Directorate General of Foreign Trade
Ministry of Commerce and Industry
Government of India
E-Commerce Exports Handbook for MSMEs
With the launch of the New Foreign Trade Policy 2023, Government of India has set a target of USD 1 Trillion of merchandise exports by 2030 aiming for a compounded annual growth rate of 12.2%. To achieve these targets, export growth is expected from new and emerging sources. One such source is Cross-border E-Commerce trade. Global Cross-border E-Commerce is estimated to grow to USD 800 Billion by 2025 and up to USD 2 Trillion by 2030.
E-Commerce would account for around 6.6% of overall global merchandise trade India’s share in the growing E-Commerce Exports segment is also poised to grow at
an accelerated pace.
This handbook by Directorate General of Foreign Trade offers an introduction to Cross-border E-Commerce, and the benefits & opportunities that Cross-border E-Commerce offers to new Entrepreneurs and Exporters.

E-Commerce offers access to a larger global market in addition to domestic sales. As shown in figure 1, the sellers on E-Commerce platforms can utilise a suite
of integrated service such as – cataloguing, marketing, pick-up & delivery as well as receive and reconcile the export payments. This results in reduced time & cost for the seller, allowing more time & focus on their product, packaging, marketing etc.
Fostering E-Commerce Exports through DGFT Initiatives
The Foreign Trade Policy(FTP) 2023 has a stated objective to enable cross-border E-Commerce for artisans, weavers, craftsmen and MSMEs, in coordination with stakeholder Departments.
DGFT Regional Authorities are working to actively promote E-Commerce Exports through collaborative efforts with Customs Authorities, Department of Posts
Industry Partners, and Knowledge Partners, with an emphasis on creating awareness & skills, and knowledge-sharing with exporters and entrepreneurs.
DGFT is also working with government stakeholders to resolve payment and banking issues, Customs-related matters to provide a leveled platform to E-Commerce Exporters.
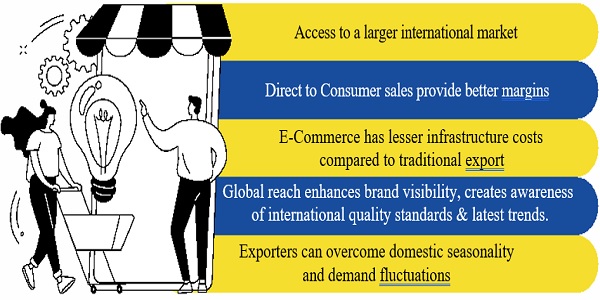
Figure 2: Advantages of Selling through E-Commerce
Globally around two-thirds of international parcels weighing up to 2 kilograms are shipped through Postal route. To provide a similar competitive advantage in India and to accelerate India’s export growth through the Postal Route, Department of Post is expanding India’s postal export network in a hub-and-spoke model by linking the Dak Niryat Kendras (DNKs) to Foreign Post Offices(FPOs). The target for year 2023 is to operatialise 1000+ DNKs.
DGFT endeavours to work with the regional Dak Niryat Kendras to facilitate new entrepreneurs for increasing B2C Exports through the Postal Route.
In the next few pages we provide some details that would be helpful for new E-Commerce Entrepreneurs and Exporters.
What to Sell
Focus – on India’s Strengths
India has a comparative advantage in certain sectors/ products. Focusing on these sectors/ products will enable the seller to garner higher profit margins, establish their brand identity and would require lesser marketing/ promotion as such Indian products are already well recognised. The following is a list of such sectors:
- Textiles, handloom and apparel
- Leather & Leather goods
- Handicrafts and Home Décor
- Beauty and Personal care
- Semi-precious jewellery & accessories
- Automotive parts
- Ayush and Herbal products
- Spices and food products
- Tea and Coffee
- Engineering goods
- Religious artifacts
Explore Foreign Demand Sources
The next step towards exporting is to analyse the foreign demand for the product and target the market segments, age-groups that are best suited for your product.
