CA Chaitanya Kumar
Invoice under general parlance vs. tax parlance:
Invoice in simple terms is nothing but a document specifying list of goods sent or services provided and a statement of the sum due against those items. Invoice is often understood as ‘proof of sale’ but this common understanding is far from the truth.
Invoice is a document recording the terms of an arrangement already entered into either orally or on a paper. An invoice does not bring into existence a sale agreement but merely records the terms of whatever arrangement that may have been entered into by the parties, involving the subject matter.
Most of the Indirect tax laws require the preparation of an invoice which does not mean that the absence of an invoice defeats the levy but prescribes an unambiguous occasion when the tax may become recoverable with a proper record of the terms of the underlying arrangement. Therefore, an invoice can evidence not only a sale but every other form of supply such as transfer, barter, exchange, license, rental, lease or disposal. If issuance of an invoice is uncommon for barter or a rental arrangement, then it is to do with our own unfamiliarity and nothing to do with its impermissibility.
Invoice under GST:
GST requires that a tax invoice or bill of supply to be issued before or on the occurrence of certain event or within a prescribed time. Therefore, an invoice is required for every other form of supply such as transfer, barter, exchange, license, rental, lease or disposal.
GST allows seamless flow of Input Tax Credits (ITC) across the supply chain. One of the fundamental pillars of GST is checking the Input Tax Credit (ITC) Claims, for which data of all Invoices to be uploaded and matched. GST system is backed up by strong IT support from Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN) for matching such data. GSTN seeks all registered dealers shall file Invoice wise details in order to do such matching.
Tax Invoice:
Every registered taxable person under GST supplying Goods or services is required to issue a tax invoice for all supplies effected. The word “Every registered Taxable person” clearly specifies that issuing Tax Invoice is compulsory under GST law. However, government may notify some other document for certain category of services. Eg. Bus ticket, Bank Voucher etc.,
Bill of Supply:
A supplier supplying exempted goods or service or a supplier who has opted for composition levy scheme has to issue a bill of supply instead of a tax invoice. A bill of supply is not eligible for claiming input tax credits.
Tax Invoice Vs. Bill of Supply
I will hereby highlight few differences between a bill of supply and Tax Invoice before diving deep.
| Tax Invoice | Bill of Supply | |
| Who has to issue? | Taxable Supplier who is supplying Taxable goods or Taxable Services. | Supplier of Exempt Goods or services and Composition Tax payer |
| When need not be issued | Need not issue a Tax Invoice if the value of the goods or services supplied is less than ₹200/- and recipient is unregistered .(Need to prepare one aggregate Invoice for each day) | Need not issue a bill of supply if the value of the goods or services supplied is less than ₹200/-.(Need to prepare one aggregate BOS for each day) |
| Can Input Tax claimed? | Input Tax Credit(ITC) can be claimed based on Tax Invoice | Input Tax Credit(ITC) cannot be claimed based on ‘Bill of Supply’ |
When Tax Invoice shall be issued?

*If supplier is a bank or NBFC or any financial institution, then within 45 days from the supply of service.
Manner of issuing Tax Invoice:
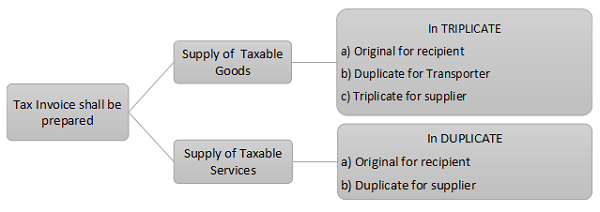
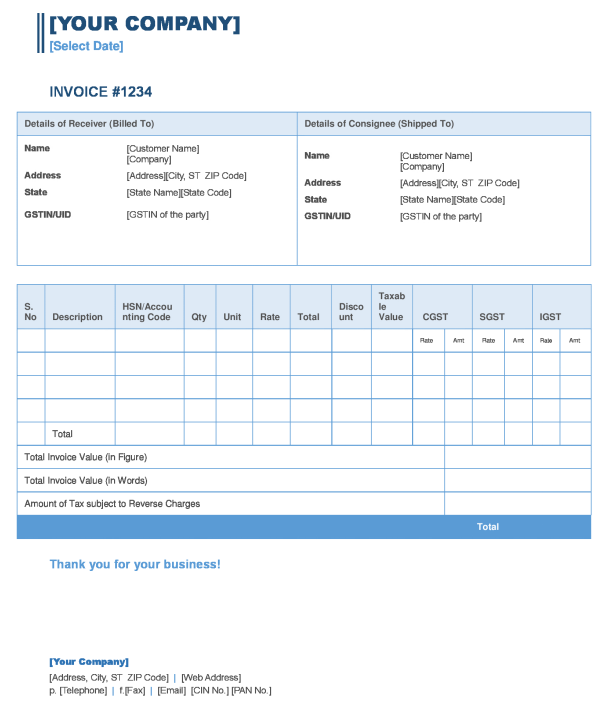
Prescribed Particulars of a Tax Invoice:
A) A tax invoice issued by the supplier shall contain the following details:-
| a. | Type of Invoice (Tax Invoice, Revised Invoice or Supplementary Invoice) |
| b. | Name, address and GSTIN of the supplier |
| c. | A consecutive serial number unique for a financial year (can have alphabets and/or numerals or “–“ and “/” and any combination thereof) |
| d. | Date of issue of Invoice |
| e. | Name, address and GSTIN/ Unique ID Number, if registered, of the recipient |
| f. | Name and address of the recipient and the address of delivery, along with the name of State and its code, if such recipient is unregistered and where the taxable value of supply is fifty thousand rupees or more. |
