Article explains Objective of E-Way Bill under GST, why E – Way Bill Mandatory, Computation of Value of consignment for e-way bill, E Way Bill in case of Inter and Intra State Movement, Who can made E Way Bill , Types Of E Way Bill, Cancellation of E Way Bill, Validity of E Way Bill, Acceptance and Rejection of E Way Bill, Exemption in case of E Way Bill, Concept Of Consolidated E Way Bill and E Way Bill in case of use of Multiple Vehicle.
Page Contents
- 1) Objective of E-Way Bill under GST
- 2) E – Way Bill Mandatory
- 3) Computation of Value of consignment
- 4) E Way Bill in case of Inter and Intra State Movement
- 5) E Way Bill Made by
- 6) Types Of E Way Bill
- 7) Cancellation of E Way Bill
- 8) Validity of E Way Bill
- 9) Acceptance and Rejection of E Way Bill
- 10) Exemption in case of E Way Bill.
- 11) Concept Of Consolidated E Way Bill.
- 12) E Way Bill in case of use of Multiple Vehicle.
1) Objective of E-Way Bill under GST
♠ Reduce tax evasion with proper invoicing of the goods and to stop the practice of bogus Invoicing of goods.
♠ Tracking of Goods with the use of robust technology like (RFID) Radio Frequency Identification Devices.
2) E – Way Bill Mandatory
♠ Yes mandatory, Every registered person who causes movement of goods of consignment value exceeding Rs. 50000*/-
♠ in relation to a supply; or
♠ for reasons other than supply; or
♠ due to inward supply from an unregistered person, shall,
before commencement of such movement, furnish information relating to the said goods in Part A of FORM GST EWB-01, electronically, on the common portal.
*The Maharashtra Government notified that no E-WAY Bill shall be required to generate for intra state movement in the state of Maharashtra, in respect of the supply of goods valuing less than Rs.100000/-
*The Limits can be different for different States.
However, in following 2 situation E Way Bill is mandatory irrespective of Value of Consignmen
i) Transfer To Jobworker :- Earlier there was a provision regarding Reversal of Credit of the Inputs and Capital goods if it is not received within the prescribed time, but there was no mechanical control on the movement of goods and it can be very well proved with the help of fake/ bogus delivery challans that the goods are received within prescribed time and the reversal provision never get attracted. To nullify this practice and to impose mechanical control on the receipt of Inputs within 1 Year and Capital goods within 3 Years the E way Bill made Mandatory for transfers made to Job-worker. The result of which reversal of ITC provisions made more active.
ii) Movement of Handicraft Goods.:- handicraft goods are transported from one State to another by a person who has been exempted from the requirement of obtaining registration under clauses (i) and (ii) of section 24, the e-way bill shall be generated by the said person irrespective of the value of the consignment.
The mandatory provisions is given to control the movement of handicraft item there shoul not be supply of any other goods with the name of Handicraft Items
3) Computation of Value of consignment
Computation of Value for E Way bill can be best explained with the help of following example.
| SR No. | Particulars of Invoice | Amount (Rs.) |
| 1) | Value of Exempted Supply | 35,000 |
| 2) | Value of Taxable Supply | 17,000 |
| 3) | Add :-GST @ 28% on Taxable Supply | 4,760 |
| 4) | Add:- Compensation Cess @ 15% on Taxable Supply | 2,550 |
| 5) | Total:- | 59,310/- |
Value For E- Way Bill :- 17000 + 4760 +2550 = Rs. 24,010/- (It Is Less than Rs.50000/- E Way Bill not required)
Value of Exempted Supply cannot be considered for Computation of Value for applicability of E Way Bill.
Each invoice/delivery challan shall be considered as one consignment and therefore for each invoice one e-way bill has to be generated irrespective of same or different consignors or consignees.
4) E Way Bill in case of Inter and Intra State Movement
E Way Bill is required for Inter as well as Intra State however, For Intra State Movement value for E Way Bill may Vary State by State.
As per provisions of Article 279 A of Constitution Of India the States can decide their own limit of value for mandating E Way Bill.
Example: – In Maharashtra the limit for E WAY Bill For Intra State Movement is Rs. 1,00,000/-
5) E Way Bill Made by
E Way Bill can be made by any of the following persons :-
1) Sender.
2) Transporter.
3) Receiver.
