In this article let’s discuss about Supply of Services By / To Government or Local Authorities Under GST.
Before Proceeding to understand the GST Implication on such Supplies, first let’s discuss What is Mean by Govt. or Local Authorities?
What is the meaning of ‘Government’?
As per section 2(53) of the CGST Act, 2017, ‘Government’ means the Central Government. In the same manner, Section 2(53) of the State GST enactment(s) define ‘Government’ to mean Government of the respective State.
As per clause (23) of section 3 of the General Clauses Act, 1897 the ‘Government’ includes both the Central Government and any State Government.
Central Government
As per clause (8) of section 3 of the said Act, the ‘Central Government’, in relation to anything done or to be done after the commencement of the Constitution, means the President.
As per Article 53 of the Constitution, the executive power of the Union shall be vested in the President and shall be exercised by him either directly or indirectly through officers subordinate to him in accordance with the Constitution.
Further, in terms of Article 77 of the Constitution, all executive actions of the Government of India shall be expressed to be taken in the name of the President. Therefore, the Central Government means the President and the officers subordinate to him while exercising the executive powers of the Union vested in the President and in the name of the President.
State Government
Similarly, as per clause (60) of section 3 of the General Clauses Act,1897, the ‘State Government’, as respects anything done after the commencement of the Constitution, shall be in a State the Governor, and in an Union Territory the Central Government.
As per Article 154 of the Constitution, the executive power of the State shall be vested in the Governor and shall be exercised by him either directly or indirectly through officers subordinate to him in accordance with the Constitution.
Further, as per article 166 of the Constitution, all executive actions of the Government of State shall be expressed to be taken in the name of Governor. Therefore, State Government means the Governor or the officers subordinate to him who exercise the executive powers of the State vested in the Governor and in the name of the Governor.
Governmental Authority & Government Entity
“Governmental Authority” means an authority or a board or any other body, – (i) set up by an Act of Parliament or a State Legislature; or (ii) established by any Government, with 90per cent. or more participation by way of equity or control, to carry out any function entrusted to a Municipality under Article 243 W of the Constitution or to a Panchayat under Article 243 G of the Constitution.
“Government Entity” means an authority or a board or any other body including a society, trust, corporation, (i) set up by an Act of Parliament or State Legislature; or (ii) established by any Government, with 90 per cent or more participation by way of equity or control, to carry out a function entrusted by the Central Government, State Government, Union Territory or a local authority.”
Who is a Local Authority?
Local authority is defined in clause (69) of section 2 of the CGST Act, 2017 and means the following:
- a “Panchayat” as defined in clause (d) of article 243 of the Constitution;
- a “Municipality” as defined in clause (e) of article 243P of the Constitution;
- a Municipal Committee, a ZillaParishad, a District Board, and any other authority legally entitled to, or entrusted by the Central Government or any State Government with the control or management of a municipal or local fund;
- a Cantonment Board as defined in section 3 of the Cantonments Act, 2006;
- a Regional Council or a District Council constituted under the Sixth Schedule to the Constitution;
- a Development Board constituted under article 371 of the Constitution; or
- a Regional Council constituted under article 371A of the Constitution;
Municipality under clause (e) of the Article 243P
The term Municipality has not been defined in the GST law. However, according to Section 2(69) of the CGST Act, 2017 the said term derives its meaning from clause (e) of the Article 243P of the Constitution of India. The said Article defines Municipality to mean an institution of self-government constituted under Article 243Q. As per Article 243Q, Municipality includes Nagar Panchayat in Transitional area, Municipal Council for smaller urban area and Municipal Corporation for larger urban area. The following are the powers specified under Article 243W of the Constitution of India which are entrusted to the Municipality:
1. Urban planning including town planning.
2. Regulation of land-use and construction of buildings.
3. Planning for economic and social development.
4. Roads and bridges.
5. Water supply for domestic, industrial and, commercial purposes.
6. Public health, sanitation conservancy and solid waste management.
7. Fire services.
8. Urban forestry protection of the environment. and promotion of ecological aspects.
9. Safeguarding the interests of weaker sections of society, including the handicapped and mentally retarded.