- To understand the product or market of your interest browse through the E-Commerce platforms of the country to check the demand and pricing of similar products.
- Actively visit and attend Trade Fairs, Buyer-Seller Meets, Reverse Buyers Seller Meets both in India and abroad.
Figure 3 : High Potential Export Products From India
Check on Regulatory Requirements for Exports
Before venturing into exports, one basic requirement is to know the Indian Tariff Classification (Harmonised System) ITC(HS) of a product. You may search for the ITC(HS) on the Customs (CBIC) or DGFT website.
Based on the ITC(HS) classification the regulatory requirements for export from India and requirements at buyers’ country need to be confirmed. Non-compliance can result in penalties in India or issues at the country of import.
Exporter must be aware of the following: Export Policy:
- Exporters must be well aware of the export policy related to their products. (as shown in figure 4)
- Certification Requirement: Partner Government Agency (PGA) certification requirement applicable on the exported products. For example- for pharma exports, certification is required from Central Drugs Standard Control Organisation (CDSCO), Organic exports are certified by APEDA, etc.
The export of goods is governed by the export policy notified by DGFT, from time to time. On the basis of ITC(HS) classification, the Export Policy broadly classifies the goods as ‘Free’, ‘Restricted’ and ‘Prohibited’.

Figure 4: Brief on Export Policy
When & Where to Sell
The “When and Where to Sell” strategy is essential for E-Commerce. It involves market research to identify target regions, population segments, etc. for expansion of sales.
- Overall demand split by age, region etc
- Cultural preferences of the buyers
- Seasonal trends in the buyer country
Focus on Shopping Behaviors
An approach to regional targeting involves understanding of a country’s shopping behaviour. Regions with a strong prosperity towards online shopping may be identified as high-potential markets and should be targeted with more focus. Some key E-Commerce intensive regions to consider:

Focus on Indian Diaspora, Festivals, Sales Events
Persons of Indian Origin living abroad are a key target demographic with demand for products from India. This presents an opportunity for Cross-border B2C E-Commerce sales, for India-centered products like handicrafts, food products, religious/festive items, Indian apparel or other items with a strong Indian theme.
Exporters should also focus on and target specific holidays/ festivals when the demand for products is higher.,
Sellers must also monitor global sales events, seasonal sales trends and festivals celebrated in the various regions.
Besides global sales events, seasonal drivers such as back-to-school shopping, etc., may also be kept in mind and leveraged suitably.
Sellers may also consider offering discounts and promotions to attract customers from different countries and regions.
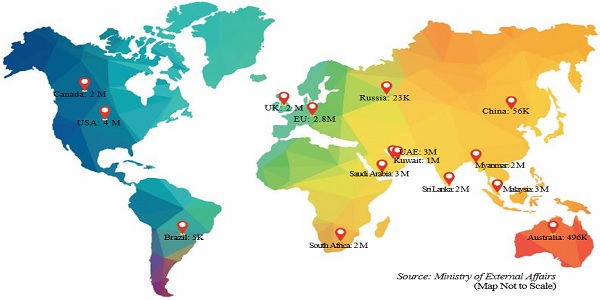
Figure 6: Key Countries with Indian Diaspora
“Exporters must leverage the larger international markets to create consistent demand throughout the year.”