Any person from Above 3 can generate E Way bill using GSTIN ( If Registerd ). If in case of Unregistered persons the E Way Bill can be generated by using PAN & AADHHAR No.
Each E Way Bill has Unique 12 Digit Number having QR Code for quick and easy verification during moment of goods.
6) Types Of E Way Bill
1) Normal E Way Bill :- Normal E Way bill shall be generated when there is transportation of goods having one type of HSN.
2) Bulk E Way Bill :- When there is transportation of multiple variety of Goods having multiple HSN code the bulk E Way bill shall be generated.
7) Cancellation of E Way Bill
- In case, an e-way bill had been generated, but the goods have not been transported or are not transported as per the details furnished in the bill, then the e-way bill can be cancelled online on the GST Portal or through a GST Facilitation Centre.
- A GST e-way bill can be cancelled easily within 24 hours of its generation. However, an e-way bill cannot be cancelled if it had been verified in transit.
8) Validity of E Way Bill
The Validity of E Way Bill is depends upon 2 factors i.e. Cargo Type and Distance
- In Case of Normal Cargo :-
| Upto 100 KM | 1 Day |
| After that for every 100 KM or Part thereof | 1 Day |
Example: – If Distance of movement is 823 KM then validity of E way Bill is 9 Days
- In Case of Over Dimensional Cargo :-
| Upto 20 KM | 1 Day |
| After that for every 20 KM or part thereof | 1 Day |
Example: – If Distance of Movement is 45 KM in case of Over Dimensional Cargo then validity of E way Bill is 3 Days.
Explanation 1.—For the purposes of this rule, the “relevant date” shall mean the date on which the e-way bill has been generated and the period of validity shall be counted from the time at which the e-way bill has been generated and each day shall be counted as the period expiring at midnight of the day immediately following the date of generation of e-way bill.
Explanation 2.— For the purposes of this rule, the expression “Over Dimensional Cargo” shall mean a cargo carried as a single indivisible unit and which exceeds the dimensional limits prescribed in rule 93 of the Central Motor Vehicle Rules, 1989, made under the Motor Vehicles Act, 1988 (59 of 1988).
Extension of Validity of E Way Bill can be done in following 2 Ways.
- The Commissioner can extend the validity period of GST e-way bill through issue of notification for certain categories of goods alone however, this extension only given in rare circumstances.
- E Way Bill generator can take a extension in case the goods cannot be transported within the validity period of the e-way bill, the transporter can produce another e-way bill for the same consignment after updating the details in the “Part B” section of form “GST EWB-01”.
9) Acceptance and Rejection of E Way Bill
- On the common portal, and the supplier or the recipient, as the case may be, shall communicate his acceptance or rejection of the consignment covered by the e-way bill.
- Where the person to whom the information specified has been made available does not communicate his acceptance or rejection within 72 hours of the details being made available to him on the common portal, or the time of delivery of goods whichever is earlier, it shall be deemed that he has accepted the said details.
10) Exemption in case of E Way Bill.
The Exemptions in case of E Way Bill is given can be given in multiple ways i.e. Goods Wise, Area Wise, Vehicle wise , Person Wise Etc.
- Goods Wise Exemption.
The goods which are specified in below link does not require E Way bill for there Movement. https://www.apct.gov.in/gstportal/GST_Portal/pdf/EXEMPTIONS/Notification-2-2017for-CGSTrate-exemption.pdf
The Movement of Following Goods also Not Require E Way Bill.
| Sr. No. | Description of Goods |
| 1 | Liquefied petroleum gas for supply to household and non domestic exempted category (NDEC) customers |
| 2 | Kerosene oil sold under PDS |
| 3 | Postal baggage transported by Department of Posts |
| 4 | Natural or cultured pearls and precious or semi-precious stones; precious metals and metals clad with precious metal (Chapter 71) |
| 5 | Jewellery, goldsmiths’ and silversmiths’ wares and other articles (Chapter 71) |
| 6 | Currency |
| 7 | Used personal and household effects |
| 8 | Coral, unworked (0508) and worked coral (9601)”; |
| 9 | where the goods being transported are alcoholic liquor for human consumption, petroleum crude, high speed diesel, motor spirit (commonly known as petrol), natural gas or aviation turbine fuel; |
| 10 | where the supply of goods being transported is treated as no supply under Schedule III of the Act. |
- Area Wise Exemption
1) where the goods are being transported from the customs port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station to an inland container depot or a container freight station for clearance by Customs.
