Introduction:
Global Supply Chain advanced due to Globalization and Increasing Free Trade among Countries. Globalization undoubtedly has many Advantages & Benefits of Better Access and Integration of Supplies at Global Level. However, Globalization & Global Supply Chains are more Prone to Supply Chain Disruptions. COVID Pandemic’s impact on global trade and Supplies is so devastating that it has exposed the Fragility of the Supply Chain and proved to be a Real Test of Corporate Ingenuity, Resilience and Flexibility to face the Crisis.
So, Businesses have started looking for Offshore to Nearshore and Local Sourcing.
In this Article, Let’s Discuss on Concept of “Glocal” – a Combination of Global & Local, and how it embraces Global Mindset, Reach & Access, but also Accommodate & Promote the Values, Cultures, Ideals, Interests and Needs of the Local Businesses.
Key Words:
Globalization, Localization, Glocal, Global Supply Chains, Global Supply Chain Disruptions, Atmanirbhar.
What is Supply Chain?
First let’s Discuss & Understand what is Supply Chain.
A supply chain is a Chain of Supplies – is the Network of all the Individuals, Organizations, Resources, Activities and Technology involved in the Creation and Supply of Products or Services, from the Point of Source to the Point of Consumption through a Series of Supplies with Value Creation at each Stage that is from Supplier to Manufacturer to Distributer to Wholesaler to Retailer and Eventually Delivery to the End User or Consumer.
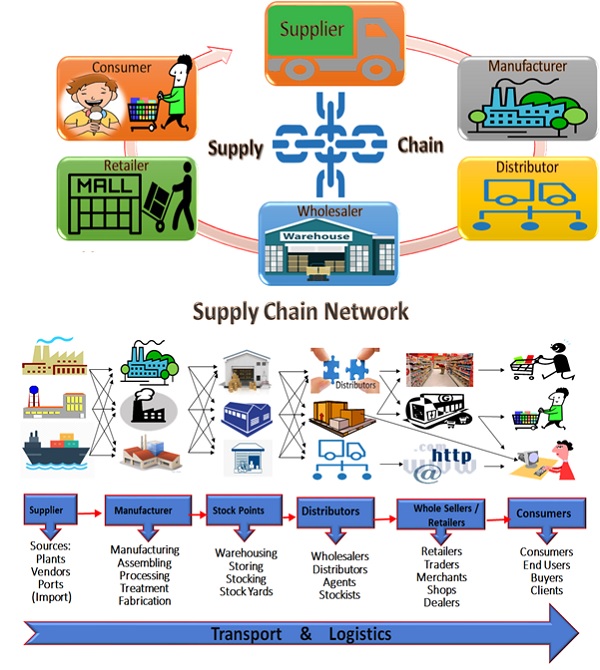
Supply Chain Management
Supply Chain Management (SCM) can be defined as Management of the Supply Chains as an Integrated Process of Acquisition and Management of Flow of Supply of Goods or Services from the Point of Origin to the Point of Consumption and Delivering Further Value Added Output to the Next Level Point of Consumption (like from supplier to manufacturer to wholesaler to retailer and to final consumer) by Balancing Supply and Demand with Optimal Management of Resources with the objective of establishing relationships for Maximizing Value for Mutual Benefits on Economically, Socially and Environmentally Sustainable basis. (As defined by the Author SN Panigrahi in his Article “Value Insights into Supply Chain” Published in August’2010 issue of MMR – IIMM)

What is Global Supply Chain
Global Supply-chains are Networks of Supplies across the National Boundaries that fuel Global Business.
Global Supply Chains involve the Flow of Goods or Services; Information; Finances; Value and Risks across the Global Partners who may span across Multiple Continents and Countries.
For example, if a company sources Raw Materials from China, Manufactures the Product in India and then sells it to customers in USA – it’s a Global Supply-Chain.
Global Supply-Chain Management is defined as Management of a Network of Supply and Distribution of Goods and Services throughout the Global Network to Gain Competitive Advantage.
Global Supply Chain Management involves Effective Planning, Organizing and Coordinating of entire supply chain functions as an integrated whole from Global Sourcing to Production, Distribution Logistics, Managing Resources and all the Related Activities to ensure successfully achieving business goals at Global Level within the given constraints.
Global Supply Chain: Advantages
Global Supply Chains have Advantages of Sourcing from Low-Cost Countries with Low Production Costs, Lower Labor Rates, Low Transactional Costs, Low Tax Incidences or other Benefits and Competitive Advantages which makes the Businesses Attractive to Expand their Operations and Transactions Globally with objective of Improving their Financial Performances and Bottom Lines.
