The Limited Liability Partnership (LLPs) is an alternative corporate business vehicle that provides the benefits of limited liability but allows its members the flexibility of organizing their internal structure as a partnership based on a mutually arrived agreement. In order to provide greater ease of doing business in India to law abiding LLPs, it was the need of the hour to review the penal provisions of the Act so as to decriminalize compoundable offences involving minor, procedural or technical violations of the Act, or offences which can be objectively identified as where no fraud or mala fide intent is present nor is there any harm to public interest.
A committee named ‘Company Law Committee’ was set up by the ‘Ministry of Corporate Affairs’ on September 18, 2019 for examining and making recommendations to the Government on various provisions and issues pertaining to implementation of the Companies Act, 2013 and the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 (LLP Act).
A report was presented which comprised of recommendation to the Government namely: Decriminalization of 12 compoundable offences along with omission of provision consequential amendments along with ancillary changes in the Act with a motive to facilitate ease of doing business and creating a business-friendly environment.
Page Contents
Highlights of the Report:
The objective of the decriminalization exercise is to remove criminality of offences from business laws where no mala fide intentions are involved. An exercise was undertaken to identify those provisions of the LLP Act, violations of which do not result in injury to the public interest but are presently criminal in nature with fine as well as punishment after conviction being provided for in the LLP Act, 2008.
The reforms introduced via the report presented by the committee are broadly divided into five categories as follows:

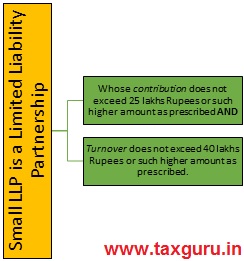
Concept of Small LLP:
The concept of small companies exists in Companies Act, 2013 on the same line a new concept of small LLPs is recommended to be introduced under the LLP Act, 2008 for promoting ease of doing business.
The rationale behind introduction of such concept is to create a class of LLP which can enjoy the privileges currently enjoyed by the small companies under the Companies Act, 2013 with the intent to reduce the cost of compliances and further to subject such class of LLP to lesser penalties in the event of default. Apart from reducing the burden of penalties on the LLP, this shall also encourage the micro and small enterprises to corporatize their business vehicles.
Recommended definition of Small LLP:
Capital Raising By LLP:
A LLP can borrow the funds for conducting of its business, but the LLP Act do not permit LLPs to raise capital by way of issuance of debt securities. This turns out to be a major hurdle in business operations of LLPs, especially in sectors such as real estate and infrastructure which are capital deficient. In light of the above, the committee recommended insertion of enabling provisions for permitting LLPs raising of funds through issuance of secured Non-Convertible Debentures to entities regulated by Securities Exchange Board of India and Reserve Bank of India. To ensure protection to investors, Committee also recommended that LLPs may not be permitted to allot/issue NCDs to individuals (retail investors).
The Committee suggested certain checkpoints for the LLP which intends to raise capital through issuance of secured Non-convertible debentures (Such LLP) which are given as under:
1. Such LLP shall insert a provision in the LLP Agreement before issuance of non- convertible debentures and the said agreement shall be registered by the Registrar.
2. Such LLP shall maintain a register of debenture holder in such form and in such manner as may be prescribed.
3. Such LLP shall create a debenture redemption reserve account out of profits of the limited liability partnership in such manner or for such quantum as may be prescribed and the amount credited to such account shall not be utilized by the limited liability partnership except for the redemption of debentures.
4. Such LLP shall not make an offer or invitation to bodies corporate or trusts exceeding two hundred in a financial year for subscription of its non-convertible debentures.
5. Such LLP shall pay interest and redeem debentures in accordance with terms and conditions of their issue.
6. Such LLP shall file with the registrar such information and documents as may be prescribed.
7. If such LLP fails to redeem the debentures on date of their maturity or fails to pay interest on debentures when it is due, the Tribunal may, without prejudice to other ordinary rights of debenture holders, on application of any or all of the debenture holders, after hearing the parties concerned, direct, by order, the limited liability to redeem the debentures forthwith on payment of principal and interest due thereon.
8. If any default is made in complying with provisions of this section, every partner shall be punishable with imprisonment of up to one year and fine between Rs. 2 Lakhs to 5 Lakhs or with both.