Some Seasonal Sales Trends/ Events
|
S. No |
Target Event | Event Period | Markets |
| 1. | New Year’s Day | 1st Day of January | World Wide |
| 2. | Boxing Day Sale | 26th December | USA, Canada EU, Australia, UK, Africa, South America |
| 3. | Halloween | October 31st | USA, Canada, Mexico, South America, Europe |
| 4. | Black Friday Sale | 24th November | |
| 5. | Valentines Day | February 14th | World Wide |
| 6. | Mother’s Day | Second Sunday of May | |
| 7. | Father’s Day | Third Sunday of June | |
| 8. | Cyber Monday | Monday after Thanksgiving | USA, Canada EU, Australia, UK, Africa, South America |
| 9. | Single’s Day | 11th November | China, South East Asia, EU |
| 10. | El Buen Fin (The Good Weekend) |
Third Monday of November | Mexico and Latin America |
| 11. | Jour XXL (XXL day) | First day of May | France |
Table1: International sales season trends/events
Focus on Global Festivals for Sales Growth
| S. No | Target Event | Event Period |
| 1. | Diwali | October – November |
| 2. | Raksha bandhan | |
| 3. | Thanksgiving | Fourth Thursday of November |
| 4. | Christmas | 25th December |
| 5. | Easter | March-April |
| 6. | Chinese New Year | Between January 21 & February 20 |
| 7. | Ochugen – Japan | July – August |
| 8. | Holi | March – April |
| 9. | Ganesh Chaturthi | September- November |
| 10. | Eid-al-Fitr | Currently in April. Varies year-to-year |
| 11. | Eid-al-Adha (Bakr-eid) | Currently in June. Varies year-to-year |
| 12. | Holi | March – April |
Table 2: Indian & International Festivals
How to Sell
Pricing Strategies
It is important to have a clear and dynamic pricing strategy in place before entering any market. Good pricing strategies help determine sales and profits while staying competitive. Some key pricing strategies are listed below:
|
S. No |
Pricing Strategy | Description |
| 1. | Cost-based | Prices are set by adding a certain margin to the total cost of goods; easy to calculate and ideal first-step for new E-Commerce businesses. |
| 2. | Price Skimming | Prices of new products are kept high initially to redeem expenditure around promotion and subsequently prices are lowered in line with the emerging competition. Ideal for new innovative products or when entering an untapped market. |
| 3. | Penetration-based | Prices are kept low in order to find a foot-hold in a highly-competitive market and gain customer base; Using early discounts is a common penetration-based pricing strategy. |
| 4. | Market Oriented/ Competitor-based | Pricing is based on competitor pricing/ overall market pricing to stay in-sync with the demand. Ideal for heavily competitive markets and generic products. |
| 5. | Charm pricing | Prices are displayed to make it more appealing to the customer. Common example is pricing an item at a decimal-value, i.e., $9.99 instead of $10. Another example is slashing the original price and placing the discounted price next to it. |
| 6. | Anchor pricing | An item is priced in comparison to its initial price point or another similar item. Some examples are: a) Discounting an item after initially setting it at higher rate b) Pricing a slightly more upscale product significantly higher than the earlier version, directs customer attention towards the upscaled product. |
Table 3: Pricing Strategies
How to Find Marketplace Online
How to Design Catalogue For Your Products
An online catalogue works like a shop window for an online E-Commerce product. Whether someone sells on their own website or through an online marketplace, it is vital to organise the catalogue to match the brand and product. A visually appealing catalogue helps draw attention of the buyer to build a strong customer base. Some key points to note when designing a catalogue are:
- Simple and concise product descriptions
The product descriptions should be informative and include all important features. A good product description should be SEO friendly, i.e., include keywords that help search engines rank them.
- Sharp and clear product images
As customers do not have the option to physically interact with the product, sharp, clear images are essential for enhancing its appeal. Features like 360-degree product views can further improve the showcasing experience.
- Functional and visually pleasing layouts
An effective seller page should offer minimal navigation and serialised product listings. For example, grouping similar products, as customers tend to purchase complementary items.
- FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Whether in chat-based or pre-documented formats, covering aspects of the product that have not been covered in the product description should be provided.
On payment of certain fees, one may also consult the E-Commerce Platform provider directly for support on listing and cataloguing services.
Sellers can also employ online resources that provide cataloguing services free of cost. Various free templates available on the internet may also be explored for catalogue designing.