| g. | HSN code of goods or Accounting Code of services.(Council may issue notification to specify number of digits to be mentioned by each class of persons) |
| h. | Description of goods or services. |
| i. | Quantity in case of goods and unit or Unique Quantity Code thereof. |
| j. | Total value of goods or services. |
| k. | Taxable value of goods or services taking into account discount or abatement, if any. |
| l. | Rate of tax (CGST, SGST/UTGST, Cess or IGST) |
| m. | Amount of tax charged in respect of taxable goods or services (CGST, SGST/UTGST, Cess or IGST) |
| n. | Place of supply along with the name of State, in case of a supply in the course of inter-State trade or commerce |
| o. | Place of delivery where the same is different from the place of supply. |
| p. | Whether the tax is payable on reverse charge. |
| q. | Signature or digital signature of the supplier or his authorized representative |
B. When tax invoice is issued by an exporter then invoice should have the additional information:
| a. | An endorsement “supply meant for export on payment of IGST” or “supply meant for export under bond or letter of undertaking without payment of IGST”, as the case may be. |
| b. | Name of the country of destination; and |
| c. | Number and date of application for removal of goods for export. |
C) When tax invoice is issued by an Input Service Distributor (ISD) then invoice should have the information
| a. | Name, address and GSTIN of the ISD |
| b. | A consecutive serial no. containing only alphabets & numerals, unique for a financial year* |
| c. | Date of issue |
| d. | Name, address and GSTIN of the supplier of service, along with serial no. & date of invoice issued by such supplier, the credit in respect of which is being distributed |
| e. | Name, address and GSTIN of the recipient of credit |
| f. | Amount of credit distributed |
| g. | Signature or digital signature of the supplier(ISD) or his authorized signatory |
D) When tax invoice is issued by a Banking company / NBFC / financial institution Information then following information is not essential
| a. | Invoice serial no. |
| b. | Address of the recipient |
D) When tax invoice is issued by a Goods transport agency then invoice should have the following additional information
| a. | Gross weight of the consignment |
| b. | Name of the consignor & the consignee |
| c. | Registered no. of goods carriage, used for transportation |
| d. | Details of goods transported |
| e. | Details of place of origin & destination |
| f. | GSTIN of person liable for paying tax. |
F) When tax invoice is issued by a supplier of passenger transport service address of the recipient is not essential.
What’s new under GST?
a) Under GST along with Tax Invoice the concept of Bill of supply is brought in. Bill of supply is issued by a composition tax payer and a registered taxable person in case of supply of Exempt goods or supplies.
b) The provision to issue revised invoice (for invoices already issued between the effective date of registration to the date of issuance of certificate) is not available at present. This document shall be issued within 30 days from date of registration and would be useful for claiming tax credit for supply of goods/services during this period.
c) At present, invoices or bills of sale etc. can be issued inclusive of tax in certain cases whereas it is mandatory to indicate the tax charged in the GST regime.
d) Self-invoice to be prepared on the date of receipt of supply, which is liable to tax under reverse charge, from an unregistered person. Such Invoices to be reported in GSTR-2.
e) Serial numbers and sequence numbers of all the invoices to be reported along with GSTR-1 in each period.
f) A receipt Voucher need to be issued when an advance is received against a Supply. It is to be noted that the receipt voucher need not be issued for all the receipts. It need not be issued for all the advances received. The need to issue receipt voucher arises only when an advance is received with respect to a supply.
g) A refund Voucher need to be issued when a receipt voucher is issued and subsequently no supply is made or no tax invoice in pursuance thereof.
h) A payment voucher need to be issued when any payment is made with respect to a Supply on which tax is payable on reverse charge basis by recipient. It is to be noted that unlike the receipt voucher it need not be issued for all the payments on which tax is payable on reverse charge basis.
