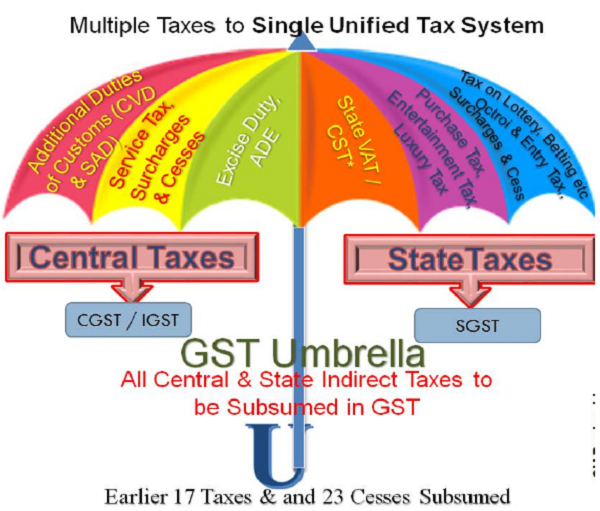
Indirect taxes in India had been a contentious subject and in a constant state of evolution. Now, with the passage of the One Hundred and First Amendment Act of the Constitution of India enabling the introduction of a comprehensive Goods and Services Tax – GST, the Indian system of indirect taxation witnessed a very significant step in the field of indirect tax reforms in India, by amalgamating a large number of Central and State taxes (Earlier 17 Taxes & and 23 Cesses Subsumed now). In this Short Notes let us understand basic Concepts of GST in a simple way.
In short, GST replaces most of indirect taxes to create a Single Tax System, Uniform across the Country making entire Nation as a Single Market. That is One Nation – One Tax – One Market.
What is GST?
For simplicity of understanding point wise description is made with some Pictorial Presentation as follows
> GST unifying Multiple Taxes into Single Tax System by subsuming 17 Taxes & 23 Cesses of earlier tax regime.
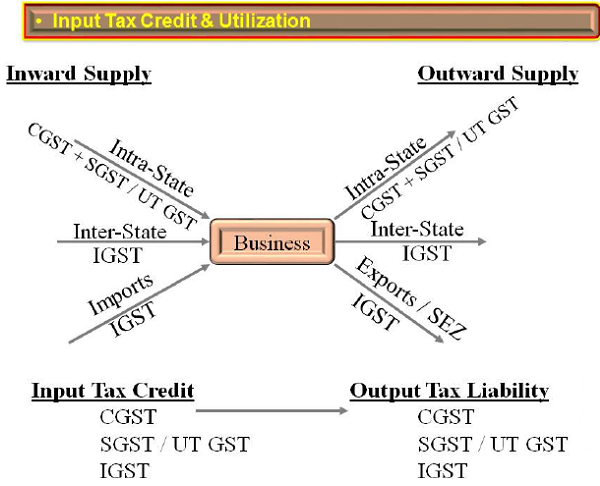
> GST is a Value Added Tax and a Multi point Levy Tax allowing Seamless Credit. GST is a consumption based tax levied incrementally, based on the surplus value, added to the price on the goods or service at each stage of supply. To ensure that tax is levied only on the amount of value addition at each stage of the supply chain, credit for the taxes paid at the previous stage is granted. As an illustration of the concept see below example where Steel manufacturer supplying Steel Sheets to Car Body Manufacturer. Since the car body manufacturer after value addition supplying car body to car manufacturer for assembling, the car body manufacturer can avail credit of tax paid on his inputs. Such credit can be utilized for his tax liability on his supply of finished goods (car body), therefore his net tax payment is reduced to the extent of credit. Likewise it goes on at every stage by availing of credit of input tax at each stage and utilizing the same while paying tax on final supply.
> Since Tax is Levied at each stage of Supply, GST is also a Multi-levy Tax.

> Seamless Credit is allowed across the entire Value Chain. However credit chain breaks at the point of final consumption.
> Credit can be utilized when there is taxable outward supplies.
GST is a Destination based Tax (as the name suggests is the taxation based on destination or consumption of the goods or services – meaning the tax shall accrue to the destination state). Hence, the place of consumption will decide the State that will collect tax. The parody behind destination-based taxation is, the producing/selling state gets nothing while the consuming states receive complete share of revenue.

> GST is a Dual Tax – Levied concurrently by both Center and State

> Supply is the basis for Levy & Collection of GST – The Event for Taxation is Supply

