The determination of residency under the provisions of Income Tax Act, 1961 (‘Act’) is critical in determining the taxable income to be offered to tax in India. One issue that has been noted is with respect to taxation of crew members of ship or individuals leaving for employment outside India during the year and another being the impact of the changes made in residency provision for individuals.
A. Residential status determination
As per Section 6 of the Act, it may be noted that the individuals residency may be determined as under (in case the image is not visible, refer the attached file):
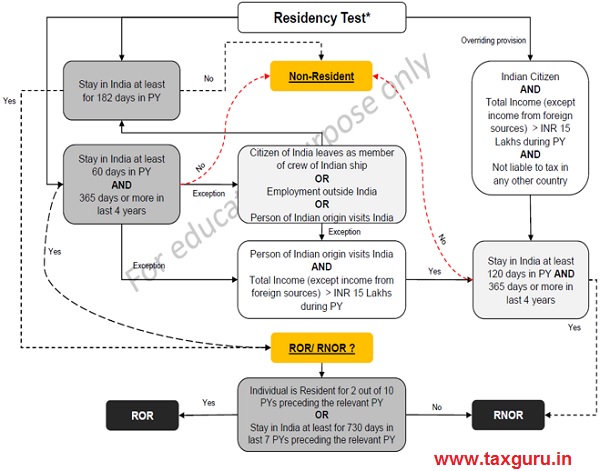
With respect to the Citizen of India being a member of crew of foreign ship and in respect to eligible voyage the period mentioned in the continuous discharge certificate (‘CDC’) shall not be considered while computing the stay in India.
Eligible voyage means where either the port of origin or port of destination is India. Also, it may be noted that the overriding provision shall not apply with respect to resident individual as per the provisions of the Act.
Once, the residential status has been determined for the individuals then can we proceed to determine the income that shall be taxable in India.
B. Taxability
Now basis the above chart, if it is determined that the person shall qualify as Non-resident then the income accruing/ deemed to accrue in India or income received/ deemed to be received in India shall be taxable. Further, the Non-resident individual claiming benefit of tax treaty shall be required to file return of income in India if the taxable income as per the provisions of the Act (i.e. without taking into account the relief under treaty) exceeds the basic exemption limit. However, if the total income only comprises of long term capital gains or short term capital gains u/s 111A only then the said income is taxable even if the basic exemption limit is not breached.
For Resident but not ordinarily resident the income from business or profession controlled from India however, the income is received outside India then in addition to income that is taxable for non-resident such business/profession income shall also be taxable.
For Resident and ordinarily resident person the global income is taxable in India. The same has been summarized in the table below:
| Nature of Income | Residential status | ||
| ROR | RNOR | NR | |
| Income which accrues or arises in India | Taxable | Taxable | Taxable |
| Income which is deemed to accrue or arise in India | Taxable | Taxable | Taxable |
| Income which is received in India | Taxable | Taxable | Taxable |
| Income which is deemed to be received in India | Taxable | Taxable | Taxable |
| Income accruing outside India from a business controlled from India or from a profession set up in India | Taxable | Taxable | Not Taxable |
| Income other than above (i.e., income which has no relation with India) |
Taxable | Not Taxable | Not Taxable |
Hope the same helps in understanding the concept of residential status and consequential taxability in India.
Disclaimer: Nothing contained in this document is to be construed as a legal opinion/ advice or recommendation and the content is to be used strictly for educative purposes only.






Not help ful.