Apart from Cost Advantages, the other Benefits of Exposures to Global Supply Chains are Large Supplier Base, Wide Range of Supply Availability with Multiple Options, Increased Competition & Better Negotiating Power, Adaptive to Global Trends, Flexibility, Ability to Quickly Sourcing, Speed of Delivery, Global Reach, Access to Creative and Innovative Products or Services of Highest Standards of Quality, Technology, Optimized Inventory, Opportunity for Organizations to Learn Current Trends in doing Business, Proactive Strategy, Sharing Expertise and Upskilling, Effective Production Methods, Innovative Business Practices, and Optimal Distribution Methods as they Interact and Transact with Multiple Global Suppliers, Supply Chain Partners and Service Providers.
Global Supply Chain: Disadvantages
Although there are many advantages of Global Supply Chains, there are many Risks, Uncertainties involved and several Difficulties & Complications associated with in Global Supply Transactions.
Whilst engaging in global supply chains offers many benefits as discussed, Global Supplies involves the management of different Transactions across Different Countries with Varied Regulations, Wide-ranging Governing Practices, Cultures, Religions, Believes, Habits, Time Zones, Languages as well as Ethical Good Practice and Different Currencies.
One has to Understand, Adapt, Adjust, Conciliate, Cooperate, Collaborate and make the Transactions mutually benefit to all the Global Partners.
The disadvantages of global supply chain management include Instability (Political, Economic, Social & Environmental Instability), Fluctuating Exchange Rates, Tax / Duty Structures, Government Regulations, Different Customs Formalities in Different Countries, Differences in Standards and Regulations, Language and Communication Barriers, Time Zone Differences etc.
Also global supply chain transactions Require Expertise for Planning, Sourcing, Negotiating Contracts with Special Terms, Difficulty of Understanding Country Specific Regulations & Restrictions, Complications in understanding International Transactions, Arranging Cross Country Logistics, Longer Lead Times, Supply Shortages, Backlogs, Bottlenecks, Challenges of Transportation & Shipping, Certain uncertainties Associated with Estimation of Costs, Challenges of Dealing with Unknown or Strange Chanel Partners, Banking & Payment Complexities, Coverage of Risks & Insurances and Financial challenges etc.
Supply-chain disruptions due to Pandemics or Natural Calamities or Wars may Drag for Longer Period which we have witnessed during COVID – 19. Civil Wars (Russia & Ukraine War; Tensions of Probable War between China & Taiwan), Trade Disputes (ongoing US – China Cold War), Trade Barriers, Blockages etc may have greater repercussions and may mute global trade, may lead to supply chain disruptions and cast doubt on the viability of many business and supply chain transactions.
Globalization
Global Supply Chain advanced due to Globalization and Increasing Free Trade among Countries.
In the economic context, Globalization refers to the Process Characterized by Liberalisation, Borderless Globe opens up new markets with Free Trade Flow of Capital & Financial Products, Investments, Goods, Services, Technology, Information and Human Capital across National Boarders with Increased Interaction, Integration and Interdependence among the Nations around the Globe to Foster Easy Access to Foreign Resources, better Exchange, Movement and Cooperation of Businesses, Organizations, and Countries to built Economic Partnerships for Mutual Benefit and Facilitate Common Good based on Competitive Advantage of each Participating Nation or Region.
Globalization enables access to global Talent, Materials, and Products that were otherwise out of reach. Globalization can enrich Business Processes by offering companies a wider more Abundant Pool of Resources to pick from. Cross Boarder Information Flows may Promote Growth. Globalization Encompasses Growth on a Worldwide Scale.
In the past few decades we have witnessed growing globalization as more countries and regions of the world become intertwined Politically, Culturally and Economically.
National Competitive Advantage
Globalization evolved and advanced on the premises of basic concept of Comparative Advantage which is defined as Ability of a Country to Produce and Sell Goods and Services on an International Scale more Efficiently and Inexpensively than another. As Technology, Infrastructure, Transportation Systems, and Communication Systems, Economic, Political, and Cultural Exchanges have improved, competition among different countries has soared.
Globalization leads to increased competition. Competition in global business environment occurs when different nations offer interchangeable services or products or other resources. National Competitiveness is a country’s ability to sustain and increase its share of international markets and at the same time to improve its people’s quality of life.
Among governments, there is a growing tendency to experiment with various policies intended to promote national competitiveness—from efforts to manage exchange rates to new measures to manage trade to policies to relax antitrust.