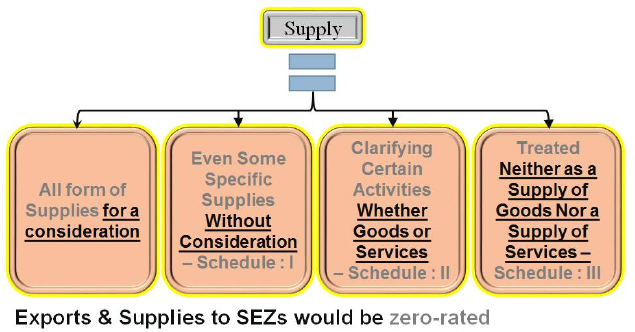
> To constitute a supply, the following elements must be satisfied:
√ The Activity Involves the Supply of Goods, Services, or Both
√ Supply is for Consideration unless otherwise expressly provided for
√ Supply Even without Consideration – Schedule -1
√ Supply is Made in the Course of Business
√ Supply is Made in a Taxable Territory
√ Supply is a Taxable Supply
√A Taxable Person Makes the Supply
> Products Not Part of GST
Crude oil, diesel, petrol, natural gas and jet fuel are temporarily kept out of GST and will be announced when to bring these items into GST.
Liquor is kept out of GST as a constitutional provision and hence it would require an amendment to Constitution if it is to be brought into GST net.
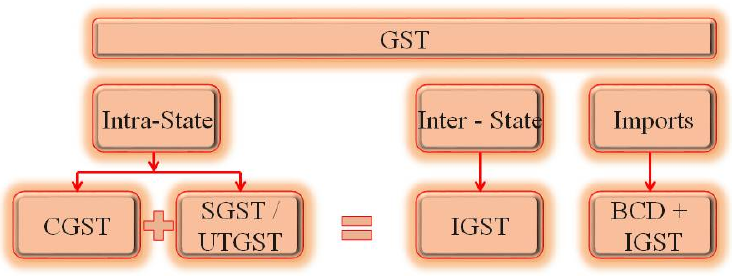
Supplies made within State are called Intra- State Supplies and attracts CGST + SGST. Supplies made out of state are called Inter-State Supplies and attracts IGST.
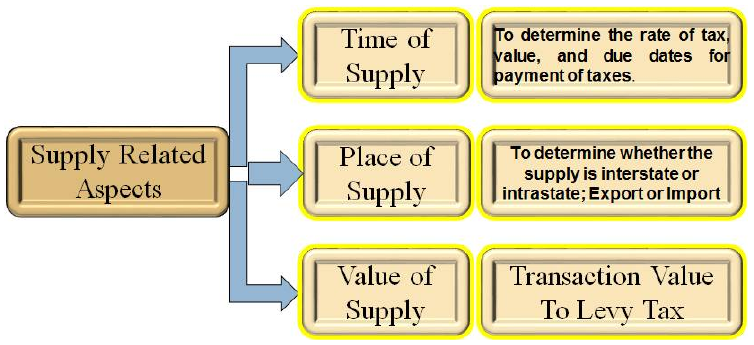
> Supply related other three aspects like Time of Supply, Place of Supply and Value of Supply are essential to determine and calculate Tax.
> Time of Supply is to determine the rate of tax, value, and due dates for payment of taxes.
> Place of Supply is to determine whether the supply is interstate or intrastate; Export or Import
> Value of Supply – Transaction value or Price charged is taken as value for levying tax.
> Goods and Services are classified into various and groups and accordingly Tax Rates are fixed. Goods are Classified based on HSN Classification and Services are Classified based on SAC (Service Accounting Codes)
> Broadly the Rates are falls into Four Categories – 5%, 12%, 18% and 28%. Apart from these there will be Nil Rate (exempted category) and Compensation Cess will be applicable to Luxury Items & Demerit Items.

> Who is liable to pay GST? Taxable Person – Businesses and traders with annual turnover above Rs 20 lakh are liable to pay GST. The threshold for paying GST is Rs 10 lakh in the case of northeastern and special category states.
> GST is applicable on inter-state trade irrespective of this threshold.
> “Aggregate Turnover” means the aggregate value of all taxable supplies (excluding the value of inward supplies on which tax is payable by a person on reverse charge basis), exempt supplies, exports of goods or services or both and inter-State supplies of persons having the same Permanent Account Number

> Every Taxable Person need to be Registered under GST
> Registration is State Specific : Registration in every such State or Union territory in which he is so liable.
> Registration is PAN Specific : Businesses with different PAN numbers need to take different GST registrations even though belongs to same group.
> Structure of Registration Number : Each taxpayer will be allotted a state wise PAN-based 15-digit Goods and Services Taxpayer Identification Number (GSTIN)
> Various digits in GSTIN will denote the following :

> Certain Category of Persons are Exempted from Registration – Like Agriculturalist, Persons Exclusively supplying Exempted items.
> Voluntary Registration Provisions are also made for Registration, irrespective of Turnover
> GST does NOT apply to Agriculturists
> Some Supplies fall into Mandatory Registration – Like Inter-State Supply, E- Commerce, Payments on Reverse Charge.

> To encourage small businesses a simplified scheme called “Composition Scheme” was introduced. Persons whose aggregate turnover in the preceding financial year did not exceed seventy five lakh rupees – may opt to pay, in lieu of the tax payable by him certain specified amount based on turnover.

> Some Category of supply required to pay tax under Reverse Charge.
> “Reverse Charge” means the liability to pay tax by the recipient of supply of goods or services or both instead of the supplier.
> Supplies from Un-registered person fall under Reverse Charge category and therefore tax liability should be discharged by the recipient of the supply.
> Supplies of some specified Goods (like cashew, silk etc) and Services (GTA, Advocate etc) also falls under Reverse Charge Mechanism.

> GST does not apply to any person engaged exclusively in the business of supplying goods and/or services that are not liable to tax or are wholly exempt from tax under this Act
With proper understanding and implementation of GST it definitely proofs to be Good and Simple Tax.
GST = Good & Simple Tax
(Author can be reached at snpanigrahi@rediffmail.com)






Very clearly made understood..
Respected sir,
I gone thru your Article and understood a small that it is very excellent.