10. Slum improvement and upgradation.
11. Urban poverty alleviation.
12. Provision of urban amenities and facilities such as parks, gardens, play-grounds.
13. Promotion of cultural, educational and aesthetic aspects.
14. Burials and burial grounds; cremations, cremation grounds and electric crematoriums.
15. Cattle ponds; prevention of cruelty to animals.
16. Vital statistics including registration of births and deaths.
17. Public amenities including street lighting, parking lots, bus stops and public conveniences.
18. Regulation of slaughter houses and tanneries.
Any services by the Government by way of activity in relation to the above functions entrusted to the municipality will be exempt in nature.
Panchayat under clause (d) of the Article 243
The term ‘Panchayat’ has not been defined in the CGST Act, 2017. However, Section 2(69) of the CGST Act which defines local authority states that the definition of Panchayat can be borrowed from clause (d) of Article 243 of the Constitution of India. It defines Panchayat to mean an institution of self-government of the rural area constituted under article 243B. As per Article 243B, there shall be constituted in every state, Panchayats at the village, intermediate and district levels.
Article 243G of the Constitution of India entrusts powers, authority and responsibilities to the Panchayat. The Constitution of India endows the Panchayat with such powers and authority to enable them to function as institution of self-government. Also, it allows enactment of laws for the devolution of powers and responsibilities upon Panchayat subject to certain conditions with respect to the following:
(a) the preparation of plans for economic development and social justice
(b) the implementation of schemes for economic development and social justice as may be entrusted to them including those in relation to the matters listed in the Eleventh Schedule
The activities specified within the Eleventh Schedule are Agriculture, including agricultural extension; Land improvement, implementation of land reforms, land consolidation and soil conservation; Minor irrigation, water management and watershed development; Animal husbandry, dairying and poultry; Fisheries; Social forestry and farm forestry; Minor forest produce; Small scale industries, including food processing industries; Khadi, village and cottage industries; Rural housing; Drinking water; Fuel and fodder; Roads, culverts, bridges, ferries, waterways and other means of communication; Rural electrification, including distribution of electricity; Non-conventional energy sources; Poverty alleviation programme; Education, including primary and secondary schools; Technical training and vocational education; Adult and non-formal education; Libraries; Cultural activities; Markets and fairs; Health and sanitation, including hospitals, primary health centers and dispensaries; Family welfare; Women and child development; Social welfare, including welfare of the handicapped and mentally retarded; Welfare of the weaker sections, and in particular, of the Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes; Public distribution system; Maintenance of community assets.
For instance, the Government provides technical training/vocational education to farmers in relation to the function of Panchayat entrusted under Article 243G of the Constitution.
Whether activities performed by Government is business or not?
Section 2(17) of the CGST Act, 2017 defines ‘business’ to includes
(a) any trade, commerce, manufacture, profession, vocation, adventure, wager or any other similar activity, whether or not it is for a pecuniary benefit;
(b) any activity or transaction in connection with or incidental or ancillary to sub-clause (a);
(c) any activity or transaction in the nature of sub-clause (a), whether or not there is volume, frequency, continuity or regularity of such transaction;
(d) supply or acquisition of goods including capital goods and services in connection with commencement or closure of business;
(e) provision by a club, association, society, or any such body (for a subscription or any other consideration) of the facilities or benefits to its members;
(f) admission, for a consideration, of persons to any premises;
(g) services supplied by a person as the holder of an office which has been accepted by him in the course or furtherance of his trade, profession or vocation;
(h) services provided by a race club by way of totalisator or a licence to book maker in such club; and
(i) any activity or transaction undertaken by the Central Government, a State Government or any local authority in which they are engaged as public authorities;
It is clearly evident from clause (i) of the Section 2(17) that for the purposes of GST any activity or transaction undertaken by the Central or State Government or any local authority, in which they are engaged as public authorities, shall be deemed to be business.
Services Provided By / To Government / Local Authorities
Let’s now Discuss about GST Applicability on services provided by / to Government / Local Authorities separately.