A straight forward way is capture some visually appealing photos of your product, then search for one of these websites online and follow the given steps
Step 1: Sign up and register yourself on the catalogue website.
Step 2: Enter the product information: Product Name: Enter a descriptive name for your product.
- Category: Choose the appropriate category or create a new one. Description: Write a detailed product description.
- Price: Set the selling price.
- Upload high-quality images of your product
Step 3: Once all product details are entered and confirmed save and download the catalogue for use on various sites or for social E-Commerce.
Packaging Your Products
Exporters must strongly focus on the ‘unboxing experience’ besides the mandatory packaging requirements
Various Packaging services are offered by E-Commerce service providers and Courier service providers. However, Exporters must ensure the following when packaging goods before shipment:
a) Every parcel must be packed & closed in a manner with due regard to:
(i) the weight & nature of the contents;
(ii) mode of transport and the length of … the journey;
b) The packing and closing must protect the contents so that these cannot be damaged in repeated handling.
c) Packaging must be such that it is not possible to tamper with the contents without leaving a trace of violation.
d) The parcel should be protected against major changes in climate, temperature, atmospheric pressure or conveyance.
e) It must be packed in a way as not to endanger the health of officials and to avoid any mishap/ injury to officials called upon to handle it or to soil/damage other parcels or postal equipment.
f) Packing or the wrapping should have sufficient space for the entry of service instructions and for affixing stamps and labels.
g) Items such as precious metals, glass, fragile objects, liquids, ointments, resin etc. must follow special packing conditions.
Key Documentation Requirements
The documentation required for undertaking E-Commerce Exports from India can be broadly divided into two categories – General documents required for exporting from India and specific product-based requirements. General Documentation requirements are as follows:
- PAN: It is necessary to a establish a firm of some nature (proprietorship, partnership, LLP, Limited company, Trust, Society etc) and to obtain a PAN for the same firm.
- Bank Account & AD Code: An Indian bank account in the name of the firm is required. The authorised dealer (AD) code of the concerned bank branch may be noted.
- GSTIN: For exporting from India an exporter is required to obtain a GST number. Refer to https://services.gst.gov.in for details.
- IEC(Importer-Exporter Code): The process of IEC issuance is fully online and automated. IEC a key business identification number as no Exports or Imports may be effected without mentioning IEC. For availing an IEC, logon to the DGFT website (https://dgft.gov.in)
The product-specific permissions and documentary requirements may vary for different products. Suitable research & due diligence may be undertaken before exporting.
Choosing the Right Logistics For Your Needs
To provide a competitive price to the consumer and in order to reach the consumer time, an optimised and efficient logistics plan is a must. While traditional domestic E-Commerce business logistics involves following 3 aspects-
- collection and storage of goods
- picking and sending orders
- processing returns or rejects
Cross-border E-Commerce logistics involve given business operations as well as border crossing procedures. A fast and reliable delivery and customs clearance in India and at the destination courtly is key factor in exports through E-Commerce.
There are four main types of cross-border E-Commerce logistics providers:
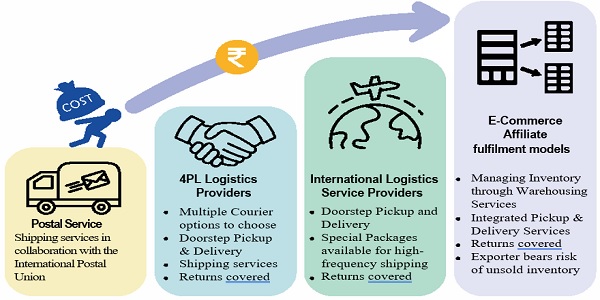
Figure 7: Types of Logistic Services and their features
Exports through the Postal Route
Exports through Postal route are shipped through Foreign Post Offices and Dak Niryat Kendra across the country.