Attributes of a National Competitive Advantage
National Competitive Advantage is measured by a set of factors, policies, and institutions that determine a country’s level of productivity and competitiveness. There are Four broad Attributes of a National Competitive Advantage : Factor Conditions (The Factors of Production, such as Natural Resources, Skilled Labor or Infrastructure); Demand Conditions ( The nature of home-market or Domestic Demand); Related and Supporting Industries (The presence or absence in the nation of supplier industries and other related industries that are internationally competitive); Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry (The conditions in the nation governing how companies are created, organized, and managed, as well as the nature of domestic rivalry).
According to prevailing thinking, Government Policies, Institutions, Infrastructure, Innovation, Technology Development & Absorption, Macro-Economic Stability, Health and Primary Education, Higher Education and Training, Market Size, Market Conditions & Efficiency, Labour Market Efficiency (Labour Cost), Financial & Capital Market, Interest Rates, Exchange Rates, Economies of Scale Country’s overall Business Networks and Supporting Industries are the most potent determinants of competitiveness.
Is a relative concept. It is an approximation of a country’s ability to grow and to compete with other countries for human capital, investments, and other resources.
Shortcomings or Flip Side of Globalization
On the flip side it develops Unequal Economic Growth, Exploits Cheaper Labour Markets, Causes Job Displacement, Increases Potential Supply Distortions in some Extreme Dangerous Circumstances and many more as mentioned below:

Global Supply Chain Disruption :
Globalization & Global Supply Chains are more Prone to Supply Chain Disruptions.
A Supply Chain Disruption is any Sudden Change or Crisis – be it Local or Global – that Severely Impact the Supply Chain Activities, Processes and operations.
Supply chain disruption is defined as a Major Breakdowns in the Production or Distribution / Supply and other Major Functions of a Supply Chain that Challenges your business’s ability to Plan, Source, Make, Deliver and / or Sell Products and other Transactions when an External Force Acts upon beyond the Control of the Business.
The Adverse Impacts of Supply Chain Disruptions may in Certain Cases overshoot the Benefits of Globalization.
You may refer to YouTube “Global Supply Chain – Uncertainties Galore” @ below Link
Global Supply Chain Disruptions : Major Causes
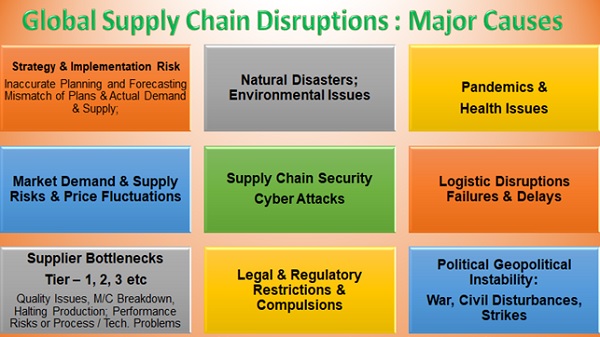
Consequences of Supply Chain Disruptions
In the aftershock of the COVID-19 epidemic, followed by many other events like Suez Canal Supply Crisis, Russia – Ukraine War, Escalation of Tensions & Disputes between China-Taiwan; Cold Trade war between USA & China etc Disrupted and Continue to Upset the Supply Chain Leading to Risks in Terms of Delivery, Quality, Costs, Service Performance, Supplier & Customer Relationships.
These Supply Chain Disruptions Reflect as Decreased Productivity, Increased Costs, Non-Availability of Inputs & Raw Materials, Delayed Deliveries or Non-Deliveries, Stockouts and Loss of Revenue, as well as Loss of Customer Trust – Rising Customer Dissatisfaction; Cash Flow & Financial Problems, Closure of Businesses or Insolvency, and more and many Economic Fall outs.
Global to Look for Local
The coronavirus pandemic and subsequent other events are forcing companies to make a Trade-off between Efficiency and Resilience in Global Supply Chains.
These Adverse and Unfavourable events Triggered Disruption of the Global Supply Chain – hampered factory operations and sown chaos in Global Supply Chains – Damaged many economies around the world. we have seen Shortage & Stockout Situations for many items including very Essentials like Food, Groceries, Household supplies, Medical, Personal Protective Equipment’s (PPP), Cloths and so on. With Lead Time Issues, Uncertain Demand & Deliveries – All the Supply Chain Targets & Measures gone awry.
Govt. Regulations / Restrictions for Mobility, Lockdowns, Increased border controls and customs regulations result in longer wait times, and lack of capacity for long-haul and last-mile fulfillment etc apart from overall Economic slowdown, Short Supplies, Labor Non-availability, Health Issues and Severe Financial Crisis created extreme challenges – challenges of keeping the businesses running & keep them stable.
Pandemic’s impact on global trade is so devastating that it has exposed the Fragility of the Supply Chain and proved to be a Real Test of Corporate Ingenuity, Resilience and Flexibility to face the Crisis.
