.
Note: Remember the new password entered. Don’t share your password with others and regularly change your password.
9. Registration
E-Invoice system provides the users to generate the Invoice reference number from different modes. One of them is the web based mode, which has been explained in chapter 5. There are other modes like android app based, API based and Suvidha based. For all these modes, the user needs to register on the web based system with other details for these modes. The following options explain the registration for these modes.

9.1 For Mobile (Android & iOS Application)
The Android & iOS App is developed to facilitate the tax payer’s work on the E-Way Bill system using his/her mobile hand set. Here, user has to download the app from the common portal and install on the mobile hand set and use it as per the instructions. Before installing on the mobile, the user needs to register the IMEI number of his or his authorised person’s hand set number on the common portal by logging in.
The e-invoice system enables the user to generate an Invoice reference number through android & iOS application as well. Once a user selects ‘For Android’ under the option ‘Registration’, the following screen is shown.

Figure 63: Android Registration, Form 1.

Figure 64: Android Registration, Form 2.
The user needs to select the concern user from the drop down list. Once the user is selected, name and place will be auto populated by the system. In order to enable the concern user with android app, user needs to enter the IMIE Number of the concern user and save the details in the e-invoice system. Once saved, the concerned user will be able to generate Invoice reference number through android applications.
9.2 For GSP
The tax payer can authorise his/her Suvidha Provider to generate the IRN on his behalf through the API mode.
User can also register their GSP’s in the system using this option. After successful validation of the OTP, system will display the following screen.

Figure 65: GSP Registration.
Once the user enters the required GSP details in the form and clicks “Add”, system registers the selected GSP for the user.
9.3 For API
This method can be used by the big tax payers by closely linking their systems with the E-invoice system for generation of IRN. Here, when the invoice is being prepared by the tax payer on his system, he will call the API interface given by the e-invoice system and system will generate IRN and pass back to him.
Please refer the API User Manual for detailed information in this regard.

Figure 66: API Registration, Form 1.
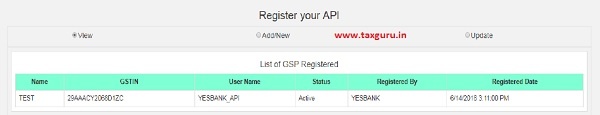
Figure 67: API Registration, Form 2.
10. Update
10.1 Pull from GSTIN from CP
E-Invoice system allows a user to update their business details from the GST common portal. Once updated successfully, these details can be auto populated in various e-invoice modules based on GSTIN as and when required.
List of Abbreviations
| Abbreviation | Full Form |
| IRP | Invoice Registration Portal |
| IRN | Invoice Reference Number |
| API | Application Program Interface |
| B2B | Business to Business |
| B2G | Business to Government |
| ITC | Input Tax Credit |
| CGST | Central Goods and Service Tax |
| EWB | e-Way Bill |
| GSP | Goods and Services Tax Suvidha Provider |
| GST | Goods and Services Tax |
| GSTIN | Goods and Services Tax Identification No. |
| GSTN | Goods and Services Tax Network |
| GSTR-1 | Goods and Services Tax Form -1 |
| HSN | Harmonized System of Nomenclature |
| ICT | Information and Communication Technology |
| IGST | Integrated Goods and Services Tax |
| IT | Information Technology |
| MIS | Management Information System |
| NIC | National Informatics Centre |
| OTP | One Time Password |
| QR | Quick Response |
| SGST | State Goods and Services Tax |
| SMS | Short Message Service |
| URL | Uniform Resource Locator |
| VAT | Value Added Tax |






If we have covered under E-Invoicing but after that can we E-way bill also require or not.
please suggest.
Under E-Invoice mechanism, lets say X is a seller who generates IRN on IRP. Is there any possibility for a third party (say X’s bank) to access the E-Inovice generated with the due permission of X. Please specify the provision regarding this?