India Post currently offers the following range of services for exports through postal route:
| Service Offered | International Speed Post (EMS) | International Reg Small Packet (EMS) | International Air Parcels | International Tracked Packet (ITPS) |
| Tracking System |
Online Track & Trace facility |
Registered. accountability, Tracking & Inquiry available |
Online Track & Trace facility |
Online Track & Trace facility |
| Weight Restrictions |
General maximum weight limit is 35 Kgs or the maximum acceptable weight limit prescribed by the destination country, whichever is lower. |
Upto 2 Kgs (Suitable for light weight) |
General maximum weight limit is 20 Kgs or the maximum acceptable weight limit prescribed by the destination country, whichever is lower. |
General maximum weight limit is 2 Kgs |
| Countries covered |
100+ | 200+ | 200+ | 39+ |
| Compensation | a) Upto 13000/- INR b) For Delay in delivery of EMS Articles, 5% of the Postage charges for the delay of more than 5 days from published norms |
Upto 3000/- INR | Upto 13000/- INR | Upto 1000/- INR |
| Discounts available |
Discount of up to 15% based on Monthly International EMS Revenue |
Discount of up to 10% based on yearly revenue |
Table 4: Details on Postal Exports
To Ship via India Post
1. An exporter has to register with the Customs authorities with IEC and AD Code of the their merchant bank.
2. Choose the appropriate Postal Bill of Export (PBE) form:
- PBE I for E-Commerce exports
- PBE II for Exports other than E- Commerce
3. Complete the necessary declaration forms based on the value of your articles:
- CN22 for articles below SDR 300 in value
- CN23 for articles with a value of SDR 300 or above
4. For International Tracked Packet Service articles, a Harmonized Label is to be used.
5. Drop your shipment at the nearest Dak Niryat Kendra or FPO for acknowledgment and tracking number assignment.
6. Present the PBE consignment to Customs for review and obtain a “Let Export Order”. .Customs will keep the original PBE form and provide the duplicate.
7. The Postal Authorities will furnish proof of export, such as copies of relevant CN/ CP forms, to Customs at the Foreign Post Office (FPO).
Note: For all Postal related Orders/ Circulars/ Notifications please visit the Department of Posts website regularly.
Exports through the Courier Route
Courier Shipping Bill (CSB) is the main document in the export process via courier services which is to be filed on the Express Cargo Clearance System(ECCS) website. 1….Choose the appropriate Courier Shipping bill form:
- CSB-4 : for exports under INR 50,000 for Samples/Non-Commercial Value
- CSB-5 : for exports under INR 10,00,000 (Commercial Shipments)
2. Gather necessary documents: GST details, IEC, AD code and HSN code of the product.
3. Create a detailed invoice with itemized pricing and relevant information. may also check eligibility for potential benefits under the Government of India schemes.
4. Prepare shipment details, including product description, quantity, value, and
recipient’s information.
5. Contact an authorised courier service provider (as notified on the ECCS platform) and provide them with shipment details including product info, GST, IEC, HSN code, and AD code.
6. Provide shipment details for GST compliance.
7. Ensure all information and documents are in order before the courier provider ships your goods.
Note: For all the latest Custom related updates please refer to the notifications and circulars, published on the customs website: www.cbic.gov.in
Filing of IGST Refunds under Courier/ Postal Exports
Exporters are also eligible for refund of any IGST paid on their E-Commerce Exports. Basic Steps for claiming refund are as follows –
(i) Copy of Shipping Bill: Ensure that all the required information, such as invoice number, port code etc, are accurately filled out in the shipping bill document.
(ii) GSTR-1 Form: All registered users need to file the GSTR-1 form on the GST portal. Within the GSTR-1 form, locate and select “Table-6A.” This is the section where you need to provide details related to your export consignment.
(iii) Information required in the Table-6A typically includes: Invoice number for the exported goods, port, shipping bill details etc.
It may be noted that the filing of the shipping bill and claim for IGST Refund depends on the mode of shipment:
- For postal exports through India Post, the Department of Posts will handle the shipping bill filing on your behalf.