So, Businesses have started looking for Offshore to Nearshore and Local Sourcing to offset and Counterbalance the Adverse Impacts of Global Sourcing and the Associated Supply Disruptions. Among Businesses, there is a growing Tendency to Explore & Experiment with various Policies and Strategies Intended to Promote & Strengthen Local Competitiveness.
Advantages of Localization
Localisation has Advantages of Developing & Caring for Domestic Industries & Local Business Community. It also termed as Protectionism, Creating Entry Barriers to Foreign Entities, Providing Unreasonable Shelter to Domestic Industry, Greater Self-Reliance, Self-determination.
> Encourages Local Suppliers – Develops Local Competitive Advantage.
> Localization ensure Less Distortions in case of Supply Chain Disruptions as there is limited movement of people and goods in a limited local area.
> Better Utilization of Local Resources & Value Creation Locally.
> Local Resource Engagements & Creation of Better Employment Prospects for Local Talent.
> Balanced Development of Local Economy & Growth.
> Avoids Skewed Economic Growth on Misconceived (Not the True Sources) Concept of Competitive Advantage and Concentration of Development in Few Pockets of Developed
> Reduced Dependency on Supplies from Oversees.
> Saves Foreign Currency Outflow – Strengthens Balance of Payment Position of the Native Country.
> No Need for Trade Barriers – Avoids Trade Restrictions, Constraints between Nations.
> Creates a Long-Term Business Eco-System with Supporting Supply Bases in the Local and Native Country.
> Shorter Distances for Shipments & Transportation – So Less Consumption of Fossil Fuel, as a Result Lesser Emissions & Pollutions and Greater Environmental Concerns.
Balanced Approach

Like there is Two Sides of a Coin, either Globalization & Localization both have Advantages & Disadvantages.
In the name of Globalization, Allowing Free Entry of all for all with Boundaryless Borders making Homes turf a Dumping Ground is Not a Good Economics. Skewed and Concentric Economic Growth with too much Specialization in Certain Regions or Countries is Antithesis of Liberalization. Corona Exposed Weak and Fragile Points of Globalization. Semiconductor Chip Shortage – Reaching Crisis Point Worldwide really Exposed as a finer Example of shortcoming of Globalization, calling for now to Localize.
Similarly, Inward Looking, Closed Economy with Entry Barriers and too much Controls on Foreign Entry and Excessive Protection to Domestic Industry, Limits & Constraints Growth. The opposite of Economic Globalization—or Free-market Trade Across Borders—is Localization – a Protectionism, an economic policy that attempts to protect domestic businesses from foreign competition and labor markets, usually by imposing trade barriers like Tariffs and Restrictions.
Both Extremes of Globalization and Localization have Consequential Dangers to Damage & Jeopardies the Economies.
Rationally, Balancing both Globalization & Localization, proves beneficial for the Nations by taking Advantages of Globalization through Liberal and Free Trade with some Limitations & Cautions and at the same time taking due consideration of the Domestic Industry and Business by Strengthening them and Reasonably Protecting and Sheltering Native Industry from Foreign Cop is a Wise & Balanced Approach.
The term ‘Glocal’ combines the words Global and Local. Embracing Glocal means that you have a Global Mindset, Reach & Access, but you also Accommodate & Promote the Values, Cultures, Ideals, Interests and Needs of your Local Businesses.
Glocal – A Concept of Self-Reliance with Global Access
Glocal – A Concept of Self-Reliance with Local Strengths and Global Access, Trading Freedom and Liberal Integration.
Self-reliance is the Ability and Independence to Do Things and Make Decisions by a Nation on its Own, without Coercive and Forcible Gravity from other Nations or any Organizations to Influence the Key Decisions.
Three mutually reinforcing factors (3 C’s) that determine a country’s self-reliance:
Commitment: the degree to which a country’s laws, policies, actions, and informal governance mechanisms — such as cultures and norms — support progress towards self-reliance; and
Capacity: how far a country has come in its ability to manage its own development journey across the dimensions of political, social, and economic development, including the ability to work across these sectors.
Collaboration : Effective Global Collaboration requires Defining and Aligning the Country’s Vision & Goals, Addressing Trade Related Concerns, Adapting Globally Accepted Norms and Creating Partner Relationships, Engaging, Cooperating and Coordination on Mutually Beneficial Practices and Creating an Environment of Trust.
Glocal, Aligns the Local Aspirations and Development with Global Integration without Sacrificing Self-reliance, Self-sufficiency based on Local Strengths, Independence, Autonomy of Native Nations.