Additional Fees For Late Filing:
Section 69 of the LLP Act, 2008 deals with additional fees on the delayed filing of the returns of the LLPs. The Committee recommended to amend the said section. An additional fees structure is proposed to be amended to reduce the additional fee of ₹100 per day, presently applicable for the delayed filing of forms, documents.
Decriminalization of Offences:
Offences that are relevant under other laws are proposed to be omitted from the LLP Act. The committee proposed to de-clog the criminal courts by shifting the cases to be adjudicated by the In-House Adjudication Mechanism (IAM), the motive being reduction of burden upon the courts from non-serious matters.
Below is the tabular representation for the list of offences to be decriminalized and to be shifted to In-House Adjudication Mechanism (lAM):
| SR. No. | Nature of Amendment | Original Provision | Recommended Provision of the Committee |
| 1. | Section-7 Designated partners | Every LLP shall have at least 2 designated partners who are individuals and at least 1 of them shall be a resident in India.
Provided that in case of LLP in which all partners, body corporates or in which one or more partners are individuals and body corporate, at least 2 individuals who are partners of such LLP or nominees of such body corporate shall act as designated partners. Explanation – For the purpose of this section, “resident in India” means a person who has stayed in India for a period of not less than 125 days during the immediately preceding one year |
Explanation to subsection (1) of section 7 – For the purpose of this section, the terms, “resident in India” means a person who has stayed in India for a period of not less than 120 days during the financial year. |
| 2. | Section-10 Change in the Penalty. | If the LLP contravenes the provisions of section 7, 8 and 9, of the Act, the LLP and its partner shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than Rs. 10,000/- but may extend up to Rs. 1,00,000/- | Under section 10 of the Act, If the LLP contravenes the provisions of section 7 such LLP and its partner shall be liable Minimum of Rs. 10,000/- and for continuing contravention Rs. 100/- per day subject to maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/-;
If the LLP contravenes the provisions of section 8 and 9 such LLP and its partner shall be liable Minimum of Rs. 10,000/- and for continuing contravention Rs. 100/- per day maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/- for the LLP and Rs. 50,000/- for each partner |
| 3. | Section 13-Failure in comply with the provision related to notice for change in Registered Office. | Under section 13, If the LLP contravenes the provisions related to notice for change in Registered Office, such LLP and its partner shall be punishable with fine which shall not be less than Rs. 2,000/- but may extend up to Rs. 25,000/- | Amended section 13 of the LLP Act, 2008 Punishment for contravention shall be with fine for LLP and partner shall be minimum of Rs. 5,000/- which may extend up to Rs. 50,000/- |
| 4. | Section 21-Publication of name | If any LLP fails to comply with section 21, then such LLP shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 2,000/- to Rs. 25,000/- | If any LLP fails to comply with section 21, then such LLP shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 10,000/- |
| 5. | Section 25- Registration of changes in partners | If any LLP fails to file a notice to the registrar in respect to change in the name or address of the partners then such LLP and designated partner shall be liable for a fine minimum of Rs. 2,000/- and maximum of Rs. 25,000/- | If any LLP fails to file a notice to the registrar in respect to change in the name or address of the partners then such LLP and designated partner shall be liable for a fin of Rs. 10,000/- |
| 6. | Section 34- Maintenance of books of account, other records and audit, etc. | If any LLP fails to comply with section 34(i) (ii) (iii) and (iv) then such LLP shall be liable for a fine minimum of Rs. 25,000/- and maximum of Rs. 5,00,000/- and every designated partner shall be liable for a fine of minimum of Rs. 10,000/- and maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/- | If any LLP fails to comply with section 34 (iii) the LLP and its designated partners shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 100/- per day for which such failure continues.
Penalty for section 34(i) (ii) and (iv) will remain same. |
| 7. | Annual Return | If any LLP fails to comply with section 35 then such LLP shall be liable for a fine minimum of Rs. 25,000/- and maximum of Rs. 5,00,000/- and every designated partner shall be liable for a fine of minimum of Rs. 10,000/- and maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/- | If any LLP fails to comply with section 35 the LLP and its designated partners shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 100/- per day for which such failure continues. Subject to maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/- for LLP and 50,000/- for designated partner. |
| 8. | Compromise, or arrangement or limited liability partnerships | If any LLP fails to comply with section 60 (iii) then such LLP and every designated partner shall be liable for a fine maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/- | If any LLP fails to comply with section 60 (iii) the LLP and its designated partners shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 10,000 and in case of continuing default a further penalty of Rs. 100/- per day after the first during which such default continues, subject to maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/- for LLP and Rs. 50,000/- for designated partner. |
| 9. | Provisions for facilitating reconstruction or amalgamation of limited liability partnerships | If any LLP fails to comply with section 62 (iii) then such LLP and every designated partner shall be liable for a fine maximum of Rs. 50,000/- | If any LLP fails to comply with section 62 (iii), the LLP and its every designated partner shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 10,000/- and in case of continuing default a further penalty of Rs. 100/- per day after the first during which such default continues, subject to maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/- for LLP and 50,000/- for designated partners.