Rectification of an error in an Invoice:

This article is an endeavor to share some learnings obtained. The views expressed are of the author and are intended solely for informational purpose only. Though due care is taken while preparing the document, possibility of errors cannot be ruled out Expert guidance, where required and user discretion is highly recommended.
Format of Tax Invoice under GST based on essential contents notified
(The author can also be reached at cachaitanyakumar@gmail.com)
What is Invoice Format Under GST?

















IT IS MADATORY TO GIVE TITLE “TAX INVOICE” ON TAX INVOICE OR ONLY ‘INVOICE’ IS ALSO WORKS.
ON REIMBURSEMENT OF SALES OR REIMBURSEMENT OF CFS CHARGES IT IS VALID TO NOT CHARGED GST IN INVOICE OR NOT ?
We got an order from a client – GST Registered Dealer.
As per Purchase order Terms we have to supply New SMF Batteries to Client and take back old SMF batteries (Scrap) from them.
Client reluctant to issue Invoice along with old Batteries (Scrap).
In such a scenario whether we can prepare a credit Note for buying back old SMF batteries (Scrap) from Client. Showing Basis price + IGST amt.
Or please suggest any other solution.
it is nessasory to mention detail that material dispatch from??
Tax invoice is generally pre-printed but usually it is found that Invoice No is written with hand and the rest of the things are preprinted. Invoice No has also to be pre-printed right, it cannot be handwritten?
Shall a GTA who is engaged in providing taxable services to registered person under RCM have to raise tax invoice?
we have purchase stockon company sent to invocie
taxable value -5000/-
CGST 450/-
SGST 450/-
Total Invoice Value 5900/-
Less:adjusmtnet 500
5400/-
How to treated adjusmnent in GST. How to taken to this adjustment amount in GSTR-1 Please Clariy to my problem. sent to Answar my mail id
How to raise self invoice under Reverse chage? whether it should raised in the regular invoice or is there any other format? how to give invoice numbers for these invoices? please help
with regards
Mala
Very Informative.
I have two queries :-
1) How will my goods be cheaper than the composition dealer ?? Bcos I will charge gst whereas he will not.
e.g : I sell at 100+9+9+profit=118+ profit whereas the same item comp dealer will sell at 100+profit. So he is bound to be cheaper.
2) What exactly is input tax credit ( in simple terms )and who can claim it ?
In above example what is ITC and who can claim what ?
FROM THE RULE I UNDERSTAND THAT THERE IS NO CANCELLATION OF INVOICE UNDER GST REGIME
Can any one help me with GST Invoice for Free Samples.
This was a really good article. It explained complex provisions in very simplistic way. I was myself confused about the self invoice provisions.
Now I am quite clear.
Thanks a lot Chaitanya
SERVICE K CASE ME BHI INTERA STATE ME TAX SGST AND CGST LAGEGA AND KEWAL IGST LAGEGA
What is format for composition dealer sales bill
CAN YOU PLEASE GIVE ME GST INVOICE FORMAT FOR HIGH SEA SALE
Sir,
If an item is falling under GST rate of 5 % and the goods are sold within the state only than the Invoice shall be prepared :
Value of Goods Rs. 1000.00
C G S T 5 % Rs. 50.00
S G S T 5 % Rs. 50.00
Total Rs. 1100.00
or it shall be as under :-
Value of Goods Rs. 1000.00
C G S T 2.5% Rs. 25.00
S G S T 2.5 % Rs. 25.00
Total Rs. 1050.00
Which is correct way ???
is it compulsory to issue invoice in the formet give above or can we add the Taxation part below the sale amount
total amount 1000
+ CGST
+ SGSt
+ IGST _____
Total Amt.
In the above what do you mean by “AMOUNT OF TAX SUBJECT TO REVERSE CHARGE” Please Reply
Is lorry no. not mention by us
thanks for the detailed and visually appealing article.
I had two queries.
I read the following somewhere.
Broad rule is as under:
– Taxpayers whose turnover is above Rs. 1.5 crores but below Rs. 5 crores shall use 2 digit code;
– Taxpayers whose turnover is Rs. 5 crores and above shall use 4 digit code;and
– Taxpayers whose turnover is below Rs. 1.5 crores are not required to mention HSN Code in their invoices.
Is it correct? your article mentions that council guidelines are awaited.
Also wanted to ask if final invoice format is released? If yes, could you please share link.
Would be glad if you could spare sometime to answer the above queries. Thanks
Whether unregistered service provider can provide interstate interstate services
Invoice number format should be simple. It makes easy the data entry operator easy. Else reconciliation issue starts. If all the vendors updates sale invoices by 10th then no issues, as the same can treated as purchases.
Good information. Will these rules apply in case of sale to the final consumer, ie a B to C scenario where the customer will not be eligible for GST credit.