Glocal – Atmanirbhar Abhiyan
Glocal in Essence is aligned to “Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan” – “A Call to the Nation for Self – Reliance” by our Visionary Prime Minister, Shree Narendra Modi Ji exhibiting his leadership ascent during Critical Crisis Situation of COVID. This Concept of “Atmanirbhar” (Self-Reliance) envisioned to be built on Five Pillars – Those are the Key Areas to Strengthen the Nation:
> Economy,
> Infrastructure,
> A system driven by Technology and forward-looking policies, Demography, and
> Economic Demand.
The Vision of Modinomics is
♦ Perform
♦ Reform &
♦ Transform
Reflecting True Vision to Strengthen the Nation’s Economy through Self-Reliance.
Atmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan lays strong foundations to for raising our economic growth and long-term sustainability through our Strengths focused on Land, Labour, Liquidity and Laws.

Vocal for Local
Prime Minister Narendra Modi pitched for the use of products manufactured in the country, saying the novel coronavirus outbreak has taught us the Importance of Local Manufacturing, Local Market and Local Supply Chain.
“In times of crisis, this local has fulfilled our demand, this local has saved us. Local is not just the need, it is our responsibility also,” he said in his address to the nation.
The prime minister said Indian has to become “Vocal for their Local“, not only to buy local products, but also to promote them proudly, in essence “we must make the local as a mantra of our life“.
“The global brands were sometimes also very local like this. But when people started using them, started promoting them, branding them, felt proud of them, they became global from local products,” he said.
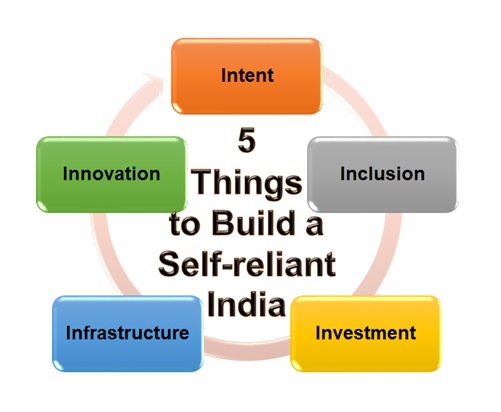
5 Things to Build a Self-reliant India
While delivering the Inaugural Address at CII Annual Session 2020, Getting Growth Back, through video conference, Prime Minister Narendra Modi on 2nd June’2020, listed five things that will help India mitigate the impact of the coronavirus pandemic and bring back the country to a high growth trajectory.
“To bring India on the path of rapid development, Five Things are very important to build a self-reliant India – Intent, Inclusion, Investment, Infrastructure and Innovation,” the PM said
Conclusion
Global Supply Chain advanced due to Globalization and Increasing Free Trade among Countries. Globalization undoubtedly has many Advantages & Benefits of Better Access and Integration of Supplies at Global Level. However, Globalization & Global Supply Chains are more Prone to Supply Chain Disruptions. COVID Pandemic’s impact on global trade and Supplies is so devastating that it has exposed the Fragility of the Supply Chain and proved to be a Real Test of Corporate Ingenuity, Resilience and Flexibility to face the Crisis.
So, Businesses have started looking for Offshore to Nearshore and Local Sourcing.
Glocal – A Concept of Self-Reliance with Local Strengths and Global Access, Trading Freedom and Liberal Integration. That means Glocal is a Combination of Globalization & Localization – Thinking Global & Acting Local – Developing, Supporting Local Industry & Business.
Developing Self-Sufficiency, Self-reliance, Strong Domestic Industry, Increase Competitiveness, Independence to Nations with Collective Cooperation among the Nations, Global Reach & Access, Knowledge & Information Sharing, Exchange of Goods & Service etc are the Glocal Mantras. These will Ensure Healthy Growth of the Nations, Collaborative Engagement among the Nations, Mutual Cooperation & Trust.
References :
> Global Logistics and Supply Chain Management, 4th Edition
John Mangan, Chandra Lalwani, Agustina Calatayud
> Global Supply Chain and Operations Management
A Decision-Oriented Introduction to the Creation of Value
Dmitry Ivanov, Alexander Tsipoulanidis, Jörn Schönberger
> Managing Supply Chain Risk and Disruptions: Post COVID-19
Aravind Raj Sakthivel, Jayakrishna Kandasamy, J. Paulo Davim
> Article “Value Insights into Supply Chain” by SN Panigrahi, Published in August’2010 issue of MMR – IIMM
> Article “Supply Chain Resilience Management Can Mitigate Disastrous Consequences of Risks” by SN Panigrahi, Published in April’2022 issue of MMR – IIMM






Very very useful.