- For courier exports, the Authorized Courier will be responsible for filing the shipping bill.
As Courier Shipping Bills are transmitted by ECCS to ICEGATE, the IGST Refund for Courier Exports may be electronically linked with the Courier SBs. For Export through Postal Route, the IGST refund request is required to be uploaded by the Customs officer using the ICANN software.
Note: Always refer to the GST portal and relevant authorities for up-to-date information on filing for IGST refunds.
Handling Returns & Rejections
- The authorised courier has to file the Courier Bill of Entry for re-import for the same Importer-Exporter Code (IEC) holder and at the same international courier terminal, for whom and where the corresponding Courier Shipping Bill (CSB) for the item was filed.
- The return E-Commerce transaction for the item is initiated by the same consignee to whom the item was exported under the corresponding Courier Shipping Bill (CSB-V) and on the same E-Commerce platform provided a courier agent. Logistics provider in the buyer’s country may also initiate the return transaction if the product could not be cleared from Customs for Import into the buyer’s country.
- The image of the return confirmation page on the E-Commerce platform is uploaded on Express Cargo Clearance System (ECCS) while filing Courier Bill of Entry for such re-import.
- The reason of re-import is provided in the Courier Bill of Entry and the returned item is re-imported along with the original packing;
- As per Courier Imports and Exports (Electronic Declaration & Processing) Amendment Regulations, 2022 new provisions have been introduced to support easy return for E-Commerce exporters.
- The newly introduced provisions under the following regulations are specific for courier re-import of jewellery subject to certain conditions. However, the Regulations do not provide for specific exemption of import duty on re-imports.
- Exemption on import duty for reimport is governed by Customs Notification 45/2017 dated 30.06.2017.
Onboarding E-Commerce Platforms
To generate Export demand, one must present their goods on Global E-Commerce planforms Onboarding on such .
E-Commerce platforms is a multi-step process. Some of the cost involved in the said process is presented as follows –
| S. No | Type of fees | Details |
| 1 | Referral fees | Fee charged as a percentage of the sales made by selling any product |
| 2 | Closing fees | Fee charged in addition to Referral Fee, based on your product price |
| 3 | Shipping fees | Fee incurred for delivering your order through any channel |
| 4 | Fee for availment of platform’s logistic services | Fee to pick, pack, deliver & store your orders |
| 5 | Cataloguing Fee | Fee incurred for availing the cataloguing services of E-Commerce Platform |
Table 5: Various Fee Incurred on E-Commerce Platforms
Exporting through Social E-Commerce
Exporters should also leverage Social Media for promoting their products and services. For example: selling through sites like Facebook marketplace, WhatsApp business, Instagram, Telegram etc. Social E-Commerce helps create awareness, generate leads, build trust, and drive conversions for exports through a large social media user base. Some steps to sell through Social E-Commerce as follows:
Step 1- Setup a Business Account: Sellers must register and set up a business account, complete their Business Profile, including contact details on the platform. .
Step 2- Get Approved: Comply with policies for trustworthiness. Verifying your domain, enhances authenticity and reach.
Step 3- List/Catalogue: Using Catalogue Manager Tool, add images, title, price, description, & other relevant details of the product. Categorise products carefully in order to reach out to the target audience.
Step 4- Setup a Checkout Account: Set up a checkout account to enable buyers to purchase from listings.
Step 5- Upload Content regularly: Regularly posting quality social media content is key to building reach and visibility.
Selecting the Right Payment Method
The payment settlement while exporting through E-Commerce can be broadly classified into three categories.
- E-Commerce platforms’ integrated
- Online payment gateway service providers.
- International money transfer services through agents.

Payment Terms & Methods of Receiving Payments
When you register on any E-Commerce platform for the purpose of exports, the platform may charge a certain commission for processing your items and delivering it to the end user. A breakup of some of the charges are given in Table-5.