Insertion of explanation in section 62- A LLP shall not be amalgamated with the Company. |
| 10. | Order of Tribunal | Whoever fails to comply with any order of the Tribunal under any provision of this act, shall be punishable with imprisonment which may extend to 6 months and also be liable to fine for minimum of Rs. 50,000/- | This section is omitted. |
| 11. | General penalties | Any person guilty of any offence under this Act, for which no punishment is expressly provided under this Act, shall be liable for a fine of minimum of Rs. 5,000/- which may extend to Rs. 5,00,000/-. And with a further fine which may extend to Rs. 50/- for every day after the first day after which the defaults continues. | Any person guilty of any offence under this Act, for which no punishment is expressly provided under this Act, shall be liable for a penalty of Rs. 5,000/- and in case of continuing contravention with a further penalty of Rs. 1,000/- for every day after the first day after which the contravention continues. Subject to maximum of Rs. 1,00,000/- |
Accounting Standard:
After deliberate efforts as to decide whether accounting standards prescribed for Small Companies / MSMEs be applicable to the LLPs particularly functioning under the manufacturing sector, the Committee recommended insertion of provision pertaining to which the Central Government can prescribe applicability of Accounting Standards and Standards for Auditing to certain classes of LLPs.
Accordingly, Section 34A and 34AA after Section 34 under Chapter VII of the LLP Act is as follows:
Section 34A / 34AA- The Central Government may prescribe to a class or classes of limited liability partnership the standards of accounting, as recommended by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of India, constituted under Section 3 of the Chartered Accountants Act, 1949 (38 of 1949), in consultation with and after examination of the recommendations made by the National Financial Reporting Authority constituted under Section 132 of the Companies Act, 2013 (18 of 20 13).
Insertion of New Section ‘77A’:
Section 77A in the Act is inserted for adjudication penalty. As per the aforesaid section the Central Government may appoint as many officers by an order published in the Official Gazette not below the rank of Registrar, as adjudication officers for adjudicating penalty under the Act in the manner as may be prescribed.
Conclusion:
It was evident from the report that the Committee mainly focused on decriminalization of offences along with many other reforms aligning the LLPs with the Companies thereby enabling the LLPs to enjoy the privileges currently enjoyed by the Companies under the Companies Act, 2013. MCA on February 25, 2021 via message on the MCA website has clued-up about the applicability of certain sections of the Companies Act, 2013 to Limited Liability Partnerships (LLP) subject to certain modifications and adaptions soon. Thus, it can be concluded that LLP Act, 2008 is propose to undergo momentous amendments.
Sources:
http://mca.gov.in/Ministry/pdf/Report%20of%20the%20Company%20Law%20Committee%20on%20Decriminalization%20of%20The%20Limited%20Liability%20Partnership%20Act,%202008.pdf
https://www.hindustantimes.com/business/govt-to-decriminalise-12-offences-under-llp-act-101612371113326.html
http://www.lawstreetindia.com/experts/column?sid=524
*****
Disclaimer : The entire contents of this article have been prepared on the basis of relevant provisions and as per the information existing at the time of the preparation. Although care has been taken to ensure the accuracy, completeness and reliability of the information provided, we assume no responsibility therefore. Users of this information are expected to refer to the relevant existing provisions of applicable Laws. We assume no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information. In no event shall we shall be liable for any direct, indirect, special or incidental damage resulting from, arising out of or in connection with the use of the information. This is only a knowledge sharing initiative and author does not intend to solicit any business or profession.

| Mehul Solanki | Menakshi Bajaj |
| Research Associate | Junior Associate |
| Jaya Sharma & Associates | Jaya Sharma & Associates |
| bodha@jsa-cs.com | bodha@jsa-cs.com |