2) In respect of movement of goods within such areas as are notified under clause (d) of sub-rule (14) of rule 138 of the State or Union territory Goods and Services Tax Rules in that particular State or Union territory.
3) where the goods are being transported under customs bond from an inland container depot or a container freight station to a customs port, airport, air cargo complex and land customs station, or from one customs station or customs port to another customs station or customs port.
4) where the goods are being transported under customs supervision or under customs seal.
5) where the goods being transported are transit cargo from or to Nepal or Bhutan.
6) where empty cargo containers are being transported.
7) where the goods are being transported upto a distance of 20 KM from the place of the business of the consignor to a weighbridge for weighment or from the weighbridge back to the place of the business of the said consignor subject to the condition that the movement of goods is accompanied by a delivery challan issued in accordance with rule 55.
- Vehicle Wise Exemption
1) where the goods are being transported by a non-motorised conveyance.
2) where the consignor of goods is the Central Government, Government of any State or a local authority for transport of goods by rail.
- Person Wise Exemption
1) Any movement of goods caused by defence formation under Ministry of defence as a consignor or consignee.
2) Where the consignor of goods is the Central Government, Government of any State or a local authority for transport of goods by rail.
11) Concept Of Consolidated E Way Bill.
In case of transportation of goods from same origin of different HSN codes of multiple taxpayers the transporter has to carry multiple E Way bill while carrying out movement of goods. If the consignment is verified by the GST Officer then transporter has to produce multiple E Way Bill for there verification. To overcome this practical difficult the Concept of consolidated E Way bill was introduced, consolidated e-way bill is a document that comprises of multiple E-Way bills for multiple consignments which are being carried out in one transportation. Transporters consolidated E Way Bill with information of all sender and 1 QR Code precisely, transporter transporting multiple consignments of various consignors and consignees in one vehicle can generate and carry one consolidated e-way bill instead of carrying multiple e-way bills for those consignments. Therefore, a transporter can create a consolidated e-way bills for movement of multiple consignments in single vehicle.
12) E Way Bill in case of use of Multiple Vehicle.
Taking consideration into the practical difficulties during the course of transportation of goods i.e. Road accident, Non-Availability of National Permit, Vehicle Breakdown, there must be a change of transportation vehicle in this situation the E Way bill needs to be Updated as follows.
Situation 1:-

However, In case of Intra State Movement of goods and the distance is upto 50 KM then there is no need to give details of Transporter.
Situation 2:-
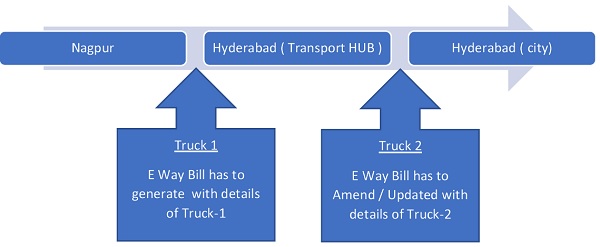
However, In case of Intra State Movement of goods and the distance is upto 50 KM( Ex. Transport Hub to City) then there is no need to give details of Transporter( Part B of E Way Bill)
(Author is a CA In Practice associated with Manish Watmode & Associates, Nagpur.)






if my invoice is cancelled after delivery of products then whats the procedure of goods return
sir our e-way bill is exprier we can not extent the eway bill validity what to do for extent the validity of eway bill
Hi sir,
If invoice value change after generation of E way Bill how much value different is acceptable E way Bill and Invoice?
if e-way bill is created in other company name by mistake, is it offence
first of all it is very useful and lucid explanation,
my query is, sir, do i need to generate to part B, if goods are transported to dealer in mumbai within 50km limits
what if on one vehicle four diffetent consignor issu invoice 48000 for each consignor and consignee is same or four differents and there is no transporter then is thete required any e way bill or not
If Movement of goods is from head office to warehouses(where there is no separate GST registration for warehouses) and sales is made from both head office and warehouses. Is there a requirement of E-way bill for the stock movement from head office to warehouses?
Can you share e-mail ID and phone no. of CA Mr.Manish Dattaraj Watmode,Nagpur