Few points to keep in mind when selecting a payment transfer service are:
- Exchange Rates: Banks and transfer services use the mid-market rate to trade with one another. Different providers may offer different rates. May compare the rate offered to the standard rate to choose the one with the smallest difference.
- Transfer Fees: Service providers charge transfer fees that can be a fixed flat rate or a percentage of the transfer amount.
- Transfer Speed: If you need quick transfers, you may have to pay extra for express delivery.
- Transfer Limits: Check the allowable limit and choose the best suited service.
- Discounts: Check for deals like free transfers on sign up and discounts for large transfers by various service providers.
- Safety: To ensure safe transfers, use service providers that comply with the laws and regulations specified by RBI and by the buyers’ country.
RBI Guidelines
Period of realization
It is obligatory on the part of the exporter to realise and repatriate the full value of goods to India within 9 months from the date of exports.
For goods exported to a warehouse established outside India, the proceeds should be realised within 15 months from the date of shipment of goods.
RBI also allows AD Category – I banks to extend the payment period from the export date up to 6 months at a time, regardless of the invoice value, as long as certain conditions are met.
Manner of receipt
(i) Please follow the rules in the Foreign Exchange Management (Manner of Receipt & Payment) Regulations, 2016, as in RBI Master Circulars (as amended from time to time).
(ii) Processing of export related receipts through Online Payment Gateway Service Providers (OPGSPs) is available for export of goods of value not exceeding $ 10,000.
“Write-off” of unrealized export bills In case an exporter is not able to realise the outstanding export dues, the exporter may either self-write off or approach the AD bank concerned, who had handled the relevant shipping alongwith appropriate supporting documentary evidence.
AD bank, on request of the exporter, may in respect of certain cases, also write-off unrealised export bill without any limit, provided the bank is satisfied with the documentary evidence produced.
The limits prescribed for write-offs of unrealized export bills are as in Table 6.
Opening/ Hiring Warehouses Abroad
As per the RBI Master Circular, AD Category – I Banks may consider the applications received from exporters and grant permission for opening/ hiring warehouses abroad subject to certain conditions:
- Applicant’s export outstanding does not exceed 5% of exports made during the previous financial year.
- Applicant has a minimum export turnover of USD 100,000/- during the last financial year.
|
S. No |
Particulars | Limit | Limit (%) in relation to |
| 1 | Self-write-off by an exporter (Other than the Status Holder Exporter) | 5% | Total export proceeds realized during the calendar year preceding the year in which the write-off is being done |
| 2 | Self-write-off by Status Holder Exporter | 10% | |
| 3 | Write-off by AD Category-1 Bank | 10% |
Table 6: Write-Offs Limits Prescribed by RBI
Export Data Processing and Monitoring System (EDPMS)
EDPMS is an online module for all Indian banks to record exporters’ inward trade remittances online. As per RBI Master circular, AD banks should maintain Export Bills Register, in physical or electronic form aligned with EDPMS. The bill number should be given to all type of export transactions on a financial year basis (i.e., April to March) and same should be reported in EDPMS. While Courier Exports are registered under EDPMS, exports through Postal Route are not updated in EDPMS as on date.
Electronic Bank Realisation Certificate (e-BRC)
Banks also generate Electronic Bank Realisation Certificate (e-BRC) for purposes as specified under the Foreign Trade Policy. The e-BRC system is currently being revamped to provided a self-certification option for exporters to reconcile their export realisation directly.
Note: For updated guidelines regarding realisation of export proceeds and other banking/payment related provisions, please refer to RBI’s Master Circular on Export of Goods and Services.

For any Feedback or Assistance on E-Commerce Exports, Write to:
Email: ecommerce-dgft@gov.in
Website: https://dgft.gov.in
Directorate General of Foreign Trade, Vanijya Bhawan,
16, Akbar Road, New Delhi – 110 001