Services Supplied by Government / Local Authorities
Services Supplied by Government / Local Authorities can be Classified in to three Categories for understanding GST applicability :
> Services Provided by Govt. Attracting RCM
> Services Provided by Govt. Exempted from GST
> Services Provided by Govt. Attracting GST (Forward Charge)

Services Provided by Govt. Attracting RCM:
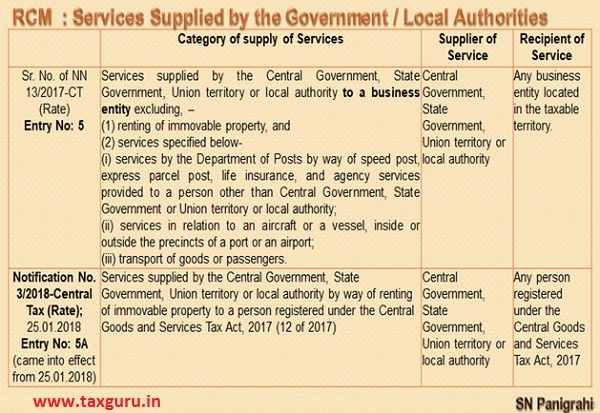
Following Notifications provide Services falls under Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM)
Notification No. 13/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dt. 28.06.2017
and
Notification No. 10/2017-Integrated Tax (Rate) dt. 28.06.2017
Entry Nos: 5 & 5A Notification No. 13/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dt. 28.06.2017 are related to Government / Local Authority Services which falls under RCM, that means when the Government / Local Authority Services any of such services to Registered Business Entity, the Recipient has to Pay GST
Exempted Services Provided by the Government or the Local Authority
Entry Nos: 4, 5, 6, 7,8,9, 9C, 34A, 42, 47, 61, 62, 63,64, 65, 65B of Notification No. 12/2017- Central Tax (Rate); 28th June, 2017 are the Exempted Services Provided by Government or the Local Authority.

–

–

–

–

–

Services Provided by Govt. Attracting GST (Forward Charge)
Other than Services Falling under Notification: 13/2017-Central Tax (Rate) & Notification : 12/2017- Central Tax (Rate) i.e other than Exempted Services & Services under RCM

Notification : 12/2017- Central Tax (Rate) i.e other than Exempted Services & Services under RCM

Services Supplied to Government / Local Authorities: Exempted
Entry Nos: 3, 11A, 16, 21B, 40, 45, 51, 72 of Notification No. 12/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dt. 28.06.2017 provides Services Supplied to Government / Local Authorities which are Exempted.

–

Services Supplied to Government / Local Authorities: Taxable
Other than Exempted Services as per Notification No. 12/2017-Central Tax (Rate) dt. 28.06.2017 are Taxable under GST
Disclaimer : The views and opinions; thoughts and assumptions; analysis and conclusions expressed in this article are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect any legal standing.
Author : SN Panigrahi, GST & Foreign Trade Consultant, Practitioner, Corporate Trainer & Author.
Available for Corporate Trainings & Consultancy
Can be reached @ snpanigrahi1963@gmail.com






sir , we rendering service by quality control & Quality assurance ( Technical inspection & reporting -raods ,drains building Etc)to Municipal Corporation & local bodies like Panchayati whether G S T applicable on these service or Not
If accomodation and other service provide by resort to government Officer, then gst applicable on that or not?
What if passenger transport service, which is covered under Urban amenities of twelfth Schedule as per AAR, is provided by Municipality in AC buses. Will this service be exempt under Sr. No. 4 of notification 12/2017 or GST will be payable under Sr. No.6 read with Sr. No. 15 of the notification
is service rendered to BEST undertaking, a municipal corporation transport and electric supply undertaking , taxable. i.e. should we levy GST on bills raised
Is there any provision for panchayat to get GST Registration….
Is service provided by an individual to Municipal corporation/ Local Govt. taxable under GST law?
BMC is taking charges for waste water sewerage from a trust. Whether there would be exemption with respect to services supplied by BMC as per S. No. 4 of Notfn 13/2017 considering that BMC would qualify as Governmental Authority?
BMC is taking charges for waste water sewerage from a trust. Whether there would be exemption with respect to services supplied by BMC as per S. No. 3 of Notfn 13/2017 considering that BMC would qualify as Governmental Authority?
Do we have to charge GST on supply made to State government ? or not ? What is the procure for not charging the GST ? and ITC have to be claimed or not on the said supply to government ? which is through Tender
The Consultancy Service is being provided as a PPP Expert(Public, Private Partnership Expert) to the Government of Andhra Pradesh and includes Procurement appraisal and advice on projects referred by the other departments to finance department of Government of AP. This service is provided on a full time basis to the finance dept of Andhra Pradesh Government.
Can you please confirm whether services provided above is exempt from GST?
As per entry 9C service provided by govt entities to government against consideration in form grant is exempt. In that case will the government entity be required to reverse the input tax credit as per rule 42?
further as per definition of consideration “subisidy from CG or SG” does not form part of consideration. This means receipt of any subsidy from the government is outside GST purview.
The above provisions are contradictory in itself. If anyone could throw some light on this issue.
Does renting of immovable property owned by State Govt to Central Govt attracts GST?
is construction of buildings for noon meal scheme (anganwadi buildings) after 01.03.2015 will attract service tax
great article. thanks a lot.
Thank you sir. Good Article.
Dear Sir,
Supply of Manpower Services to Local Authority whether applicable GST or Not?